|
NAMD
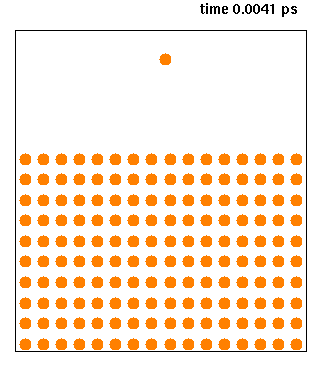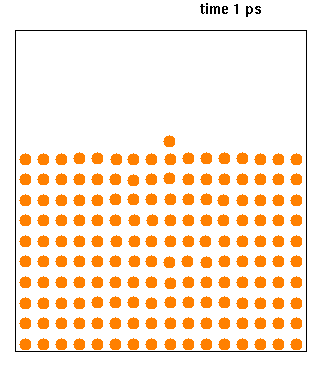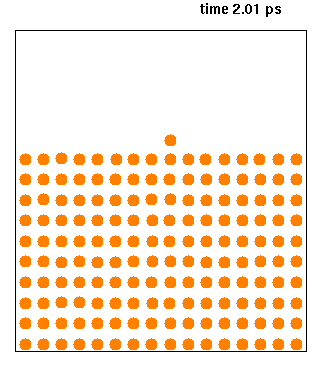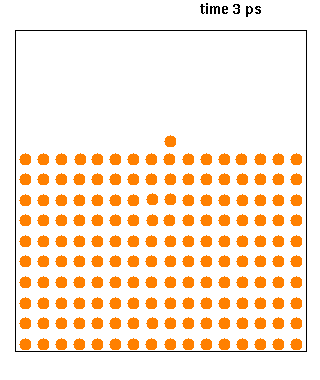
Nanoscale Molecular Dynamics (NAMD, formerly Not Another Molecular Dynamics Program) is computer software for molecular dynamics simulation, written using the Charm++ parallel programming model (not to be confused with CHARMM). It is noted for its parallel efficiency and is often used to simulate large systems (millions of atoms). It has been developed by the collaboration of the Theoretical and Computational Biophysics Group (TCB) and the Parallel Programming Laboratory (PPL) at the University of Illinois Urbana–Champaign. It was introduced in 1995 by Nelson ''et al.'' as a parallel molecular dynamics code enabling interactive simulation by linking to the visualization code VMD. NAMD has since matured, adding many features and scaling beyond 500,000 processor cores. NAMD has an interface to quantum chemistry packages ORCA and MOPAC, as well as a scripted interface to many other quantum packages. Together with Visual Molecular Dynamics (VMD) and QwikMD, NAMD's interface provides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Visual Molecular Dynamics
Visual Molecular Dynamics (VMD) is a molecular modelling and Visualization (computer graphics), visualization computer program. VMD is developed mainly as a tool to view and analyze the results of molecular dynamics simulations. It also includes tools for working with volumetric data, sequence data, and arbitrary graphics objects. Molecular scenes can be exported to external rendering tools such as POV-Ray, RenderMan (software), RenderMan, Tachyon (software), Tachyon, Virtual Reality Modeling Language (VRML), and many others. Users can run their own Tcl and Python (programming language), Python scripts within VMD as it includes embedded Tcl and Python interpreters. VMD runs on Unix, Apple Mac macOS, and Microsoft Windows. VMD is available to non-commercial users under a distribution-specific license which permits both use of the program and modification of its source code, at no charge. History VMD has been developed under the aegis of principal investigator Klaus Schulten in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charm++
Charm++ is a parallel object-oriented programming paradigm based on C++ and developed in the Parallel Programming Laboratory at the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. Charm++ is designed with the goal of enhancing programmer productivity by providing a high-level abstraction of a parallel program while at the same time delivering good performance on a wide variety of underlying hardware platforms. Programs written in Charm++ are decomposed into a number of cooperating message-driven objects called ''chares''. When a programmer invokes a method on an object, the Charm++ runtime system sends a message to the invoked object, which may reside on the local processor or on a remote processor in a parallel computation. This message triggers the execution of code within the chare to handle the message asynchronously. Chares may be organized into indexed collections called ''chare arrays'' and messages may be sent to individual chares within a chare array or to the entire chare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of Illinois Urbana–Champaign
The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC, U of I, Illinois, or University of Illinois) is a public land-grant research university in the Champaign–Urbana metropolitan area, Illinois, United States. Established in 1867, it is the founding campus and flagship institution of the University of Illinois System. With over 59,000 students, the University of Illinois is one of the largest public universities by enrollment in the United States. The university contains 16 schools and colleges and offers more than 150 undergraduate and over 100 graduate programs of study. The university holds 651 buildings on and its annual operating budget in 2016 was over $2 billion. The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign also operates a research park home to innovation centers for over 90 start-up companies and multinational corporations. The University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign is a member of the Association of American Universities and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the Motion (physics), physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamics (mechanics), dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectory, trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by Numerical integration, numerically solving Newton's laws of motion, Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where Force (physics), forces between the particles and their potential energy, potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanics, molecular mechanical Force field (chemistry), force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics. Because molecular systems typically consist of a vast number of particles, it is impossible to determine the properties of such complex systems analyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Comparison Of Software For Molecular Mechanics Modeling
This is a list of computer programs that are predominantly used for molecular mechanics calculations. See also *Car–Parrinello molecular dynamics *Comparison of force-field implementations *Comparison of nucleic acid simulation software *List of molecular graphics systems *List of protein structure prediction software *List of quantum chemistry and solid-state physics software *List of software for Monte Carlo molecular modeling *List of software for nanostructures modeling *Molecular design software *Molecular dynamics *Molecular modeling on GPUs *Molecule editor *PyMOL Notes and references External linksSINCRIS [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
CHARMM
Chemistry at Harvard Macromolecular Mechanics (CHARMM) is the name of a widely used set of force fields for molecular dynamics, and the name for the molecular dynamics simulation and analysis computer software package associated with them. The CHARMM Development Project involves a worldwide network of developers working with Martin Karplus and his group at Harvard to develop and maintain the CHARMM program. Licenses for this software are available, for a fee, to people and groups working in academia. Force fields The CHARMM force fields for proteins include: united-atom (sometimes termed ''extended atom'') CHARMM19, all-atom CHARMM22 and its dihedral potential corrected variant CHARMM22/CMAP, as well as later versions CHARMM27 and CHARMM36 and various modifications such as CHARMM36m and CHARMM36IDPSFF. In the CHARMM22 protein force field, the atomic partial charges were derived from quantum chemical calculations of the interactions between model compounds and water. Furthermor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Molecular Dynamics
Molecular dynamics (MD) is a computer simulation method for analyzing the Motion (physics), physical movements of atoms and molecules. The atoms and molecules are allowed to interact for a fixed period of time, giving a view of the dynamics (mechanics), dynamic "evolution" of the system. In the most common version, the trajectory, trajectories of atoms and molecules are determined by Numerical integration, numerically solving Newton's laws of motion, Newton's equations of motion for a system of interacting particles, where Force (physics), forces between the particles and their potential energy, potential energies are often calculated using interatomic potentials or molecular mechanics, molecular mechanical Force field (chemistry), force fields. The method is applied mostly in chemical physics, materials science, and biophysics. Because molecular systems typically consist of a vast number of particles, it is impossible to determine the properties of such complex systems analyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
X86-64
x86-64 (also known as x64, x86_64, AMD64, and Intel 64) is a 64-bit extension of the x86 instruction set architecture, instruction set. It was announced in 1999 and first available in the AMD Opteron family in 2003. It introduces two new operating modes: 64-bit mode and compatibility mode, along with a new four-level paging mechanism. In 64-bit mode, x86-64 supports significantly larger amounts of virtual memory and physical memory compared to its 32-bit computing, 32-bit predecessors, allowing programs to utilize more memory for data storage. The architecture expands the number of general-purpose registers from 8 to 16, all fully general-purpose, and extends their width to 64 bits. Floating-point arithmetic is supported through mandatory SSE2 instructions in 64-bit mode. While the older x87 FPU and MMX registers are still available, they are generally superseded by a set of sixteen 128-bit Processor register, vector registers (XMM registers). Each of these vector registers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Proprietary Software
Proprietary software is computer software, software that grants its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner a legal monopoly by modern copyright and intellectual property law to exclude the recipient from freely sharing the software or modifying it, and—in some cases, as is the case with some patent-encumbered and EULA-bound software—from making use of the software on their own, thereby restricting their freedoms. Proprietary software is a subset of non-free software, a term defined in contrast to free and open-source software; non-commercial licenses such as CC BY-NC are not deemed proprietary, but are non-free. Proprietary software may either be closed-source software or source-available software. Types Origin Until the late 1960s, computers—especially large and expensive mainframe computers, machines in specially air-conditioned computer rooms—were usually leased to customers rather than Sales, sold. Service and all software available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Freeware
Freeware is software, often proprietary, that is distributed at no monetary cost to the end user. There is no agreed-upon set of rights, license, or EULA that defines ''freeware'' unambiguously; every publisher defines its own rules for the freeware it offers. For instance, modification, redistribution by third parties, and reverse engineering are permitted by some publishers but prohibited by others. Unlike with free and open-source software, which are also often distributed free of charge, the source code for freeware is typically not made available. Freeware may be intended to benefit its producer by, for example, encouraging sales of a more capable version, as in the freemium and shareware business models. History The term ''freeware'' was coined in 1982 by Andrew Fluegelman, who wanted to sell PC-Talk, the communications application he had created, outside of commercial distribution channels. Fluegelman distributed the program via the same process as ''shareware''. As s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications. The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital computers in the mid-20th century. Early programs were written in the machine language specific to the hardware. The introduction of high-level programming languages in 1958 allowed for more human-readable instructions, making software development easier and more portable across different computer architectures. Software in a programming language is run through a compiler or Interpreter (computing), interpreter to execution (computing), execute on the architecture's hardware. Over time, software has become complex, owing to developments in Computer network, networking, operating systems, and databases. Software can generally be categorized into two main types: # operating systems, which manage hardware resources and provide services for applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cross-platform
Within computing, cross-platform software (also called multi-platform software, platform-agnostic software, or platform-independent software) is computer software that is designed to work in several Computing platform, computing platforms. Some cross-platform software requires a separate build for each platform, but some can be directly run on any platform without special preparation, being written in an interpreted language or compiled to portable bytecode for which the Interpreter (computing), interpreters or run-time packages are common or standard components of all supported platforms. For example, a cross-platform application software, application may run on Linux, macOS and Microsoft Windows. Cross-platform software may run on many platforms, or as few as two. Some frameworks for cross-platform development are Codename One, ArkUI-X, Kivy (framework), Kivy, Qt (software), Qt, GTK, Flutter (software), Flutter, NativeScript, Xamarin, Apache Cordova, Ionic (mobile app framework ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |