|
Norpress (company)
Nortriptyline, sold under the brand name Pamelor, among others, is a medication used to treat depression. This medicine is used for: neuropathic pain, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), smoking cessation and anxiety. As with many antidepressants, its use for young people with depression and other psychiatric disorders may be limited due to increased suicidality in the 18-24 population initiating treatment. Nortriptyline is a less preferred treatment for ADHD and stopping smoking. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include dry mouth, constipation, blurry vision, sleepiness, low blood pressure with standing, and weakness. Serious side effects may include seizures, an increased risk of suicide in those less than 25 years of age, urinary retention, glaucoma, mania, and a number of heart issues. Nortriptyline may cause problems if taken during pregnancy. Use during breastfeeding appears to be relatively safe. It is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) and is believed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
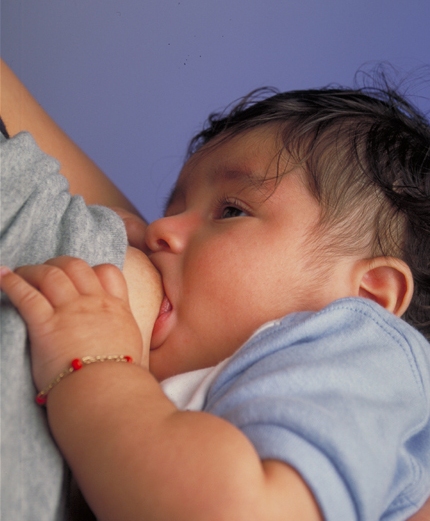
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, or nursing, is the process by which human breast milk is fed to a child. Breast milk may be from the breast, or may be expressed by hand or pumped and fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's life and continue as often and as much as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. Breastfeeding has a numb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochrane (organisation)
Cochrane (previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration) is a British international charitable organisation formed to organise medical research findings to facilitate evidence-based choices about health interventions involving health professionals, patients and policy makers. It includes 53 review groups that are based at research institutions worldwide. Cochrane has approximately 30,000 volunteer experts from around the world. The group conducts systematic reviews of health-care interventions and diagnostic tests and publishes them in the Cochrane Library. According to the Library, articles are available via one-click access, but some require paid subscription or registration before reading. A few reviews, in occupational health for example, incorporate results from non-randomised observational studies as well as controlled before–after (CBA) studies and interrupted time-series studies. History Cochrane, previously known as the Cochrane Collaboration, was founded in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporomandibular Joint Disorder
Temporomandibular joint dysfunction (TMD, TMJD) is an umbrella term covering pain and dysfunction of the muscles of mastication (the muscles that move the jaw) and the temporomandibular joints (the joints which connect the mandible to the skull). The most important feature is pain, followed by restricted mandibular movement, and noises from the temporomandibular joints (TMJ) during jaw movement. Although TMD is not life-threatening, it can be detrimental to quality of life; this is because the symptoms can become chronic and difficult to manage. In this article, the term ''temporomandibular disorder'' is taken to mean any disorder that affects the temporomandibular joint, and ''temporomandibular joint dysfunction'' (here also abbreviated to TMD) is taken to mean symptomatic (e.g. pain, limitation of movement, clicking) dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint. However, there is no single, globally accepted term or definition concerning this topic. TMDs have a range of cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuralgia
Neuralgia (Greek ''neuron'', "nerve" + ''algos'', "pain") is pain in the distribution of one or more nerves, as in intercostal neuralgia, trigeminal neuralgia, and glossopharyngeal neuralgia. Classification Under the general heading of neuralgia are trigeminal neuralgia (TN), atypical trigeminal neuralgia (ATN), occipital neuralgia, glossopharyngeal neuralgia and postherpetic neuralgia (caused by shingles or herpes). The term ''neuralgia'' is also used to refer to pain associated with sciatica and brachial plexopathy. Atypical (trigeminal) Atypical trigeminal neuralgia (ATN) is a rare form of neuralgia and may also be the most misdiagnosed form. The symptoms can be mistaken for migraines, dental problems such as temporomandibular joint disorder, musculoskeletal issues, and hypochondriasis. ATN can have a wide range of symptoms and the pain can fluctuate in intensity from mild aching to a crushing or burning sensation, and also to the extreme pain experienced with the more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Migraine
Migraine (, ) is a common neurological disorder characterized by recurrent headaches. Typically, the associated headache affects one side of the head, is pulsating in nature, may be moderate to severe in intensity, and could last from a few hours to three days. Non-headache symptoms may include nausea, vomiting, and photophobia, sensitivity to light, hyperacusis, sound, or Osmophobia, smell. The pain is generally made worse by physical activity during an attack,as PDF although regular physical exercise may prevent future attacks. Up to one-third of people affected have Aura (symptom), aura: typically, it is a short period of visual disturbance that signals that the headache will soon occur. Occasionally, aura can occur with little or no headache follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain and or abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may occur over a long time, sometimes for years. IBS can negatively affect quality of life and may result in missed school or work (absenteeism) or reduced productivity at work (presenteeism). Disorders such as anxiety, major depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome are common among people with IBS.The cited review is based on sources ranging from 1988 to 2001 and is probably biased relative to a more recent research. The causes of IBS may well be multi-factorial. Theories include combinations of "gut–brain axis" problems, alterations in gut motility, visceral hypersensitivity, infections including small intestinal bacterial overgrowth, neurotransmitters, genetic factors, and food sensitivity. Onset may be triggered by an intestinal infec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is a mental disorder, mental and Abnormal behavior, behavioral disease#Disorder, disorder, specifically an anxiety disorder characterized by reoccurring unexpected panic attacks. Panic attacks are sudden periods of intense fear that may include palpitations, sweating, shaking, shortness of breath, numbness, or a feeling that something terrible is going to happen. The maximum degree of symptoms occurs within minutes. There may be ongoing worries about having further attacks and avoidance of places where attacks have occurred in the past. The cause of panic disorder is unknown. Panic disorder often runs in families. Risk factors include smoking, psychological stress, and a history of child abuse. Diagnosis involves ruling out other potential causes of anxiety including other mental disorders, medical conditions such as heart disease or hyperthyroidism, and drug use. Screening for the condition may be done using a Patient Health Questionnaire, questionnaire. Panic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Off-label Use
Off-label use is the use of pharmaceutical drugs for an unapproved indication (medicine), indication or in an unapproved age group, dose (biochemistry), dosage, or route of administration. Both prescription drugs and over-the-counter drugs (OTCs) can be used in off-label ways, although most studies of off-label use focus on prescription drugs. Off-label use is very common and generally legal unless it violates ethical guidelines or safety regulations. The ability to prescribe drugs for uses beyond the officially approved indications is commonly used to good effect by healthcare providers. For example, methotrexate is commonly used off-label because its immunomodulatory effects relieve various disorders. However, off-label use can entail health risks and differences in legal liability. Pharmaceutical marketing, Marketing of pharmaceuticals for off-label use is usually prohibited. Indications and labeling laws An ''Indication (medicine), indication'' is when a drug is medically ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nocturnal Enuresis
Nocturnal enuresis, also informally called bedwetting, is urinary incontinence, involuntary urination while sleep, asleep after the age at which bladder control usually begins. Bedwetting in children and adults can result in emotional stress. Complications can include urinary tract infections. Most bedwetting is a Specific developmental disorder, developmental delay—not an emotional problem or physical illness. Only a small percentage (5 to 10%) of bedwetting cases have a specific medical cause. Bedwetting is commonly associated with a Family history (medicine), family history of the condition. Nocturnal enuresis is considered ''primary'' when a child has not yet had a prolonged period of being dry. ''Secondary'' nocturnal enuresis is when a child or adult begins wetting again after having stayed dry. Treatments range from Behaviour therapy, behavioral therapy, such as bedwetting alarms, to medication, such as Hormone replacement therapy, hormone replacement, and even surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generic Medication
A generic drug is a pharmaceutical drug that contains the same chemical substance as a drug that was originally protected by chemical patents. Generic drugs are allowed for sale after the patents on the original drugs expire. Because the active chemical substance is the same, the medical profile of generics is equivalent in performance. A generic drug has the same active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) as the original, but it may differ in some characteristics such as the manufacturing process, formulation, excipients, color, taste, and packaging. Although they may not be associated with a particular company, generic drugs are usually subject to government regulations in the countries in which they are dispensed. They are labeled with the name of the manufacturer and a generic non-proprietary name such as the United States Adopted Name (USAN) or International Nonproprietary Name (INN) of the drug. A generic drug must contain the same active ingredients as the original brand-name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1.jpg)
.png)
