|
NEAT Particles
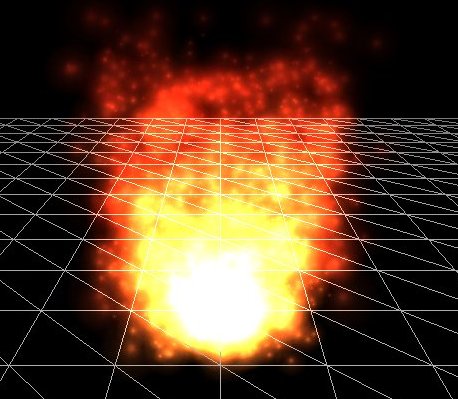
NEAT Particles is an interactive evolutionary computation program that enables users to evolve particle systems intended for use as special effects in video games or movie graphics. Rather than being hand-coded like typical particle systems, the behaviors of NEAT Particle effects are evolved by user preference. Therefore, non-programmer, non-artist users may evolve complex and unique special effects in real time. NEAT Particles is meant to augment and assist the time-consuming computer graphics content generation process. NEAT is short for Neuroevolution of Augmenting Topologies. Method In NEAT Particles, each particle system is controlled by a Compositional pattern-producing network (CPPN), a type of artificial neural network, or ANN. In other words, the usually hand-coded 'rules' of a particle system are replaced by automatically generated CPPNs. The CPPNs are evolved and complexified by NeuroEvolution of Augmenting Topologies (NEAT). A simple, interactive evolutionary comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interactive Evolutionary Computation
Interactive evolutionary computation (IEC) or aesthetic selection is a general term for methods of evolutionary computation that use human evaluation. Usually human evaluation is necessary when the form of fitness function is not known (for example, visual appeal or attractiveness; as in Dawkins, 1986) or the result of optimization should fit a particular user preference (for example, taste of coffee or color set of the user interface). IEC design issues The number of evaluations that IEC can receive from one human user is limited by user fatigue which was reported by many researchers as a major problem. In addition, human evaluations are slow and expensive as compared to fitness function computation. Hence, one-user IEC methods should be designed to converge using a small number of evaluations, which necessarily implies very small populations. Several methods were proposed by researchers to speed up convergence, like interactive constrain evolutionary search (user intervention) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle System
A particle system is a technique in game physics, motion graphics, and computer graphics that uses many minute sprites, 3D models, or other graphic objects to simulate certain kinds of "fuzzy" phenomena, which are otherwise very hard to reproduce with conventional rendering techniques – usually highly chaotic systems, natural phenomena, or processes caused by chemical reactions. Introduced in the 1982 film '' Star Trek II: The Wrath of Khan'' for the fictional "Genesis effect", other examples include replicating the phenomena of fire, explosions, smoke, moving water (such as a waterfall), sparks, falling leaves, rock falls, clouds, fog, snow, dust, meteor tails, stars and galaxies, or abstract visual effects like glowing trails, magic spells, etc. – these use particles that fade out quickly and are then re-emitted from the effect's source. Another technique can be used for things that contain many strands – such as fur, hair, and grass – involving rendering an entir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroevolution Of Augmenting Topologies
NeuroEvolution of Augmenting Topologies (NEAT) is a genetic algorithm (GA) for the generation of evolving artificial neural networks (a neuroevolution technique) developed by Kenneth Stanley and Risto Miikkulainen in 2002 while at The University of Texas at Austin. It alters both the weighting parameters and structures of networks, attempting to find a balance between the fitness of evolved solutions and their diversity. It is based on applying three key techniques: tracking genes with history markers to allow crossover among topologies, applying speciation (the evolution of species) to preserve innovations, and developing topologies incrementally from simple initial structures ("complexifying"). Performance On simple control tasks, the NEAT algorithm often arrives at effective networks more quickly than other contemporary neuro-evolutionary techniques and reinforcement learning methods.Kenneth O. Stanley and Risto Miikkulainen (2002). "Evolving Neural Networks Through Augmenting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEAT PARTICLES 1
Neat may refer to: * Neat (bartending), a single, unmixed liquor served in a rocks glass * Neat, an old term for horned oxen * Neat Records, a British record label * Neuroevolution of augmenting topologies (NEAT), a genetic algorithm (GA) for the generation of evolving artificial neural networks See also * Neet (other) * NEAT (other) * "Neat Neat Neat" * Neate Neate is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Adam Neate (born 1977), British painter, conceptual artist, and street artist * Andy Neate (born 1974), British racing driver * Charles Neate (1806–1879), English politician and acad ..., a surname * Neat Volume {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEAT PARTICLES 2
Neat may refer to: * Neat (bartending), a single, unmixed liquor served in a rocks glass * Neat, an old term for horned oxen * Neat Records, a British record label * Neuroevolution of augmenting topologies (NEAT), a genetic algorithm (GA) for the generation of evolving artificial neural networks See also * Neet (other) * NEAT (other) * "Neat Neat Neat" * Neate Neate is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Adam Neate (born 1977), British painter, conceptual artist, and street artist * Andy Neate (born 1974), British racing driver * Charles Neate (1806–1879), English politician and acad ..., a surname * Neat Volume {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compositional Pattern-producing Network
Compositional pattern-producing networks (CPPNs) are a variation of artificial neural networks (ANNs) that have an architecture whose evolution is guided by genetic algorithms.Stanley, Kenneth O. "Compositional pattern producing networks: A novel abstraction of development." Genetic programming and evolvable machines 8.2 (2007): 131-162. While ANNs often contain only sigmoid functions and sometimes Gaussian functions, CPPNs can include both types of functions and many others. The choice of functions for the canonical set can be biased toward specific types of patterns and regularities. For example, periodic functions such as sine produce segmented patterns with repetitions, while symmetric functions such as Gaussian produce symmetric patterns. Linear functions can be employed to produce linear or fractal-like patterns. Thus, the architect of a CPPN-based genetic art system can bias the types of patterns it generates by deciding the set of canonical functions to include. Furthermore, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Neural Network
