|
NDRG4
Protein NDRG4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NDRG4'' gene. This gene is a member of the N-myc downregulated gene family which belongs to the alpha/beta hydrolase superfamily. The protein encoded by this gene is a cytoplasmic protein that may be involved in the regulation of mitogenic signalling in vascular smooth muscles Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit mus ... cells. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Human proteins {{gene-16-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolase
Hydrolase is a class of enzyme that commonly perform as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond, which typically results in dividing a larger molecule into smaller molecules. Some common examples of hydrolase enzymes are esterases including lipases, phosphatases, glycosidases, peptidases, and nucleosidases. Esterases cleave ester bonds in lipids and phosphatases cleave phosphate groups off molecules. An example of crucial esterase is acetylcholine esterase, which assists in transforming the neuron impulse into the acetate group after the hydrolase breaks the acetylcholine into choline and acetic acid. Acetic acid is an important metabolite in the body and a critical intermediate for other reactions such as glycolysis. Lipases hydrolyze glycerides. Glycosidases cleave sugar molecules off carbohydrates and peptidases hydrolyze peptide bonds. Nucleosidases hydrolyze the bonds of nucleotides. Hydrolase enzymes are important for the body because they have degra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitogen
A mitogen is a small bioactive protein or peptide that induces a cell to begin cell division, or enhances the rate of division (mitosis). Mitogenesis is the induction (triggering) of mitosis, typically via a mitogen. The mechanism of action of a mitogen is that it triggers signal transduction pathways involving mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), leading to mitosis. The cell cycle Mitogens act primarily by influencing a set of proteins which are involved in the restriction of progression through the cell cycle. The G1 checkpoint is controlled most directly by mitogens: further cell cycle progression does not need mitogens to continue. The point where mitogens are no longer needed to move the cell cycle forward is called the "restriction point" and depends on cyclins to be passed.Bohmer et al. "Cytoskeletal Integrity Is Required throughout the Mitogen Stimulation Phase of the Cell Cycle and Mediates the Anchorage-dependent Expression of Cyclin DI". January 1996, Molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
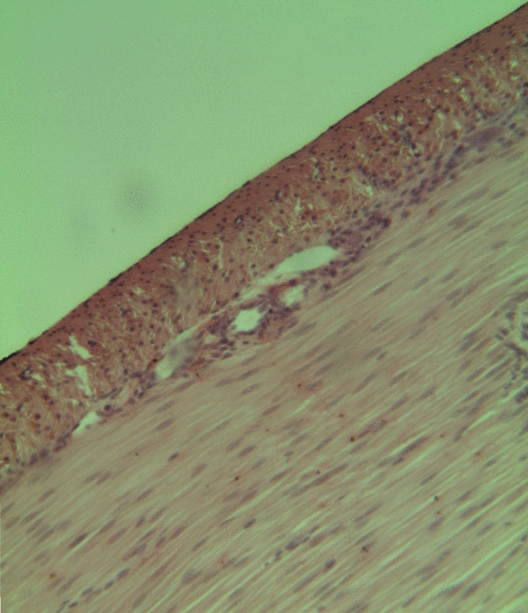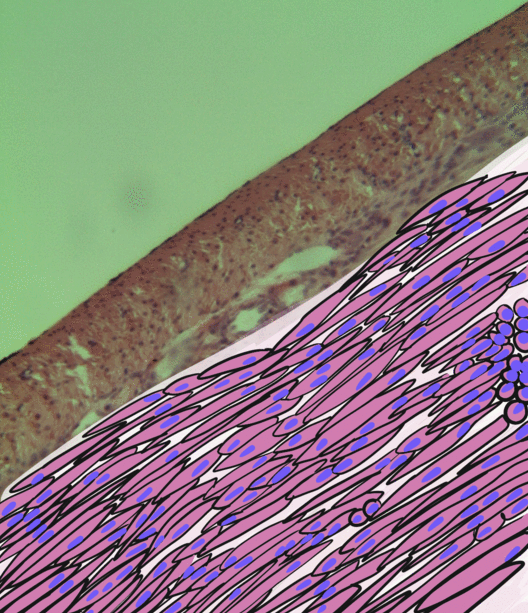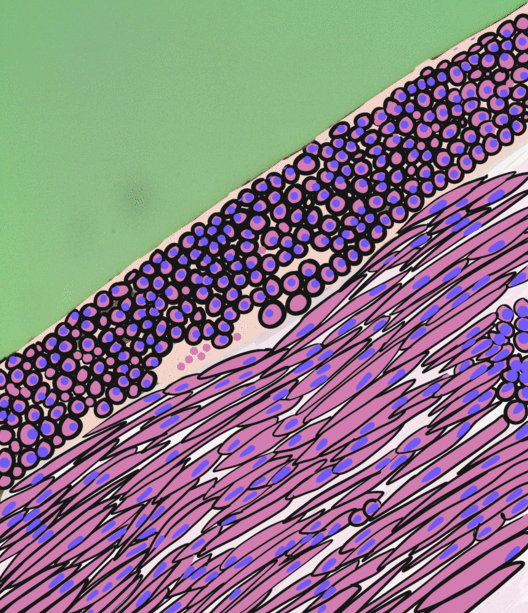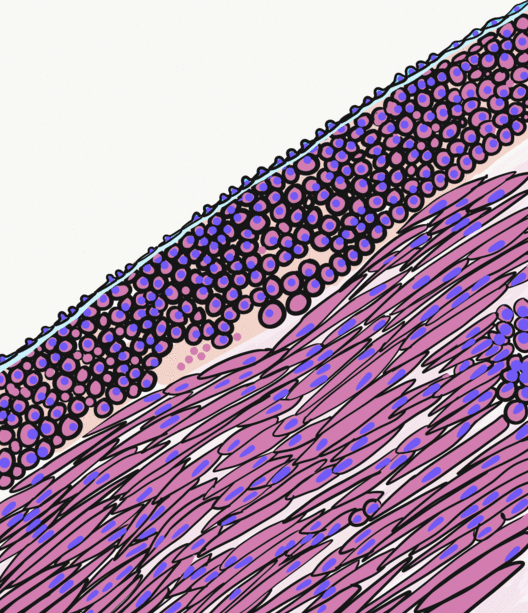
Smooth Muscles
Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus; in the walls of passageways, such as blood, and lymph vessels, and in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, a type of smooth muscle, dilate and contract the iris and alter the shape of the lens. In the skin, smooth muscle cells such as those of the arrector pili cause hair to stand erect in response to cold temperature or fear. Structure Gross anatomy Smooth muscle is grouped into two types: single-unit smooth muscle, also known as visceral smooth muscle, and multiunit smooth muscle. Most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |