|
Nuclear Safety And Security
Nuclear safety is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "The achievement of proper operating conditions, prevention of accidents or mitigation of accident consequences, resulting in protection of workers, the public and the environment from undue radiation hazards". The IAEA defines nuclear security as "The prevention and detection of and response to, theft, sabotage, unauthorized access, illegal transfer or other malicious acts involving nuclear materials, other radioactive substances or their associated facilities". This covers nuclear power plants and all other nuclear facilities, the transportation of nuclear materials, and the use and storage of nuclear materials for medical, power, industry, and military uses. The nuclear power industry has improved the safety and performance of reactors, and has proposed new and safer reactor designs. However, a perfect safety cannot be guaranteed. Potential sources of problems include human errors and external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
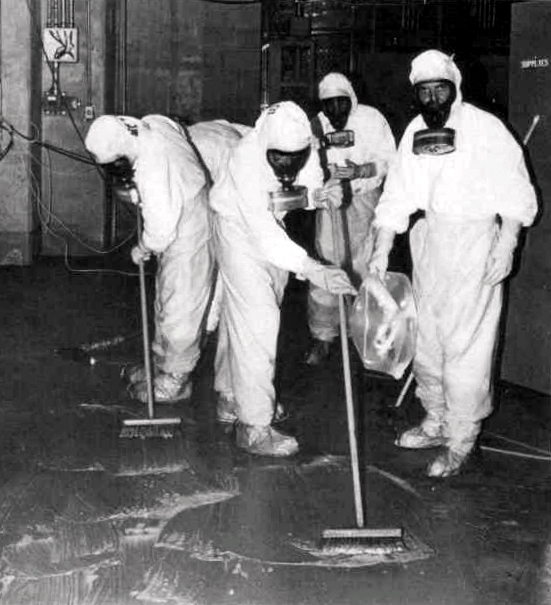
TMI Cleanup-2
TMI may refer to: Organizations * TMI Associates, a Japanese law firm * TMI Episcopal, formerly Texas Military Institute, a preparatory school affiliated with the Episcopal Church * Taiwan Music Institute, a musical institute` in Taiwan * Teen Missions International, an interdenominational mission organization based in Florida * Three Mile Island Nuclear Generating Station, a nuclear power station in Pennsylvania, USA * Time Module (TMI), a member of the Seiko Group, manufacturer of watch movements * Toastmasters International, an international public speaking organization * Tolani Maritime Institute, a Merchant Navy training institute * The Monroe Institute, a nonprofit education and research organization * Thomas More Institute, a secular academic institution located in Montreal, Quebec, Canada Science * Trans-Mars injection, a propulsive maneuver used to set a spacecraft on a trajectory which will cause it to arrive to Mars * Transmarginal inhibition, a mental response t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Power Weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first test of a fission ("atomic") bomb released an amount of energy approximately equal to . The first thermonuclear ("hydrogen") bomb test released energy approximately equal to . Nuclear bombs have had yields between 10 tons TNT (the W54) and 50 megatons for the Tsar Bomba (see TNT equivalent). A thermonuclear weapon weighing as little as can release energy equal to more than . A nuclear device no larger than a conventional bomb can devastate an entire city by blast, fire, and radiation. Since they are weapons of mass destruction, the proliferation of nuclear weapons is a focus of international relations policy. Nuclear weapons have been deploye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Committed Dose
The committed dose in radiological protection is a measure of the stochastic health risk due to an intake of radioactive material into the human body. Stochastic in this context is defined as the ''probability'' of cancer induction and genetic damage, due to low levels of radiation. The SI unit of measure is the sievert. A committed dose from an internal source represents the same effective risk as the same amount of effective dose applied uniformly to the whole body from an external source, or the same amount of equivalent dose applied to part of the body. The committed dose is not intended as a measure for deterministic effects, such as radiation sickness, which are defined as the ''severity'' of a health effect which is certain to happen. The radiation risk proposed by the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP) predicts that an effective dose of one sievert carries a 5.5% chance of developing cancer. Such a risk is the sum of both internal and external ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fusion Experiments
Experiments directed toward developing fusion power are invariably done with dedicated machines which can be classified according to the principles they use to confine the plasma fuel and keep it hot. The major division is between magnetic confinement and inertial confinement. In magnetic confinement, the tendency of the hot plasma to expand is counteracted by the Lorentz force between currents in the plasma and magnetic fields produced by external coils. The particle densities tend to be in the range of to and the linear dimensions in the range of . The particle and energy confinement times may range from under a millisecond to over a second, but the configuration itself is often maintained through input of particles, energy, and current for times that are hundreds or thousands of times longer. Some concepts are capable of maintaining a plasma indefinitely. In contrast, with inertial confinement, there is nothing to counteract the expansion of the plasma. The confinement time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermonuclear Weapon
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lower mass, or a combination of these benefits. Characteristics of nuclear fusion reactions make possible the use of non-fissile depleted uranium as the weapon's main fuel, thus allowing more efficient use of scarce fissile material such as uranium-235 () or plutonium-239 (). The first full-scale thermonuclear test was carried out by the United States in 1952; the concept has since been employed by most of the world's nuclear powers in the design of their weapons. Modern fusion weapons consist essentially of two main components: a nuclear fission primary stage (fueled by or ) and a separate nuclear fusion secondary stage containing thermonuclear fuel: the heavy hydrogen isotopes deuterium and tritium, or in modern weapons lithium deuteri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |