|
NoScript
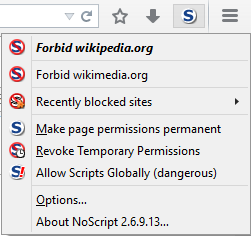
NoScript (or NoScript Security Suite) is a free software extension for Mozilla Firefox, SeaMonkey, other Mozilla-based web browsers and Google Chrome, written and maintained by Giorgio Maone, an Italian software developer and member of the Mozilla Security Group. Features Active content blocking By default, NoScript blocks active (executable) web content, which can be wholly or partially unblocked by allowlisting a site or domain from the extension's toolbar menu or by clicking a placeholder icon. In the default configuration, active content is globally denied, although the user may turn this around and use NoScript to block specific unwanted content. The allowlist may be permanent or temporary (until the browser closes or the user revokes permissions). Active content may consist of JavaScript, web fonts, media codecs, WebGL, and Flash. The add-on also offers specific countermeasures against security exploits. Because many web browser attacks require active content that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NoScript Screenshot
NoScript (or NoScript Security Suite) is a free software extension for Mozilla Firefox, SeaMonkey, other Mozilla-based web browsers and Google Chrome, written and maintained by Giorgio Maone, an Italian software developer and member of the Mozilla Security Group. Features Active content blocking By default, NoScript blocks active (executable) web content, which can be wholly or partially unblocked by allowlisting a site or domain from the extension's toolbar menu or by clicking a placeholder icon. In the default configuration, active content is globally denied, although the user may turn this around and use NoScript to block specific unwanted content. The allowlist may be permanent or temporary (until the browser closes or the user revokes permissions). Active content may consist of JavaScript, web fonts, media codecs, WebGL, and Flash. The add-on also offers specific countermeasures against security exploits. Because many web browser attacks require active content th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clickjacking
Clickjacking (classified as a user interface redress attack or UI redressing) is a malicious technique of tricking a user into clicking on something different from what the user perceives, thus potentially revealing confidential information or allowing others to take control of their computer while clicking on seemingly innocuous objects, including web pages. Clickjacking is an instance of the confused deputy problem, wherein a computer is tricked into misusing its authority.The Confused Deputy rides again! Tyler Close, October 2008 History In 2002, it had been noted that it was possible to load a transparent layer over a web page and have the user's input affect the transparent layer without the user noticin ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-site Scripting
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is a type of security vulnerability that can be found in some web applications. XSS attacks enable attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users. A cross-site scripting vulnerability may be used by attackers to bypass access controls such as the same-origin policy. Cross-site scripting carried out on websites accounted for roughly 84% of all security vulnerabilities documented by Symantec up until 2007.During the second half of 2007, 11,253 site-specific cross-site vulnerabilities were documented by XSSed, compared to 2,134 "traditional" vulnerabilities documented by Symantec, in XSS effects vary in range from petty nuisance to significant security risk, depending on the sensitivity of the data handled by the vulnerable site and the nature of any security mitigation implemented by the site's owner network. Background Security on the web depends on a variety of mechanisms, including an underlying concept of trust known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTPS Everywhere
HTTPS Everywhere is a Free and open-source software, free and open-source browser extension for Google Chrome, Microsoft Edge, Firefox, Mozilla Firefox, Opera (web browser), Opera, Brave (web browser), Brave, Vivaldi (web browser), Vivaldi and Firefox for Android, which is developed collaboratively by The Tor Project, Inc, The Tor Project and the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF). It automatically makes websites use a more secure HTTPS connection instead of Hypertext Transfer Protocol, HTTP, if they support it. The option "Encrypt All Sites Eligible" makes it possible to block and unblock all non-HTTPS browser connections with one click. Due to the widespread adoption of HTTPS on the World Wide Web, and the integration of HTTPS-only mode on major browsers, the extension will be retired at the end of 2022. Development HTTPS Everywhere was inspired by Google's increased use of HTTPS and is designed to force the usage of HTTPS automatically whenever possible. The code, in part, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-site Request Forgery
Cross-site request forgery, also known as one-click attack or session riding and abbreviated as CSRF (sometimes pronounced ''sea-surf'') or XSRF, is a type of malicious exploit of a website or web application where unauthorized commands are submitted from a user that the web application trusts. There are many ways in which a malicious website can transmit such commands; specially-crafted image tags, hidden forms, and JavaScript fetch or XMLHttpRequests, for example, can all work without the user's interaction or even knowledge. Unlike cross-site scripting (XSS), which exploits the trust a user has for a particular site, CSRF exploits the trust that a site has in a user's browser. In a CSRF attack, an innocent end user is tricked by an attacker into submitting a web request that they did not intend. This may cause actions to be performed on the website that can include inadvertent client or server data leakage, change of session state, or manipulation of an end user's account. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paywall
A paywall is a method of restricting access to content, with a purchase or a paid subscription, especially news. Beginning in the mid-2010s, newspapers started implementing paywalls on their websites as a way to increase revenue after years of decline in paid print readership and advertising revenue, partly due to the use of ad blockers. In academics, research papers are often subject to a paywall and are available via academic libraries that subscribe. Paywalls have also been used as a way of increasing the number of print subscribers; for example, some newspapers offer access to online content plus delivery of a Sunday print edition at a lower price than online access alone. Newspaper websites such as that of '' The Boston Globe'' and ''The New York Times'' use this tactic because it increases both their online revenue and their print circulation (which in turn provides more ad revenue). History In 1996, ''The Wall Street Journal'' set up and has continued to maintain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adobe Flash
Adobe Flash (formerly Macromedia Flash and FutureSplash) is a multimedia software platform used for production of animations, rich web applications, desktop applications, mobile apps, mobile games, and embedded web browser video players. Flash displays text, vector graphics, and raster graphics to provide animations, video games, and applications. It allows streaming of audio and video, and can capture mouse, keyboard, microphone, and camera input. Artists may produce Flash graphics and animations using Adobe Animate (formerly known as Adobe Flash Professional). Software developers may produce applications and video games using Adobe Flash Builder, FlashDevelop, Flash Catalyst, or any text editor combined with the Apache Flex SDK. End users view Flash content via Flash Player (for web browsers), Adobe AIR (for desktop or mobile apps), or third-party players such as Scaleform (for video games). Adobe Flash Player (which is available on Microsoft Windows, macOS, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefox 57
Firefox was created by Dave Hyatt and Blake Ross as an experimental branch of the Mozilla browser, first released as Firefox 1.0 on November 9, 2004. Starting with version 5.0, a rapid release cycle was put into effect, resulting in a new major version release every six weeks. This was gradually accelerated further in late 2019, so that new major releases occur on four-week cycles starting in 2020. Current and future releases Current supported official releases :* Firefox 109.0 :* Firefox 102.7.0 ESR Current supported test releases :* Firefox 110.0 Developer Edition :* Firefox 110.0 Beta :* Firefox 111.0 Nightly Future official releases ;Rapid :* Firefox 110.0 :* Firefox 111.0 :* Firefox 112.0 :* Firefox 113.0 :* Firefox 114.0 :* Firefox 115.0 :* Firefox 116.0 :* Firefox 117.0 :* Firefox 118.0 :* Firefox 119.0 :* Firefox 120.0 :* Firefox 121.0 ;ESR :* Firefox 102.8 ESR :* Firefox 102.9 ESR :* Firefox 102.10 ESR :* Firefox 102.11 ESR :* Firefox 102.12 ESR ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNS Rebinding
DNS rebinding is a method of manipulating resolution of domain names that is commonly used as a form of computer attack. In this attack, a malicious web page causes visitors to run a client-side script that attacks machines elsewhere on the network. In theory, the same-origin policy prevents this from happening: client-side scripts are only allowed to access content on the same host that served the script. Comparing domain names is an essential part of enforcing this policy, so DNS rebinding circumvents this protection by abusing the Domain Name System (DNS). This attack can be used to breach a private network by causing the victim's web browser to access computers at private IP addresses and return the results to the attacker. It can also be employed to use the victim machine for spamming, distributed denial-of-service attacks, or other malicious activities. How DNS rebinding works The attacker registers a domain (such as attacker.com) and delegates it to a DNS server that is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Firefox
Mozilla Firefox, or simply Firefox, is a free and open-source web browser developed by the Mozilla Foundation and its subsidiary, the Mozilla Corporation. It uses the Gecko rendering engine to display web pages, which implements current and anticipated web standards. In November 2017, Firefox began incorporating new technology under the code name " Quantum" to promote parallelism and a more intuitive user interface. Firefox is available for Windows 7 and later versions, macOS, and Linux. Its unofficial ports are available for various Unix and Unix-like operating systems, including FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, illumos, and Solaris Unix. It is also available for Android and iOS. However, as with all other iOS web browsers, the iOS version uses the WebKit layout engine instead of Gecko due to platform requirements. An optimized version is also available on the Amazon Fire TV as one of the two main browsers available with Amazon's Silk Browser. Firefox was created in 2002 unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HTTP Secure
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It is used for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or, formerly, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). The protocol is therefore also referred to as HTTP over TLS, or HTTP over SSL. The principal motivations for HTTPS are authentication of the accessed website, and protection of the privacy and integrity of the exchanged data while in transit. It protects against man-in-the-middle attacks, and the bidirectional encryption of communications between a client and server protects the communications against eavesdropping and tampering. The authentication aspect of HTTPS requires a trusted third party to sign server-side digital certificates. This was historically an expensive operation, which meant fully authenticated HTTPS connections were usually found only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
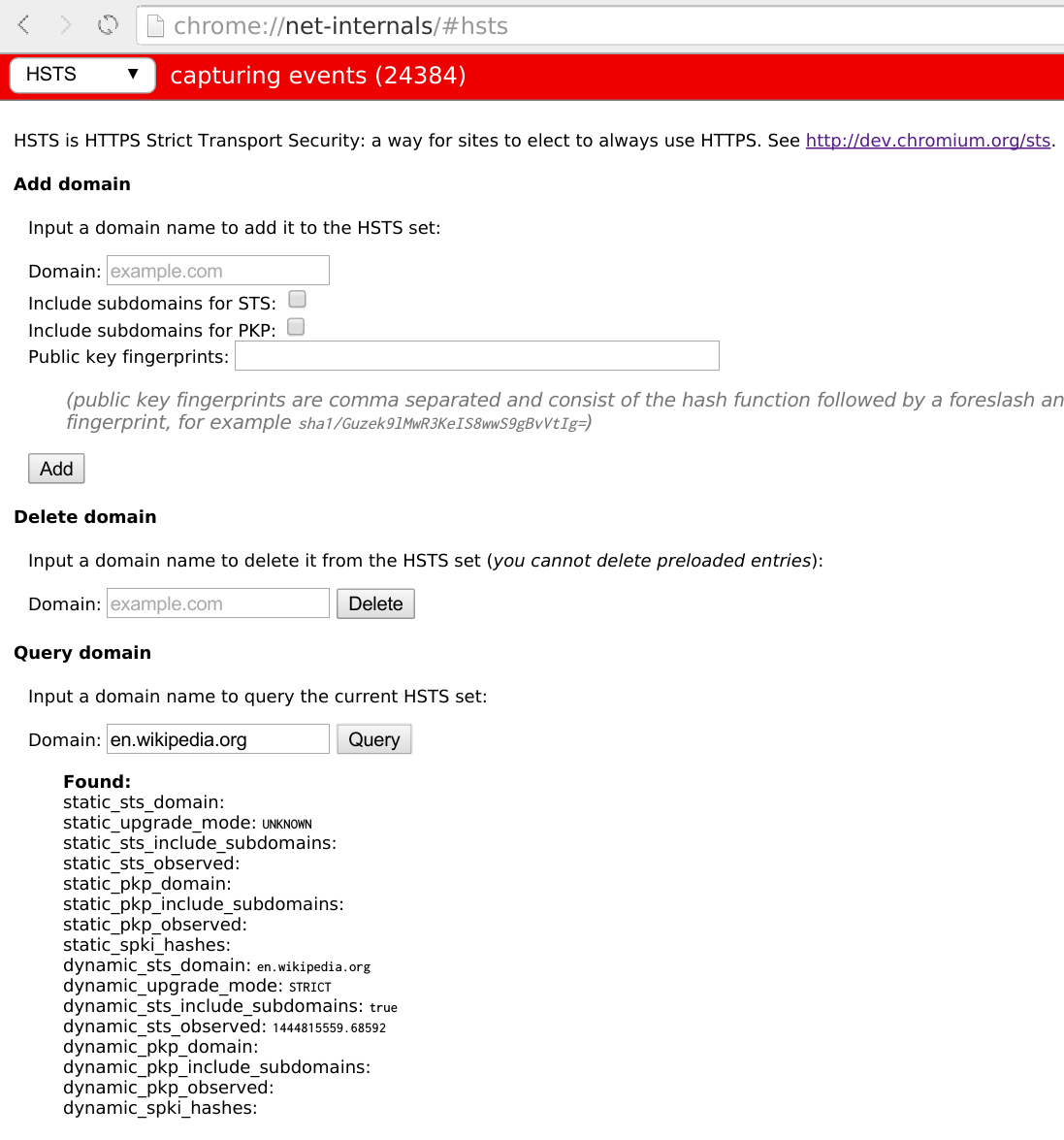
HTTP Strict Transport Security
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) is a policy mechanism that helps to protect websites against man-in-the-middle attacks such as protocol downgrade attacks and cookie hijacking. It allows web servers to declare that web browsers (or other complying user agents) should automatically interact with it using only HTTPS connections, which provide Transport Layer Security (TLS/SSL), unlike the insecure HTTP used alone. HSTS is an IETF standards track protocol and is specified in . The HSTS Policy is communicated by the server to the user agent via an HTTP response header field named "Strict-Transport-Security". HSTS Policy specifies a period of time during which the user agent should only access the server in a secure fashion. Websites using HSTS often do not accept clear text HTTP, either by rejecting connections over HTTP or systematically redirecting users to HTTPS (though this is not required by the specification). The consequence of this is that a user-agent not capable of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |