|
NER Class G
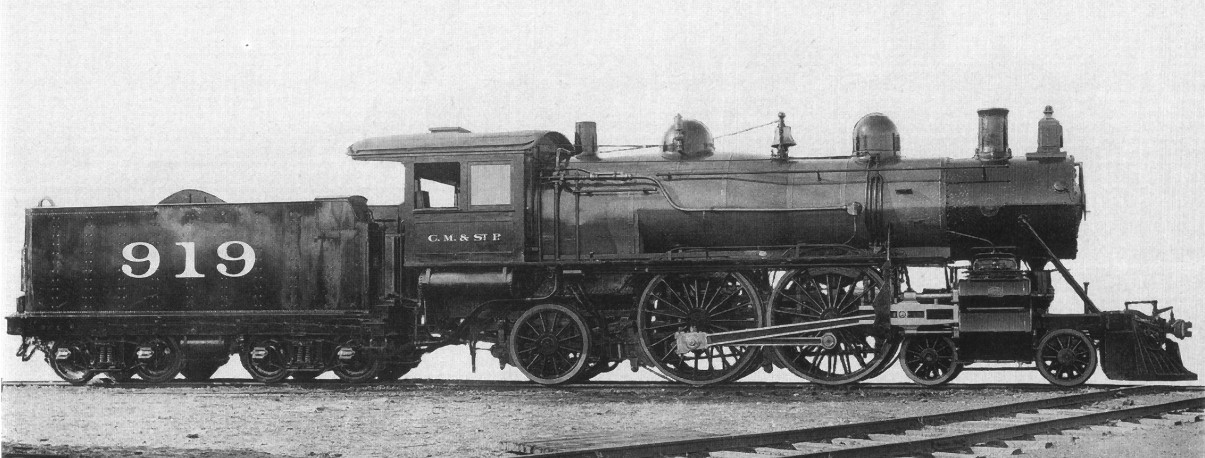
The NER Class G (LNER Class D23) was a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotives of the North Eastern Railway. It was designed by Thomas William Worsdell and introduced in 1887. History The engines were built as Class G1 2-4-0s. They had simple expansion cylinders, slide valves, and Joy valve gear. Twenty locomotives were built at Darlington Works in 1887-1888. They were initially classed as "G1" to leave the classification "G" available for a compound version. However, the compound version was not built and they were reclassified as "G" in 1914. Modifications Between 1900 and 1904, they were rebuilt as 4-4-0s. At the same time, they were fitted with piston valves and Stephenson valve gear. Superheaters were fitted between 1913 and 1916. Use The engines were initially used for secondary passenger duties. By the time of the 1923 Grouping Grouping may refer to: * Muenchian grouping * Principles of grouping * Railways Act 1921, also known as Grouping Act, a reorganisation of the Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas William Worsdell
Thomas William Worsdell (14 January 1838 – 28 June 1916) was an English locomotive engineer. He was born in Liverpool into a Quaker family. Family T. W. Worsdell – normally known as William – was the eldest son of Nathaniel Worsdell (1809–1886), and grandson of the coachbuilder Thomas Clarke Worsdell (1788–1862). His younger brother, Wilson Worsdell (1850–1920), was also a locomotive engineer. T. C. Worsdell had become a Quaker at some point between 1812 and 1816, and his descendants, including Nathaniel, William and Wilson, were brought up in the Quaker faith. William was born at his parents' house in Liverpool on 14 January 1838. He began school at the age of two, and in 1847 was sent as a boarder to Ackworth, a Quaker school in Yorkshire, where he remained until 1852. Career He worked at the Crewe Works of the LNWR under John Ramsbottom but in 1865 moved to the United States to the Pennsylvania Railroad. In 1871 he was invited by Francis William Webb to re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Locomotive
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in France, Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to maintenance issues and because superheating provided similar efficiencies at lower cost. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway right up to 1952. Introduction In the usual arrangement for a compound engine the steam is first expanded in one or two high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinders, then having given up some heat and lost some pressure, it exhausts into a larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinder, (or two, - or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scrapped Locomotives
Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap has monetary value, especially recovered metals, and non-metallic materials are also recovered for recycling. Once collected, the materials are sorted into types — typically metal scrap will be crushed, shredded, and sorted using mechanical processes. Scrap recycling is important for creating a more sustainable economy or creating a circular economy, using significantly less energy and having far less environmental impact than producing metal from ore. Metal recycling, especially of structural steel, ships, used manufactured goods, such as vehicles and white goods, is a major industrial activity with complex networks of wrecking yards, sorting facilities and recycling plants. Processing Scrap metal originates both in business and residential environments. Typically a "scrapper" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Locomotives Introduced In 1887
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Eastern Railway Locomotives
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography. Etymology The word ''north'' is related to the Old High German ''nord'', both descending from the Proto-Indo-European unit *''ner-'', meaning "left; below" as north is to left when facing the rising sun. Similarly, the other cardinal directions are also related to the sun's position. The Latin word ''borealis'' comes from the Greek '' boreas'' "north wind, north", which, according to Ovid, was personified as the wind-god Boreas, the father of Calais and Zetes. ''Septentrionalis'' is from ''septentriones'', "the seven plow oxen", a name of ''Ursa Major''. The Greek ἀρκτικός (''arktikós'') is named for the same constellation, and is the source of the English word ''Arctic''. Other languages have other derivations. For example, in Lezgian, ''kefer'' can mean b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 (c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an Act of Parliament enacted by the British government and intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four large companies dubbed the " Big Four". This was intended to move the railways away from internal competition, and retain some of the benefits which the country had derived from a government-controlled railway during and after the Great War of 1914–1918. The provisions of the Act took effect from the start of 1923. History The British railway system had been built up by more than a hundred railway companies, large and small, and often, particularly locally, in competition with each other. The parallel railways of the East Midlands and the rivalry between the South Eastern Railway and the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway at Hastings were two examples of such local competition. During the First World War the railways were under st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superheater
A superheater is a device used to convert saturated steam or wet steam into superheated steam or dry steam. Superheated steam is used in steam turbines for electricity generation, steam engines, and in processes such as steam reforming. There are three types of superheaters: radiant, convection, and separately fired. A superheater can vary in size from a few tens of feet to several hundred feet (a few metres to some hundred metres). Types * A radiant superheater is placed directly in radiant zone of the combustion chamber near the water wall so as to absorb heat by radiation. * A convection superheater is located in the convective zone of the furnace usually ahead of economizer (in the path of the hot flue gases). These are also called primary superheaters. * A separately fired superheater is a superheater that is placed outside the main boiler, which has its own separate combustion system. This superheater design incorporates additional burners in the area of superheater pipes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephenson Valve Gear
The Stephenson valve gear or Stephenson link or shifting link is a simple design of valve gear that was widely used throughout the world for various kinds of steam engines. It is named after Robert Stephenson but was invented by his employees. Historical background During the 1830s, the most popular valve drive for steam locomotives was known as '' gab motion'' in the United Kingdom and'' V-hook motion'' in the United States. The gab motion incorporated two sets of eccentrics and rods for each cylinder; one eccentric was set to give forward and the other backwards motion to the engine and one or the other could accordingly engage with a pin driving the distribution valve by means of the gabs: - vee-shaped ends to the eccentric rods supposed to catch the rocker driving the valve rod whatever its position. It was a clumsy mechanism, difficult to operate, and only gave fixed valve events. In 1841, two employees of Robert Stephenson and Company, draughtsman William Howe and patte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston Valve (steam Engine)
Piston valves are one form of valve used to control the flow of steam within a steam engine or locomotive. They control the admission of steam into the cylinders and its subsequent exhausting, enabling a locomotive to move under its own power. The valve consists of two piston heads on a common spindle moving inside a steam chest, which is essentially a mini-cylinder located either above or below the main cylinders of the locomotive. Overview In the 19th century, steam locomotives used slide valves to control the flow of steam into and out of the cylinders. In the 20th century, slide valves were gradually superseded by piston valves, particularly in engines using superheated steam. There were two reasons for this: * It is difficult to lubricate slide valves adequately in the presence of superheated steam * With piston valves, the steam passages can be made shorter. This, particularly following the work of André Chapelon, reduces resistance to the flow of steam and improves eff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darlington Works
Darlington Works was established in 1863 by the Stockton and Darlington Railway in the town of Darlington in the north east of England. The main part of the works, the North Road Shops was located on the northeast side of the Stockton and Darlington Railway (now part of the Tees Valley Line) History NER period The first new locomotive was built at the works in 1864. Though the railway had amalgamated with the North Eastern Railway (NER) in 1863, it continued to build its own designs for a number of years. In 1877, the first North Eastern designs appeared. Additionally works (paint and boilershop) were constructed west of the S&DR railway in the Stooperdale area of Darlington. Grandiose offices for the NER were also constructed in the Stooperdale area in 1911, to the design of William Bell. The offices were used by NER chief mechanical engineer Vincent Raven until 1917. In 1914, a class of NER Bo-Bo electric locomotives was built at the works to run between Shildon and Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)