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains. An ANN is based on a collection of connected units or nodes called artificial neurons, which loosely model the neurons in a biological brain. Each connection, like the synapses in a biological brain, can transmit a signal to other neurons. An artificial neuron receives signals then processes them and can signal neurons connected to it. The "signal" at a connection is a real number, and the output of each neuron is computed by some non-linear function of the sum of its inputs. The connections are called ''edges''. Neurons and edges typically have a ''weight'' that adjusts as learning proceeds. The weight increases or decreases the strength of the signal at a connection. Neurons may have a threshold such that a signal is sent only if the aggregate signal crosses that threshold. Typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NeuroEvolution Of Augmenting Topologies
NeuroEvolution of Augmenting Topologies (NEAT) is a genetic algorithm (GA) for the generation of evolving artificial neural networks (a neuroevolution technique) developed by Kenneth Stanley and Risto Miikkulainen in 2002 while at The University of Texas at Austin. It alters both the weighting parameters and structures of networks, attempting to find a balance between the fitness of evolved solutions and their diversity. It is based on applying three key techniques: tracking genes with history markers to allow crossover among topologies, applying speciation (the evolution of species) to preserve innovations, and developing topologies incrementally from simple initial structures ("complexifying"). Performance On simple control tasks, the NEAT algorithm often arrives at effective networks more quickly than other contemporary neuro-evolutionary techniques and reinforcement learning methods.Kenneth O. Stanley and Risto Miikkulainen (2002). "Evolving Neural Networks Through Augmenting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3D Model
In 3D computer graphics, 3D modeling is the process of developing a mathematical coordinate-based representation of any surface of an object (inanimate or living) in three dimensions via specialized software by manipulating edges, vertices, and polygons in a simulated 3D space. Three-dimensional (3D) models represent a physical body using a collection of points in 3D space, connected by various geometric entities such as triangles, lines, curved surfaces, etc. Being a collection of data ( points and other information), 3D models can be created manually, algorithmically (procedural modeling), or by scanning. Their surfaces may be further defined with texture mapping. Outline The product is called a 3D model. Someone who works with 3D models may be referred to as a 3D artist or a 3D modeler. A 3D Model can also be displayed as a two-dimensional image through a process called 3D rendering or used in a computer simulation of physical phenomena. 3D Models may be created auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shader
In computer graphics, a shader is a computer program that calculates the appropriate levels of light, darkness, and color during the rendering of a 3D scene - a process known as ''shading''. Shaders have evolved to perform a variety of specialized functions in computer graphics special effects and video post-processing, as well as general-purpose computing on graphics processing units. Traditional shaders calculate rendering effects on graphics hardware with a high degree of flexibility. Most shaders are coded for (and run on) a graphics processing unit (GPU), though this is not a strict requirement. ''Shading languages'' are used to program the GPU's rendering pipeline, which has mostly superseded the fixed-function pipeline of the past that only allowed for common geometry transforming and pixel-shading functions; with shaders, customized effects can be used. The position and color (hue, saturation, brightness, and contrast) of all pixels, vertices, and/or textures us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interactive Evolutionary Computation
Interactive evolutionary computation (IEC) or aesthetic selection is a general term for methods of evolutionary computation that use human evaluation. Usually human evaluation is necessary when the form of fitness function is not known (for example, visual appeal or attractiveness; as in Dawkins, 1986) or the result of optimization should fit a particular user preference (for example, taste of coffee or color set of the user interface). IEC design issues The number of evaluations that IEC can receive from one human user is limited by user fatigue which was reported by many researchers as a major problem. In addition, human evaluations are slow and expensive as compared to fitness function computation. Hence, one-user IEC methods should be designed to converge using a small number of evaluations, which necessarily implies very small populations. Several methods were proposed by researchers to speed up convergence, like interactive constrain evolutionary search (user intervention) or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle System
A particle system is a technique in game physics, motion graphics, and computer graphics that uses many minute sprites, 3D models, or other graphic objects to simulate certain kinds of "fuzzy" phenomena, which are otherwise very hard to reproduce with conventional rendering techniques – usually highly chaotic systems, natural phenomena, or processes caused by chemical reactions. Introduced in the 1982 film '' Star Trek II: The Wrath of Khan'' for the fictional "Genesis effect", other examples include replicating the phenomena of fire, explosions, smoke, moving water (such as a waterfall), sparks, falling leaves, rock falls, clouds, fog, snow, dust, meteor tails, stars and galaxies, or abstract visual effects like glowing trails, magic spells, etc. – these use particles that fade out quickly and are then re-emitted from the effect's source. Another technique can be used for things that contain many strands – such as fur, hair, and grass – involving rendering an entir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
