|
Noisy Investigation
Noisy investigations are used by the Church of Scientology to intimidate, harass, and attack their enemies. The Church used to openly label such people as Fair Game. The goal of a noisy investigation may not be to find out anything, but to harass the person being investigated. The procedure is to contact friends, neighbours, co-workers, etc. and inform them that they are investigating crimes by the targeted individual.Atack, JoA Piece of Blue Sky, Chapter 5: Hubbard's Travels © Jon Atack 1990. (convenience link provided by Xenu.net) A 1966 Hubbard Communications Office Executive Letter entitled "How to do a NOISY Investigation" described the practice as: The investigation may also be undertaken by hired detectives. A memo, reprinted in the British paper "People", said: "We want at least one bad mark on every psychiatrist in England, a murder, an assault, or a rape or more than one.... This is Project Psychiatry. We will remove them." Some Scientologists claim that their p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of Scientology
The Church of Scientology is a group of interconnected corporate entities and other organizations devoted to the practice, administration and dissemination of Scientology, which is variously defined as a cult, a scientology as a business, business, or a new religious movement. The movement has been the subject of a number of Scientology controversies, controversies, and the Church of Scientology has been described by government inquiries, international parliamentary bodies, scholars, law lords, and numerous superior court judgements as both a dangerous cult and a manipulative Scientology as a business, profit-making business. In 1979, several executives of the organization were United States v. Hubbard, convicted and imprisoned for multiple offenses by a U.S. Federal Court. The Church of Scientology itself was convicted of fraud by a French court in 2009, a decision upheld by the supreme Court of Cassation (France), Court of Cassation in 2013. The Scientology in Germany, Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fair Game (Scientology)
The term Fair Game is used to describe policies and practices carried out by the Church of Scientology towards people and groups it perceives as its enemies. Founder of Scientology, L. Ron Hubbard, established the policy in the 1950s, in response to criticism both from within and outside his organization. Individuals or groups who are "Fair Game" are judged to be a threat to the Church and, according to the policy, can be punished and harassed using any and all means possible. In 1968, Hubbard officially canceled use of the term "Fair Game" because of negative public relations it caused, although the Church's aggressive response to criticism continued. Applying the principles of Fair Game, Hubbard and his followers targeted many individuals as well as government officials and agencies, including a program of covert and illegal infiltration of the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and other United States government agencies during the 1970s. They also conducted private investigati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foster Report
The Foster Report is a 1971 report titled ''Enquiry into the Practice and Effects of Scientology'', written by Sir John Foster for the government of the United Kingdom, regarding the Church of Scientology. The report made its case with L. Ron Hubbard's own words and reprinted a number of internal Ethics Orders. It concluded that it would be unfair to ban Scientology outright, but asked for legislation to ensure that psychotherapy in the United Kingdom is delivered in an ethical manner. He regarded the Scientology version of "ethics" as inappropriate. Documents seized by the FBI in raids on the Church's US headquarters in July 1977 revealed that an agent had been sent to investigate Sir John Foster in an attempt to link him to Paulette Cooper, author of ''The Scandal of Scientology'' and victim of Operation Freakout. The documents showed that Lord Balniel, who had requested the official inquiry, was also a target. Hubbard had written, "get a detective on that lord's past to unearth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
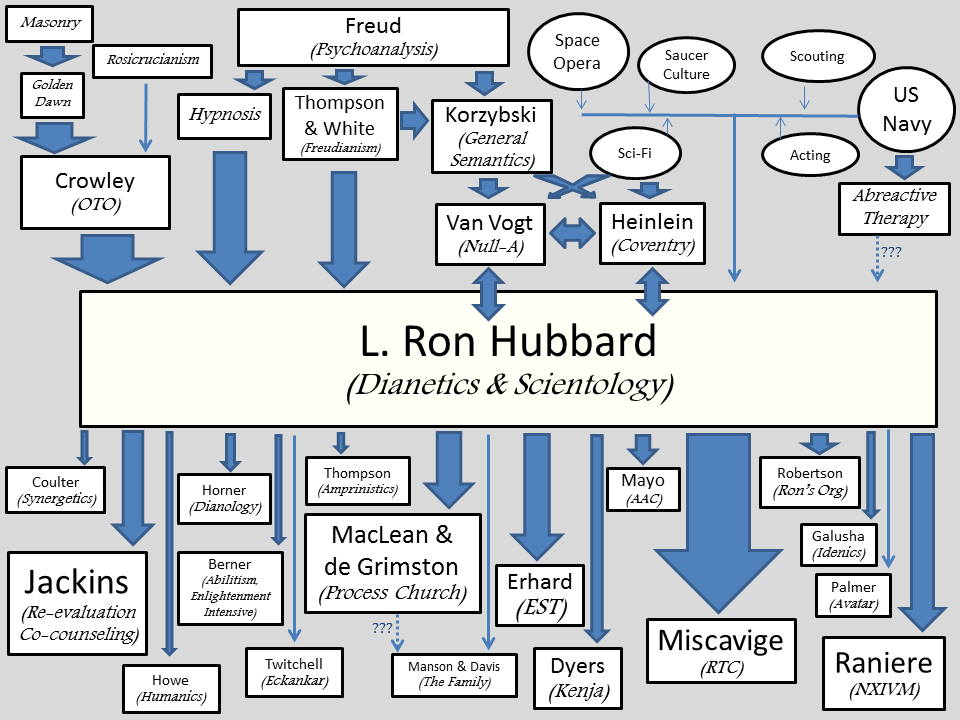
Scientology
Scientology is a set of beliefs and practices invented by American author L. Ron Hubbard, and an associated movement. It has been variously defined as a cult, a business, or a new religious movement. The most recent published census data indicate that there were about 25,000 followers in the United States (in 2008); around 1,800 followers in England (2021); 1,400 in Canada (2021); and about 1,600 in Australia (2016). Hubbard initially developed a set of ideas that he called Dianetics, which he represented as a form of therapy. This he promoted through various publications, as well as through the Hubbard Dianetic Research Foundation that he established in 1950. The foundation went bankrupt, and Hubbard lost the rights to his book ''Dianetics'' in 1952. He then recharacterized the subject as a religion and renamed it Scientology, retaining the terminology, doctrines, and the practice of "auditing". By 1954 he had regained the rights to Dianetics and retained both subjects under t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientology Controversy
Since its inception in 1954, the Church of Scientology has been involved in a number of controversies, including its stance on psychiatry, Scientology's legitimacy as a religion, the Church's aggressive attitude in dealing with its perceived enemies and critics, allegations of mistreatment of members, and predatory financial practices; for example, the high cost of religious training:191 and perceived exploitative practices. When mainstream media outlets have reported alleged abuses, representatives of the church have tended to deny such allegations. Secrecy The church maintains strict control over the use of its symbols, names and religious texts. Although U.S. intellectual property law allows for "fair use" of material for commentary, parody, educational purposes, etc., critics of the church such as Gerry Armstrong have argued the church unfairly and illegally uses the legal system to suppress "fair" uses, including suppressing any mention of the space opera aspects of the rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suppressive Person
Suppressive Person, often abbreviated SP, is a term used in Scientology to describe the "antisocial personalities" who, according to Scientology's founder L. Ron Hubbard, make up about 2.5% of the population. A statement on a Church of Scientology website describes this group as including notorious historic figures such as Adolf Hitler. The term is often applied to those whom the Church perceives as its enemies, such as those whose "disastrous" and "suppressive" acts are said to impede the progress of individual Scientologists or the Scientology movement. One of the reasons Scientology doctrines portray Suppressive Persons as such a danger is that they are supposed to make people around them become Potential Trouble Sources (abbreviated PTS). Scientology defines a PTS as "a person who is in some way connected to and being adversely affected by a suppressive person. Such a person is called a potential trouble source because he can be a lot of trouble to himself and to others." Hub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R2-45
R2-45 is the name given by L. Ron Hubbard to what he described as "an enormously effective process for exteriorization but its use is frowned upon by this society at this time". In Scientology doctrine, exteriorization refers to the separation of the thetan (soul) from the body, a phenomenon which Hubbard asserts can be achieved through Scientology auditing. R2-45 is said to be a process by which exteriorization could be produced by shooting a person in the head with a .45 pistol. This literal meaning is acknowledged by the Church of Scientology, although they deny that it is meant seriously. Origins of R2-45 In the book ''The Creation of Human Ability'', Hubbard describes two training "Routes", with the exercises in Route 1 numbered R1-4 to R1-15, and the exercises in Route 2 numbered R2-16 to R2-75. R2-45 is simply described as "an enormously effective process for exteriorization but its use is frowned upon by this society at this time". Several conflicting accounts exist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientology Beliefs And Practices
The Church of Scientology maintains a wide variety of beliefs and practices. The core belief holds that a human is an immortal, spiritual being (thetan) that is resident in a physical body. The thetan has had innumerable past lives, some of which, preceding the thetan's arrival on Earth, were lived in extraterrestrial cultures. Based on case studies at advanced levels, it is predicted that any Scientologist undergoing auditing will eventually come across and recount a common series of events. Scientology describes itself as the study and handling of the spirit in relationship to itself, others, and all of life. Scientologists also believe that people have innate, yet suppressed, power and ability which can be regained if cleared of unwanted behavioural patterns and discomforts. Scientology is described as "a religion to help people use scientific approaches to self-actualize their full potential." Believers reach their full potential "when they understand themselves in their tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |