|
Nominal Group (functional Grammar)
In systemic functional grammar (SFG), a nominal group is a group of words that represents or describes an entity, for example ''The nice old English police inspector who was sitting at the table with Mr Morse''. Grammatically, the wording "The nice old English police inspector who was sitting at the table with Mr Morse" can be understood as a nominal group (a description of someone), which functions as the subject of the information exchange and as the person being identified as "Mr Morse". A nominal group is widely regarded as synonymous with noun phrase in other grammatical models. However, there are two major differences between the functional notion of a ''nominal group'' and the formal notion of a ''noun phrase'' that must be taken into account. Firstly, the coiner of the term, Halliday, and some of his followers draw a theoretical distinction between the terms ''group'' and ''phrase''. Halliday argues that "A phrase is different from a group in that, whereas a group is an ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arkansas Black Apples
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the South Central United States. It is bordered by Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, and Texas and Oklahoma to the west. Its name is from the Osage language, a Dhegiha Siouan language, and referred to their relatives, the Quapaw people. The state's diverse geography ranges from the mountainous regions of the Ozark and Ouachita Mountains, which make up the U.S. Interior Highlands, to the densely forested land in the south known as the Arkansas Timberlands, to the eastern lowlands along the Mississippi River and the Arkansas Delta. Arkansas is the 29th largest by area and the 34th most populous state, with a population of just over 3 million at the 2020 census. The capital and most populous city is Little Rock, in the central part of the state, a hub for transportation, business, culture, and government. The northwestern corner of the state, including the Fayetteville–Springdale– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Functional Grammar
Systemic functional grammar (SFG) is a form of grammatical description originated by Michael Halliday. It is part of a social semiotic approach to language called '' systemic functional linguistics''. In these two terms, ''systemic'' refers to the view of language as "a network of systems, or interrelated sets of options for making meaning"; ''functional'' refers to Halliday's view that language is as it is because of what it has evolved to do (see Metafunction). Thus, what he refers to as the ''multidimensional architecture of language'' "reflects the multidimensional nature of human experience and interpersonal relations." Influences Halliday describes his grammar as built on the work of Saussure, Louis Hjelmslev, Malinowski, J.R. Firth, and the Prague school linguists. In addition, he drew on the work of the American anthropological linguists Boas, Sapir and Whorf. His "main inspiration" was Firth, to whom he owes, among other things, the notion of language as system. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun Phrase
In linguistics, a noun phrase, or nominal (phrase), is a phrase that has a noun or pronoun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently occurring phrase type. Noun phrases often function as verb subjects and objects, as predicative expressions and as the complements of prepositions. Noun phrases can be embedded inside each other; for instance, the noun phrase ''some of his constituents'' contains the shorter noun phrase ''his constituents''. In some more modern theories of grammar, noun phrases with determiners are analyzed as having the determiner as the head of the phrase, see for instance Chomsky (1995) and Hudson (1990). Identification Some examples of noun phrases are underlined in the sentences below. The head noun appears in bold. ::This election-year's politics are annoying for many people. ::Almost every sentence contains at least one noun phrase. ::Current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Halliday
