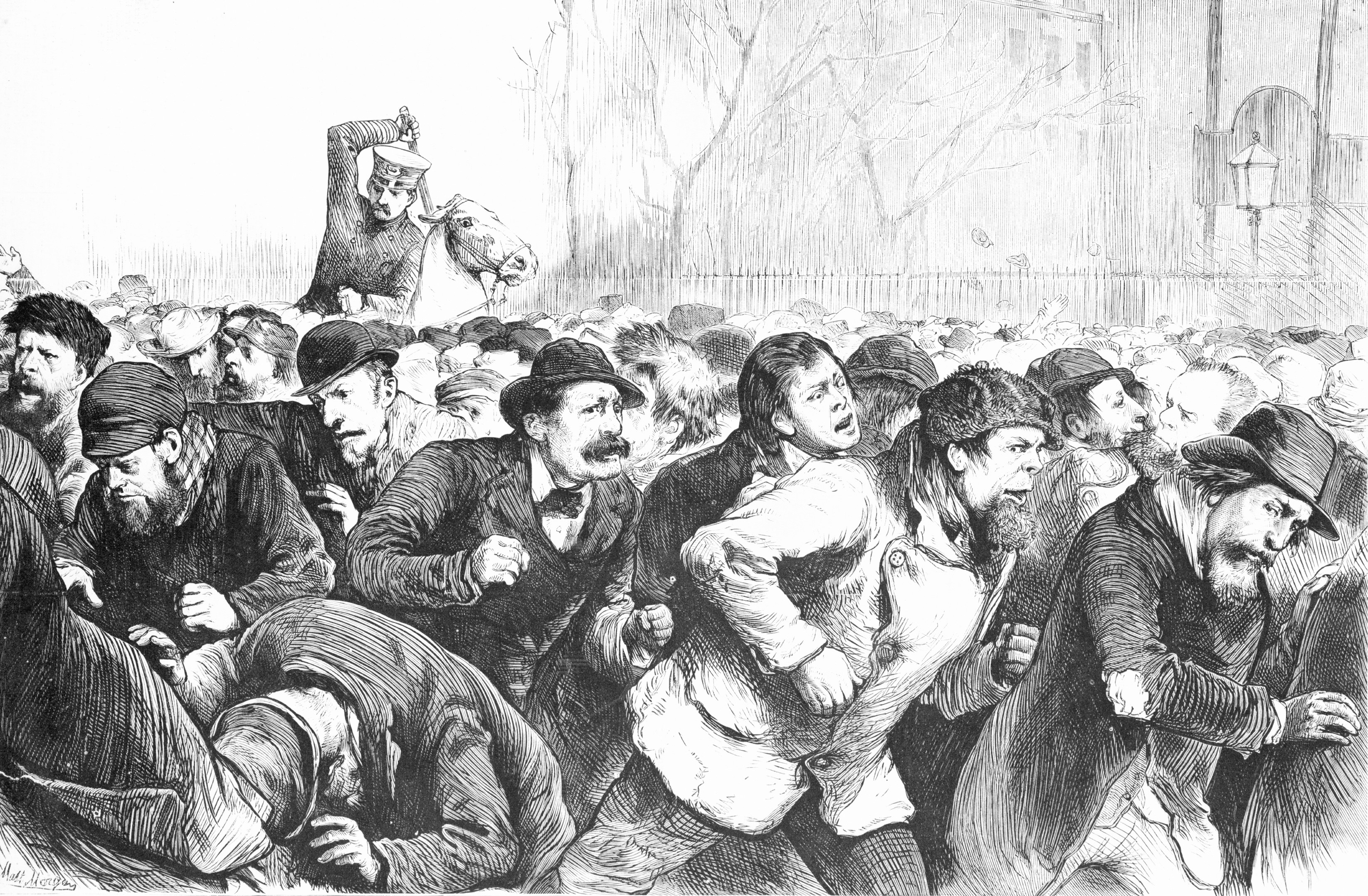|
November 2011 Uprising In Egypt
The 2011 Egyptian protest movement was rioting, strikes and melees across the country of Egypt demanding the military regime of Mohamed Hussein Tantawi to step down from power. In November 2011, dissatisfied with the progress of the reforms, almost all civilian political parties called for an accelerated end to the military rule before drafting a constitution — either an immediate handover to a civilian-led government, or a turnover to the lower house of Parliament when it is seated in April, or after a presidential election, which would be scheduled as soon as possible. A major difference between Egyptian revolutionaries is that secular groups want the election to be postponed since they believe that the election would favor religious parties and well established groups like the Muslim Brotherhood while those parties want the parliamentary elections to be held on time. On the other hand, they are united in their demand that the military should get out of politics and stop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohamed Hussein Tantawi
Mohamed Hussein Tantawi Soliman ( ar, محمد حسين طنطاوي سليمان, ; 31 October 1935 – 21 September 2021) was an Egyptian field marshal and politician. He was the commander-in-chief of the Egyptian Armed Forces and, as chairman of the Supreme Council of the Armed Forces, was the ''de facto'' head of state from the ousting of President Hosni Mubarak on 11 February 2011 until the inauguration of Mohamed Morsi as president of Egypt on 30 June 2012. Tantawi served in the government as Minister of Defense and Military Production from 1991 until Morsi ordered him to retire on 12 August 2012. Military career Tantawi, who was of Nubian origin, joined the Egyptian Military Academy in 1952 and received his commission as an Army officer on 1 April 1955 in the infantry. The following year he took part in the Suez War (or the Tripartite Aggression as it is often known in Egypt) as an infantry platoon commander. He was promoted to Major in 1961 and commanded an infantry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demonstration (political)
A political demonstration is an action by a mass group or collection of groups of people in favor of a political or other cause or people partaking in a protest against a cause of concern; it often consists of walking in a mass march formation and either beginning with or meeting at a designated endpoint, or rally, in order to hear speakers. It is different from mass meeting. Actions such as blockades and sit-ins may also be referred to as demonstrations. Demonstrations can be nonviolent or violent (usually referred to by participants as "Militant (word), militant"), or can begin as nonviolent and turn violent depending on the circumstances. Sometimes riot police or other forms of Law enforcement agency, law enforcement become involved. In some cases, this may be in order to try to prevent the protest from taking place at all. In other cases, it may be to prevent clashes between rival groups, or to prevent a demonstration from spreading and turning into a riot. History The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riots
A riot is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people. Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The property targeted varies depending on the riot and the inclinations of those involved. Targets can include shops, cars, restaurants, state-owned institutions, and religious buildings. Riots often occur in reaction to a grievance or out of dissent. Historically, riots have occurred due to poverty, unemployment, poor living conditions, governmental oppression, taxation or conscription, conflicts between ethnic groups (race riot) or religions (sectarian violence, pogrom), the outcome of a sporting event (sports riot, football hooliganism) or frustration with legal channels through which to air grievances. While individuals may attempt to lead or control a riot, riots typically consist of disorganized groups that are frequently "chaotic and exhibit herd beha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hosni Mubarak
Muhammad Hosni El Sayed Mubarak, (; 4 May 1928 – 25 February 2020) was an Egyptian politician and military officer who served as the fourth president of Egypt from 1981 to 2011. Before he entered politics, Mubarak was a career officer in the Egyptian Air Force. He served as its commander from 1972 to 1975 and rose to the rank of air chief marshal in 1973. In 1975, he was appointed vice president by President Anwar Sadat and assumed the presidency after his assassination in 1981. Mubarak's presidency lasted almost thirty years, making him Egypt's longest-serving ruler since Muhammad Ali Pasha, who ruled the country for 43 years from 1805 to 1848. Less than two weeks after the assassination of President Anwar Sadat, Mubarak quickly assumed the presidency in the single-candidate 1981 referendum, and renewed his term through single-candidate referendums in 1987, 1993, and 1999. Under United States pressure, Mubarak held the country's first multi-party election in 2005, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civilian Control Of The Military
Civilian control of the military is a doctrine in military and political science that places ultimate responsibility for a country's strategic decision-making in the hands of the civilian political leadership, rather than professional military officers. Civilian oversight over militaries, mainly used in democratic governments, puts the power to take military action in the hands of a civilian leader or legislative agency. Allowing the civilian component of government to retain control over the military or state security shows a healthy respect for democratic values and good governance. Giving power to the civilian component of the government over what the military can do and how much money it can spend protects the democratic process from abuse. Nations that can achieve legitimate relationship between the two structures serves to be more effective and provide accountability between government and military. Security relies on both sides compromising on the civilian and security ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democracy Now!
''Democracy Now!'' is an hour-long American TV, radio, and Internet news program hosted by journalists Amy Goodman (who also acts as the show's executive producer), Juan González, and Nermeen Shaikh. The show, which airs live each weekday at 8 a.m. Eastern Time, is broadcast on the Internet and via more than 1,400 radio and television stations worldwide. The program combines news reporting, interviews, investigative journalism and political commentary, with a focus on peace activism linked to environmental justice and social justice, guided by the ethics of ecofeminism as a philosophy. It documents social movements, struggles for justice, activism challenging corporate power and operates as a watchdog outfit regarding the effects of American foreign policy. ''Democracy Now!'' views as its aim to give activists and the citizenry a platform to debate people from "The Establishment". The show is described as progressive by fans as well as critics, but Goodman rejects that label ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 Egyptian Revolution
The 2011 Egyptian revolution, also known as the 25 January revolution ( ar, ثورة ٢٥ يناير; ), began on 25 January 2011 and spread across Egypt. The date was set by various youth groups to coincide with the annual Egyptian "Police holiday" as a statement against increasing police brutality during the last few years of Hosni Mubarak's presidency. It consisted of demonstrations, marches, occupations of plazas, non-violent civil resistance, acts of civil disobedience and strike action, strikes. Millions of protesters from a range of socio-economic and religious backgrounds demanded the overthrow of Egyptian President Hosni Mubarak. Violent clashes between security forces and protesters resulted in at least 846 people killed and over 6,000 injured. Protesters retaliated by burning over 90 police stations across the country. The Egyptian protesters' grievances focused on legal and political issues, including police brutality, state-of-emergency laws, lack of political free ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riots And Civil Disorder In Egypt
A riot is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people. Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The property targeted varies depending on the riot and the inclinations of those involved. Targets can include shops, cars, restaurants, state-owned institutions, and religious buildings. Riots often occur in reaction to a grievance or out of dissent. Historically, riots have occurred due to poverty, unemployment, poor living conditions, governmental oppression, taxation or conscription, conflicts between ethnic groups (race riot) or religions (sectarian violence, pogrom), the outcome of a sporting event (sports riot, football hooliganism) or frustration with legal channels through which to air grievances. While individuals may attempt to lead or control a riot, riots typically consist of disorganized groups that are frequently "chaotic and exhibit herd beha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |