|
Nucleotide Universal IDentifier
The nucleotide universal IDentifier (nuID) in molecular biology, is designed to uniquely and globally identify oligonucleotide microarray probes. Background Oligonucleotide probes of microarrays that are sequence identical may have different identifiers between manufacturers and even between different versions of the same company's microarray; and sometimes the same identifier is reused and represents a completely different oligonucleotide, resulting in ambiguity and potentially mis-identification of the genes hybridizing to that probe. This also makes data interpretation and integration of different batches of data difficult. nuID was designed to solve these problems. It is a unique, non- degenerate encoding scheme that can be used as a universal representation to identify an oligonucleotide across manufacturers. The design of nuID was inspired by the fact that the raw sequence of the oligonucleotide is the true definition of identity for a probe, the encoding algorithm uniquely an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microarray
A microarray is a multiplex lab-on-a-chip. Its purpose is to simultaneously detect the expression of thousands of genes from a sample (e.g. from a tissue). It is a two-dimensional array on a solid substrate—usually a glass slide or silicon thin-film cell—that assays (tests) large amounts of biological material using high-throughput screening miniaturized, multiplexed and parallel processing and detection methods. The concept and methodology of microarrays was first introduced and illustrated in antibody microarrays (also referred to as antibody matrix) by Tse Wen Chang in 1983 in a scientific publication and a series of patents. The "gene chip" industry started to grow significantly after the 1995 ''Science Magazine'' article by the Ron Davis and Pat Brown labs at Stanford University. With the establishment of companies, such as Affymetrix, Agilent, Applied Microarrays, Arrayjet, Illumina, and others, the technology of DNA microarrays has become the most sophisticated and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
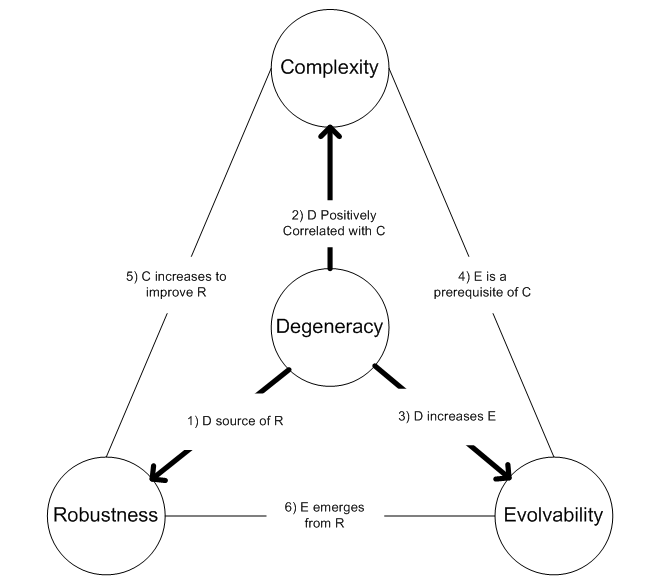
Degeneracy (biology)
Within biological systems, degeneracy occurs when structurally dissimilar components/modules/pathways can perform similar functions (i.e. are effectively interchangeable) under certain conditions, but perform distinct functions in other conditions. Degeneracy is thus a relational property that requires comparing the behavior of two or more components. In particular, if degeneracy is present in a pair of components, then there will exist conditions where the pair will appear functionally redundant but other conditions where they will appear functionally distinct. Note that this use of the term has practically no relevance to the questionably meaningful concept of evolutionarily degenerate populations that have lost ancestral functions. Biological examples Examples of degeneracy are found in the genetic code, when many different nucleotide sequences encode the same polypeptide; in protein folding, when different polypeptides fold to be structurally and functionally equivalent; in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lossless Compression
Lossless compression is a class of data compression that allows the original data to be perfectly reconstructed from the compressed data with no loss of information. Lossless compression is possible because most real-world data exhibits statistical redundancy. By contrast, lossy compression permits reconstruction only of an approximation of the original data, though usually with greatly improved compression rates (and therefore reduced media sizes). By operation of the pigeonhole principle, no lossless compression algorithm can efficiently compress all possible data. For this reason, many different algorithms exist that are designed either with a specific type of input data in mind or with specific assumptions about what kinds of redundancy the uncompressed data are likely to contain. Therefore, compression ratios tend to be stronger on human- and machine-readable documents and code in comparison to entropic binary data (random bytes). Lossless data compression is used in many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Checksum
A checksum is a small-sized block of data derived from another block of digital data for the purpose of detecting errors that may have been introduced during its transmission or storage. By themselves, checksums are often used to verify data integrity but are not relied upon to verify data authenticity. The procedure which generates this checksum is called a checksum function or checksum algorithm. Depending on its design goals, a good checksum algorithm usually outputs a significantly different value, even for small changes made to the input. This is especially true of cryptographic hash functions, which may be used to detect many data corruption errors and verify overall data integrity; if the computed checksum for the current data input matches the stored value of a previously computed checksum, there is a very high probability the data has not been accidentally altered or corrupted. Checksum functions are related to hash functions, fingerprints, randomization functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illumina (company)
Illumina, Inc. is an American biotechnology company, headquartered in San Diego, California. Incorporated on April 1, 1998, Illumina develops, manufactures, and markets integrated systems for the analysis of genetic variation and biological function. The company provides a line of products and services that serves the sequencing, genotyping and gene expression, and proteomics markets. Illumina's technology had purportedly reduced the cost of sequencing a human genome to by 2014. Its customers include genomic research centers, pharmaceutical companies, academic institutions, clinical research organizations, and biotechnology companies. History Illumina was founded in April 1998 by David Walt, Larry Bock, John Stuelpnagel, Anthony Czarnik, and Mark Chee. While working with CW Group, a venture-capital firm, Bock and Stuelpnagel uncovered what would become Illumina's BeadArray technology at Tufts University and negotiated an exclusive license to that technology. In 1999, Illumin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioconductor
Bioconductor is a Free software, free, Open-source software, open source and Open source software development, open development software project for the analysis and comprehension of Genome, genomic data generated by Wet laboratory, wet lab experiments in molecular biology. Bioconductor is based primarily on the statistics, statistical R (programming language), R programming language, but does contain contributions in other programming languages. It has two Software release life cycle, releases each year that follow the semiannual releases of R. At any one time there is a Software versioning, release version, which corresponds to the released version of R, and a Software versioning, development version, which corresponds to the development version of R. Most users will find the release version appropriate for their needs. In addition there are many genome annotation packages available that are mainly, but not solely, oriented towards different types of microarrays. While computati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumi (software)
lumi is a free, open source and open development software project for the analysis and comprehension of Illumina expression and methylation microarray data. The project was started in the summer of 2006 and set out to provide algorithms and data management tools of Illumina in the framework of Bioconductor. It is based on the statistical R programming language. Features The lumi package provides an analysis pipeline for probe-level Illumina expression and methylation microarray data, including probe-identifier management ( nuID), updated probe-to-gene mapping and annotation using the latest release of RefSeq (nuIDblast), probe-intensity transformation (VST) and normalization (RSN), quality control (QA/QC) and preprocessing methods specific for Illumina methylation data. By extending the ExprSet object with Illumina-specific features, lumi is designed to work with other Bioconductor packages, such as Limma and GOstats to detect differential genes and conduct Gene Ontology analysis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Footnotes
A note is a string of text placed at the bottom of a page in a book or document or at the end of a chapter, volume, or the whole text. The note can provide an author's comments on the main text or citations of a reference work in support of the text. Footnotes are notes at the foot of the page while endnotes are collected under a separate heading at the end of a chapter, volume, or entire work. Unlike footnotes, endnotes have the advantage of not affecting the layout of the main text, but may cause inconvenience to readers who have to move back and forth between the main text and the endnotes. In some editions of the Bible, notes are placed in a narrow column in the middle of each page between two columns of biblical text. Numbering and symbols In English, a footnote or endnote is normally flagged by a superscripted number immediately following that portion of the text the note references, each such footnote being numbered sequentially. Occasionally, a number between brack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)