Michael Alexander Kirkwood Halliday (often M. A. K. Halliday; 13 April 1925 – 15 April 2018) was a British linguist who developed the internationally influential systemic functional linguistics (SFL) model of language. His grammatical descriptions go by the name of systemic functional grammar. Halliday described language as a semiotic system, "not in the sense of a system of signs, but a systemic resource for meaning". For Halliday, language was a "meaning potential"; by extension, he defined linguistics as the study of "how people exchange meanings by 'languaging'". Halliday described himself as a ''generalist'', meaning that he tried "to look at language from every possible vantage point", and has described his work as "wander ngthe highways and byways of language". But he said that "to the extent that I favoured any one angle, it was the social: language as the creature and creator of human society". Halliday's grammar differs markedly from traditional accounts that emphasi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morpheme
A morpheme is the smallest meaningful Constituent (linguistics), constituent of a linguistic expression. The field of linguistics, linguistic study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology (linguistics), morphology. In English, morphemes are often but bound and free morphemes, not necessarily word, words. Morphemes that stand alone are considered root (linguistics), roots (such as the morpheme ''cat''); other morphemes, called affix, affixes, are found only in combination with other morphemes. For example, the ''-s'' in ''cats'' indicates the concept of plurality but is always bound to another concept to indicate a specific kind of plurality. This distinction is not universal and does not apply to, for example, Latin, in which many roots cannot stand alone. For instance, the Latin root ''reg-'' (‘king’) must always be suffixed with a case marker: ''rex'' (''reg-s''), ''reg-is'', ''reg-i'', etc. For a language like Latin, a root can be defined as the main lexical morpheme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clause
In language, a clause is a constituent that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject and a syntactic predicate, the latter typically a verb phrase composed of a verb with any objects and other modifiers. However, the subject is sometimes unvoiced if it is retrievable from context, especially in null-subject language but also in other languages, including English instances of the imperative mood. A complete simple sentence includes a single clause with a finite verb. Complex sentences contain multiple clauses including at least one ''independent clause'' (meaning, a clause that can stand alone as a simple sentence) coordinated either with at least one dependent clause (also called an embedded clause) or with one or more independent clauses. Two major distinctions A primary division for the discussion of clauses is the distinction between independent clauses and dependent clauses. An independent clause can s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thematic Equative
In systemic functional grammar, a thematic equative is a thematic resource in which two or more separate elements in a clause are grouped together to form a single constituent of the theme-plus-rheme structure. An example of this is: :What the guests need for breakfast is an omelette. Here, the theme—the grammatical point of departure—is in bold text; it announces at the start to the listener or reader what the message will be about—the writer's or speaker's angle ("I'm going to tell you what they need for breakfast"). The rheme (the rest of the clause) is in regular text. This type of clause sets up the theme-plus-rheme structure in the form of an equation, where theme = rheme. The equation is always expressed by some form of the verb ''be''. A thematic equative allows for all possible parts of a clause to be shifted to the start, to be the theme, so that the message can be structured in whatever way the speaker or writer wants. For example: :An omelette is what the guest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Functional Linguistics
# * Systemic functional linguistics (SFL) is an approach to linguistics, among functional linguistics Functional linguistics is an approach to the study of language characterized by taking systematically into account the speaker's and the hearer's side, and the communicative needs of the speaker and of the given language community. Linguistic fun ..., that considers language as a Social semiotics, social semiotic system. It was devised by Michael Halliday, who took the notion of system from J. R. Firth, his teacher (Halliday, 1961). Firth proposed that systems refer to possibilities subordinated to structure; Halliday "liberated" choice from structure and made it the central organising dimension of SFL. In more technical terms, while many approaches to linguistic description place structure and the syntagmatic analysis, syntagmatic axis foremost, SFL adopts the paradigmatic analysis, paradigmatic axis as its point of departure. ''Systemic'' foregrounds Saussure's "paradigmatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formalism (philosophy)
The term ''formalism'' describes an emphasis on form over content or meaning in the arts, literature, or philosophy. A practitioner of formalism is called a ''formalist''. A formalist, with respect to some discipline, holds that there is no transcendent meaning to that discipline other than the literal content created by a practitioner. For example, formalists within mathematics claim that mathematics is no more than the symbols written down by the mathematician, which is based on logic and a few elementary rules alone. This is as opposed to non-formalists, within that field, who hold that there are some things inherently true, and are not, necessarily, dependent on the symbols within mathematics so much as a greater truth. Formalists within a discipline are completely concerned with "the rules of the game," as there is no other external truth that can be achieved beyond those given rules. In this sense, formalism lends itself well to disciplines based upon axiomatic systems. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
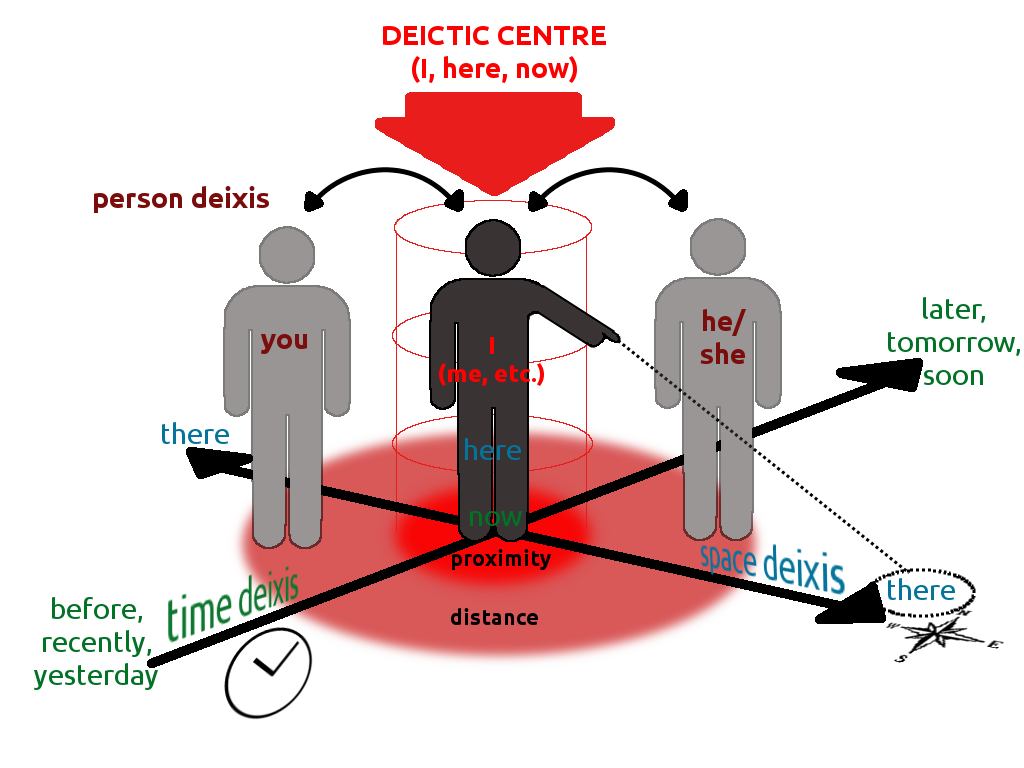
Deictic
In linguistics, deixis (, ) is the use of general words and phrases to refer to a specific time, place, or person in context, e.g., the words ''tomorrow'', ''there'', and ''they''. Words are deictic if their semantic meaning is fixed but their denoted meaning varies depending on time and/or place. Words or phrases that require contextual information to be fully understood—for example, English pronouns—are deictic. Deixis is closely related to anaphora. Although this article deals primarily with deixis in spoken language, the concept is sometimes applied to written language, gestures, and communication media as well. In linguistic anthropology, deixis is treated as a particular subclass of the more general semiotic phenomenon of indexicality, a sign "pointing to" some aspect of its context of occurrence. Although this article draws examples primarily from English, deixis is believed to be a feature (to some degree) of all natural languages.Lyons, John (1977) "Deixis, space and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun Phrase
In linguistics, a noun phrase, or nominal (phrase), is a phrase that has a noun or pronoun as its head or performs the same grammatical function as a noun. Noun phrases are very common cross-linguistically, and they may be the most frequently occurring phrase type. Noun phrases often function as verb subjects and objects, as predicative expressions and as the complements of prepositions. Noun phrases can be embedded inside each other; for instance, the noun phrase ''some of his constituents'' contains the shorter noun phrase ''his constituents''. In some more modern theories of grammar, noun phrases with determiners are analyzed as having the determiner as the head of the phrase, see for instance Chomsky (1995) and Hudson (1990). Identification Some examples of noun phrases are underlined in the sentences below. The head noun appears in bold. ::This election-year's politics are annoying for many people. ::Almost every sentence contains at least one noun phrase. ::Current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |