|
NGC 5694
NGC 5694 (also known as Caldwell 66) is a globular cluster in the constellation Hydra. It was discovered in 1784 by William Herschel. Characteristics This globular cluster is located at a distance of from the Sun and from the Galactic Center and is one of the oldest known globular clusters in the Milky Way Galaxy, forming nearly 12 billion years ago. Its chemical composition is highly peculiar, being highly (to nearly solar levels) enriched in alpha elements, suggesting an extragalactic origin before being captured by the Milky Way. See also *NGC 4372 NGC 4372 (also known as Caldwell 108) is a globular cluster in the southern constellation of Musca. It is southwest of γ Muscae (Gamma Muscae) and west of the southern end of the Dark Doodad Nebula (Sandqvist 149), a 3° thin streak of black acr ... References External links * * {{DEFAULTSORT:NGC 5694 Globular clusters Hydra (constellation) 5694 066b Astronomical objects discovered in 1783 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's ''General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New General Catalogue'' (RNGC) by Jack W. Sulent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Center
The Galactic Center or Galactic Centre is the rotational center, the barycenter, of the Milky Way galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a compact radio source which is almost exactly at the galactic rotational center. The Galactic Center is approximately away from Earth in the direction of the constellations Sagittarius, Ophiuchus, and Scorpius, where the Milky Way appears brightest, visually close to the Butterfly Cluster (M6) or the star Shaula, south to the Pipe Nebula. There are around 10 million stars within one parsec of the Galactic Center, dominated by red giants, with a significant population of massive supergiants and Wolf–Rayet stars from star formation in the region around 1 million years ago. The core stars are a small part within the much wider galactic bulge. Discovery Because of interstellar dust along the line of sight, the Galactic Center cannot be studied at v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC Objects
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxies, star clusters and emission nebulae. Dreyer published two supplements to the NGC in 1895 and 1908, known as the ''Index Catalogues'' (abbreviated IC), describing a further 5,386 astronomical objects. Thousands of these objects are best known by their NGC or IC numbers, which remain in widespread use. The NGC expanded and consolidated the cataloguing work of William and Caroline Herschel, and John Herschel's ''General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars''. Objects south of the celestial equator are catalogued somewhat less thoroughly, but many were included based on observation by John Herschel or James Dunlop. The NGC contained multiple errors, but attempts to eliminate them were made by the ''Revised New General Catalogue'' (RNGC) by Jack W. Sulenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globular Clusters
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars. Their name is derived from Latin (small sphere). Globular clusters are occasionally known simply as "globulars". Although one globular cluster, Omega Centauri, was observed in antiquity and long thought to be a star, recognition of the clusters' true nature came with the advent of telescopes in the 17th century. In early telescopic observations globular clusters appeared as fuzzy blobs, leading French astronomer Charles Messier to include many of them in his catalog of astronomical objects that he thought could be mistaken for comets. Using larger telescopes, 18th-century astronomers recognized that globular clusters are groups of many individual stars. Early in the 20th century the distribution of globular clusters in the sky wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monthly Notices Of The Royal Astronomical Society
''Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (MNRAS) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in astronomy and astrophysics. It has been in continuous existence since 1827 and publishes letters and papers reporting original research in relevant fields. Despite the name, the journal is no longer monthly, nor does it carry the notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. History The first issue of MNRAS was published on 9 February 1827 as ''Monthly Notices of the Astronomical Society of London'' and it has been in continuous publication ever since. It took its current name from the second volume, after the Astronomical Society of London became the Royal Astronomical Society (RAS). Until 1960 it carried the monthly notices of the RAS, at which time these were transferred to the newly established ''Quarterly Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society'' (1960–1996) and then to its successor journal ''Astronomy & Geophysics'' (since 1997). Until 1965, MNRAS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 4372
NGC 4372 (also known as Caldwell 108) is a globular cluster in the southern constellation of Musca. It is southwest of γ Muscae (Gamma Muscae) and west of the southern end of the Dark Doodad Nebula (Sandqvist 149), a 3° thin streak of black across a southern section of the great plane of the Milky Way. NGC 4372 "is partially obscured by dust lanes, but still appears as a large object some 10 arcseconds in diameter," according to ''Astronomy of the Milky Way'' (2004). The cluster has highly peculiar chemistry similar to NGC 5694, being extremely iron-poor yet having super-solar abundances of magnesium and titanium. References External links * NGC 4372at Wikisky at Astrosurf * * {{DEFAULTSORT:NGC 4372 Globular clusters Musca NGC objects, 4372 Caldwell objects, 108b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
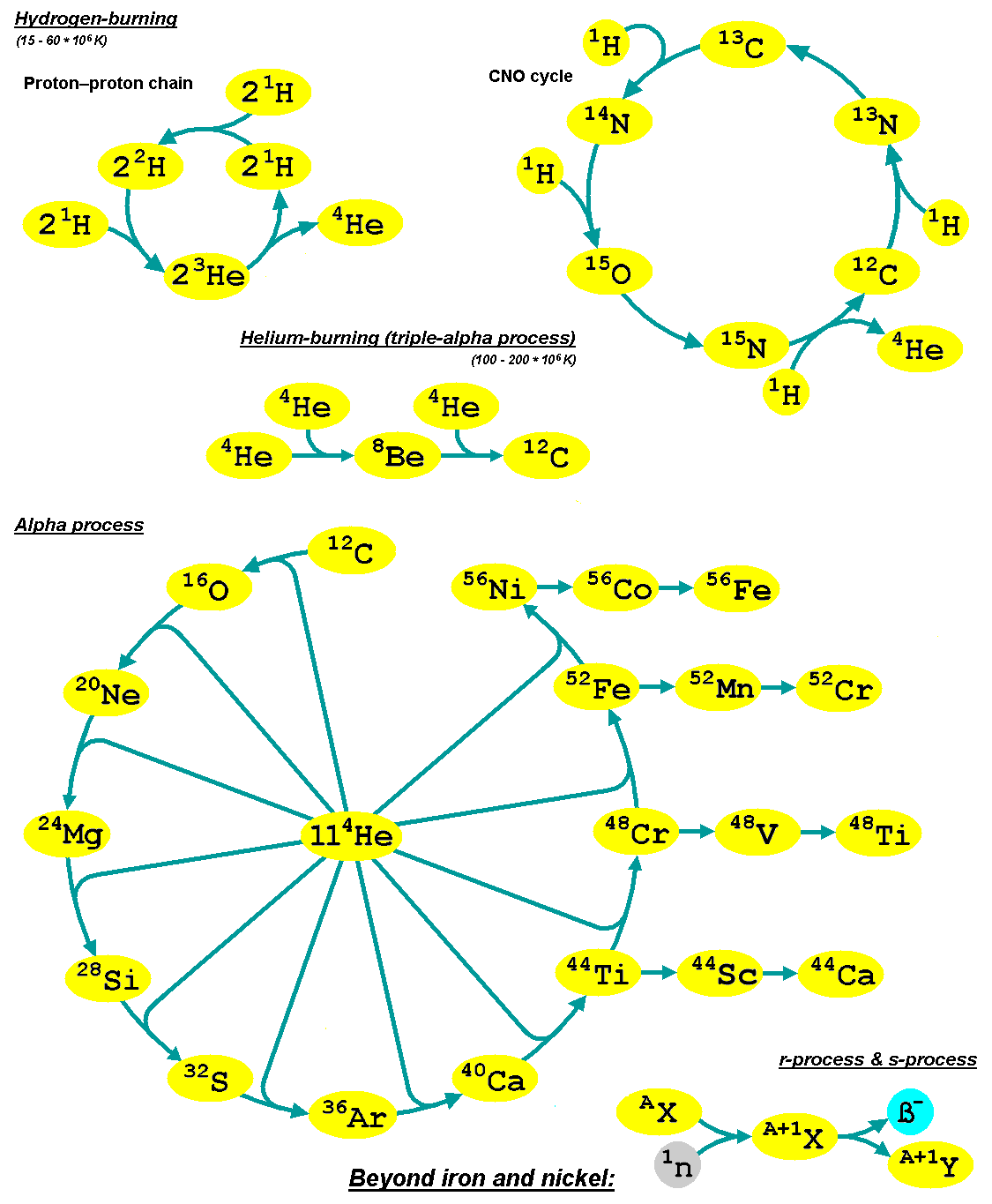
Alpha Process
The alpha process, also known as the alpha ladder, is one of two classes of nuclear fusion reactions by which stars convert helium into heavier elements, the other being the triple-alpha process. The triple-alpha process consumes only helium, and produces carbon. After enough carbon has accumulated, further reactions below take place, listed below. Each step only consumes helium and the product of the previous reaction. :\begin \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \\ \ce& E=\mathsf \end The energy produced each the reaction, , is primarily in the gamma ray (), with a small amount taken by the byproduct element, as added momentum. It is a common misconception that the above sequence ends at \, _^\mathrm \, (or \, _^\mathrm \,, which is a decay product of \, _^\mathrm \,) because it is the most tightly bound nuclide - i.e., having the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way Galaxy
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The term ''Milky Way'' is a translation of the Latin ', from the Greek ('), meaning "milky circle". From Earth, the Milky Way appears as a band because its disk-shaped structure is viewed from within. Galileo Galilei first resolved the band of light into individual stars with his telescope in 1610. Until the early 1920s, most astronomers thought that the Milky Way contained all the stars in the Universe. Following the 1920 Great Debate between the astronomers Harlow Shapley and Heber Curtis, observations by Edwin Hubble showed that the Milky Way is just one of many galaxies. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with an estimated D25 isophotal diameter of , but only about 1,000 light years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulge) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel (; german: Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-born British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline Herschel (1750–1848). Born in the Electorate of Hanover, William Herschel followed his father into the military band of Hanover, before emigrating to Great Britain in 1757 at the age of nineteen. Herschel constructed his first large telescope in 1774, after which he spent nine years carrying out sky surveys to investigate double stars. Herschel published catalogues of nebulae in 1802 (2,500 objects) and in 1820 (5,000 objects). The resolving power of the Herschel telescopes revealed that many objects called nebulae in the Messier catalogue were actually clusters of stars. On 13 March 1781 while making observations he made note of a new object in the constellation of Gemini. This would, after several weeks of verification and consultation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 5694
NGC 5694 (also known as Caldwell 66) is a globular cluster in the constellation Hydra. It was discovered in 1784 by William Herschel. Characteristics This globular cluster is located at a distance of from the Sun and from the Galactic Center and is one of the oldest known globular clusters in the Milky Way Galaxy, forming nearly 12 billion years ago. Its chemical composition is highly peculiar, being highly (to nearly solar levels) enriched in alpha elements, suggesting an extragalactic origin before being captured by the Milky Way. See also *NGC 4372 NGC 4372 (also known as Caldwell 108) is a globular cluster in the southern constellation of Musca. It is southwest of γ Muscae (Gamma Muscae) and west of the southern end of the Dark Doodad Nebula (Sandqvist 149), a 3° thin streak of black acr ... References External links * * {{DEFAULTSORT:NGC 5694 Globular clusters Hydra (constellation) 5694 066b Astronomical objects discovered in 1783 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The origins of the earliest constellations likely go back to prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, or mythology. Different cultures and countries adopted their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. The 48 traditional Western constellations are Greek. They are given in Aratus' work ''Phenomena'' and Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', though their origin probably predates these works by several centuries. Constellation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globular Cluster
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars. Their name is derived from Latin (small sphere). Globular clusters are occasionally known simply as "globulars". Although one globular cluster, Omega Centauri, was observed in antiquity and long thought to be a star, recognition of the clusters' true nature came with the advent of telescopes in the 17th century. In early telescopic observations globular clusters appeared as fuzzy blobs, leading French astronomer Charles Messier to include many of them in his catalog of astronomical objects that he thought could be mistaken for comets. Using larger telescopes, 18th-century astronomers recognized that globular clusters are groups of many individual stars. Early in the 20th century the distribution of globular clusters in the sky w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |