|
No. 236 Operational Conversion Unit RAF
No. 236 Operational Conversion Unit was a Royal Air Force Operational Conversion Unit which was active between 1947 and 1992 and formed by re-numbering and merging different units. No. 236 OCU The conversion unit was formed at RAF Kinloss on 31 July 1947 and operated a variety of aircraft including Avro Lancasters, Airspeed Oxfords and Bristol Beaufighters until 30 September 1956 when it was disbanded for the first time to become the Maritime Operational Training Unit on 30 September 1956. The MOTU was formed by the merger of No. 236 OCU and No. 1 Maritime Reconnaissance School at Kinloss and operated Avro Shackletons and Nimrods until 1 July 1970 at St Mawgan. 236 OCU reformed at RAF St Mawgan on 1 July 1970 operating Hawker Siddeley Nimrods borrowed from No. 42 Squadron RAF until the unit was disbanded on 30 September 1992 at Kinloss to become No. 42 (Reserve) Squadron, the Nimrod Operational Conversion Unit History of No. 1 Maritime Reconnaissance School (1 MRS) The s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ensign Of The Royal Air Force
An ensign is the national flag flown on a vessel to indicate nationality. The ensign is the largest flag, generally flown at the stern (rear) of the ship while in port. The naval ensign (also known as war ensign), used on warships, may be different from the civil ensign (merchant ships) or the yacht ensign (recreational boats). Large versions of naval ensigns called battle ensigns are used when a warship goes into battle. The ensign differs from the jack (flag), jack, which is flown from a jackstaff at the bow of a vessel. In its widest sense, an ensign is just a flag or other standard. The European military rank of Ensign (rank), ensign, once responsible for bearing a unit's standard (whether national or regimental), derives from it (in the cavalry, the equivalent rank was Cornet (rank), cornet, named after a type of flag). Ensigns, such as the ancient Roman ensigns in the Arch of Constantine, are not always flags. National ensigns In nautical use, the ensign is flown on a shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hawker Hurricane
The Hawker Hurricane is a British single-seat fighter aircraft of the 1930s–40s which was designed and predominantly built by Hawker Aircraft Ltd. for service with the Royal Air Force (RAF). It was overshadowed in the public consciousness by the Supermarine Spitfire during the Battle of Britain in 1940, but the Hurricane inflicted 60 percent of the losses sustained by the Luftwaffe in the campaign, and fought in all the major theatres of the Second World War. The Hurricane originated from discussions between RAF officials and aircraft designer Sir Sydney Camm about a proposed monoplane derivative of the Hawker Fury biplane in the early 1930s. Despite an institutional preference for biplanes and lack of interest by the Air Ministry, Hawker refined their monoplane proposal, incorporating several innovations which became critical to wartime fighter aircraft, including retractable landing gear and the more powerful Rolls-Royce Merlin engine. The Air Ministry ordered Hawker's ''Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Conversion Units Of The Royal Air Force
Conversion units and operational conversion units (OCUs) were training units of the Royal Air Force (RAF). History With the introduction of new heavy bombers, the four-engined Short Stirling, Avro Lancaster, and Handley Page Halifax, the Royal Air Force introduced heavy conversion units (HCU). These HCUs began forming in late 1941, to qualify crews trained on medium bombers to operate the heavy bombers before final posting to the operational squadrons. Some of the HCUs were involved in bombing operations over Germany. After the end of the Second World War, the role of the HCUs was taken over by the operational conversion units (OCUs). Although the units had nominal bases, different flights and individual aircraft usually were detached nearer the operational bases. RAF OCUs are training units that prepare aircrew for operations on a particular type or types of aircraft or roles. Some OCUs have a shadow, or reserve, squadron designation, which is used if the unit has a war r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
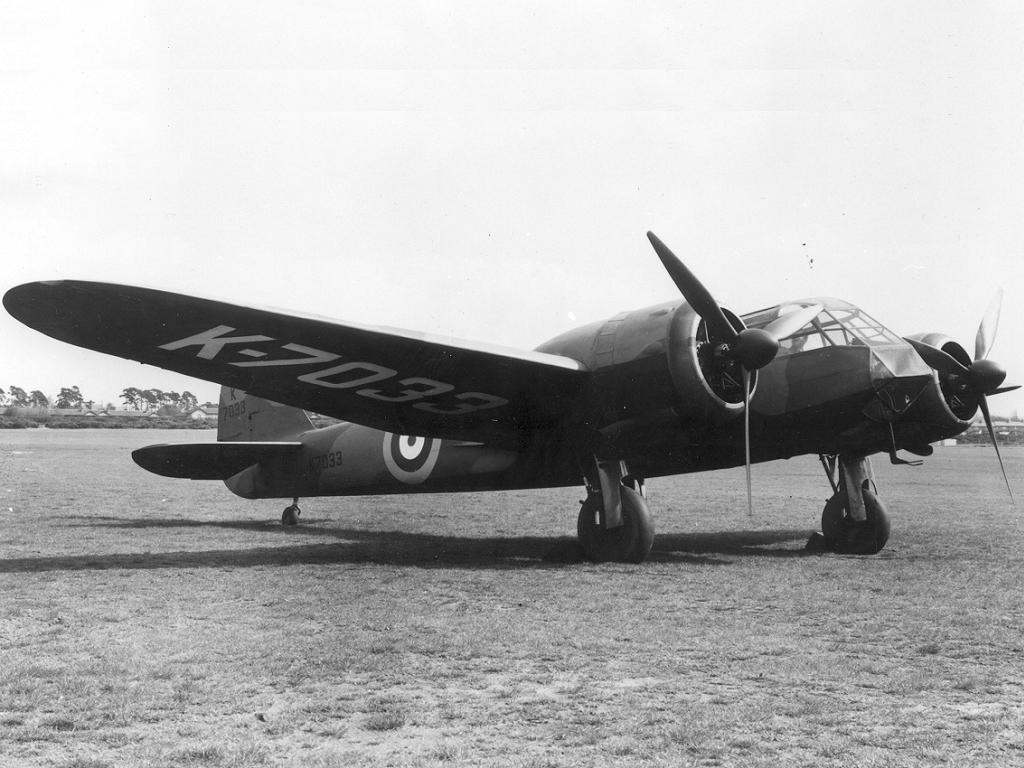
Bristol Buckmaster
The Bristol Buckmaster was an advanced British training aircraft operated by the Royal Air Force during the 1950s. Design and development By 1945, there was a serious gap in performance between the so-called advanced trainers in use – such as the Avro Anson, Airspeed Oxford, dual-control Bristol Blenheim and Lockheed Hudson – and the combat aircraft which the pilots would be expected to fly on graduation. The Bristol company's response to Air Ministry Specification T.13/43Mondey 1994, p. 70. was the Type 166 which was based on the Buckingham with a new wider front fuselage to allow side-by-side seating for an instructor and trainee and room for a radio operator. All armament and armour and military equipment was also removed. The Buckmaster was a propeller-driven, twin-engine mid-wing aircraft. The retractable undercarriage was of conventional (tailwheel) configuration. The radial engines were equipped with four-blade propellers. Two partly completed Buckinghams were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Havilland Tiger Moth
The de Havilland DH.82 Tiger Moth is a 1930s British biplane designed by Geoffrey de Havilland and built by the de Havilland Aircraft Company. It was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and other operators as a primary trainer aircraft. In addition to the type's principal use for ''ab initio'' training, the Second World War had RAF Tiger Moths operating in other capacities, including maritime surveillance and defensive anti-invasion preparations; some aircraft were even outfitted to function as armed light bombers. The Tiger Moth remained in service with the RAF until it was replaced by the de Havilland Chipmunk during the early 1950s. Many of the military surplus aircraft subsequently entered into civilian operation. Many nations have used the Tiger Moth in both military and civilian applications, and it remains in widespread use as a recreational aircraft. It is still occasionally used as a primary training aircraft, particularly for those pilots wanting to gain exper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed Hudson
The Lockheed Hudson is a light bomber and coastal reconnaissance aircraft built by the American Lockheed Aircraft Corporation. It was initially put into service by the Royal Air Force shortly before the outbreak of the Second World War and primarily operated by it thereafter. The Hudson was a military conversion of the Model 14 Super Electra airliner, and was the first significant aircraft construction contract for Lockheed — the initial RAF order for 200 Hudsons far surpassed any previous order the company had received. The Hudson served throughout the war, mainly with Coastal Command but also in transport and training roles, as well as delivering agents into occupied France. It was also used extensively with the Royal Canadian Air Force's anti-submarine squadrons and by the Royal Australian Air Force. Design and development In late 1937 Lockheed sent a cutaway drawing of the Model 14 to various publications, showing the new aircraft as a civilian aircraft and converte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAF Thornaby
Royal Air Force Thornaby or more simply RAF Thornaby was a former Royal Air Force Station located near the town of Thornaby-on-Tees, in the North Riding of Yorkshire, England. Fighter Command, Bomber Command and Coastal Command all operated from the base over its history, but its stint under Coastal Command is what the base was notable for, particularly in the air-sea rescue environment and the development of the ''Thornaby Bag''. This was an emergency bag dropped to downed aircrew at sea and contained food, cigarettes and drink. History The aerodrome was officially opened on 29 September 1929, although flying in Thornaby dates back to 1912 when Gustav Hamel used the Vale Farm for a flying display. Subsequently, the Royal Flying Corps used the same fields as a staging post between Catterick and Marske Aerodrome between 1914 and 1918.608 squadron and RAF Thornaby, E. W. Sockett In 1920, the government purchased of farm land from Thornaby Hall and developed the site. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Blenheim
The Bristol Blenheim is a British light bomber aircraft designed and built by the Bristol Aeroplane Company (Bristol) which was used extensively in the first two years of the Second World War, with examples still being used as trainers until the end of the war. Development began with the ''Type 142'', a civil airliner, in response to a challenge from Lord Rothermere to produce the fastest commercial aircraft in Europe. The ''Type 142'' first flew in April 1935, and the Air Ministry, impressed by its performance, ordered a modified design as the ''Type 142M'' for the Royal Air Force (RAF) as a bomber. Deliveries of the newly named Blenheim to RAF squadrons commenced on 10 March 1937. In service the Type 142M became the Blenheim Mk.I which would be developed into the longer Type 149, designated the Blenheim Mk.IV, except in Canada where Fairchild Canada built the Type 149 under licence as the Bolingbroke. The Type 160 Bisley was also developed from the Blenheim, but was already o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairey Battle
The Fairey Battle is a British single-engine light bomber that was designed and manufactured by the Fairey Aviation Company. It was developed during the mid-1930s for the Royal Air Force (RAF) as a monoplane successor to the Hawker Hart and Hind biplanes. The Battle was powered by the same high-performance Rolls-Royce Merlin piston engine that powered various contemporary British fighters such as the Hawker Hurricane and Supermarine Spitfire. As the Battle, with its three-man crew and bomb load, was much heavier than the fighters, it was therefore much slower. Though a great improvement over the aircraft that preceded it, its relatively slow speed, limited range and inadequate defensive armament of only two .303 (7.7 mm) machine guns left it highly vulnerable to enemy fighters and anti-aircraft fire.Ethell 1995, p. 177. The Fairey Battle was used on operations early in the Second World War. During the "Phoney War" the type achieved the distinction of scoring the first aer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miles Master
The Miles M.9 Master was a British two-seat monoplane advanced trainer designed and built by aviation company Miles Aircraft Ltd. It was inducted in large numbers into both the Royal Air Force (RAF) and Fleet Air Arm (FAA) during the Second World War. The Master can trace its origins back to the earlier M.9 Kestrel demonstrator aircraft. Following the failure of the rival de Havilland Don as a satisfactory trainer aircraft, the RAF ordered 500 ''M9A Master'' advanced trainers to meet its needs. Once in service, it provided a fast, strong and fully aerobatic aircraft that functioned as an excellent introduction to the high performance British fighter aircraft of the day: the Spitfire and Hurricane. Throughout its production life, thousands of aircraft and various variants of the Master were produced, the latter being largely influenced by engine availability. Numerous Masters were modified to enable their use as glider tows. The Master also served as the basis for the Miles M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gloster Gladiator
The Gloster Gladiator is a British biplane fighter. It was used by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) (as the Sea Gladiator variant) and was exported to a number of other air forces during the late 1930s. Developed privately as the Gloster SS.37, it was the RAF's last biplane fighter aircraft, and was rendered obsolete by newer monoplane designs even as it was being introduced. Though often pitted against more formidable foes during the early days of the Second World War, it acquitted itself reasonably well in combat. The Gladiator saw action in almost all theatres during the Second World War, with a large number of air forces, some of them on the Axis side. The RAF used it in France, Norway, Greece, the defence of Malta, the Middle East, and the brief Anglo-Iraqi War (during which the Royal Iraqi Air Force was similarly equipped). Other countries deploying the Gladiator included China against Japan, beginning in 1938; Finland (along with Swedish voluntee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
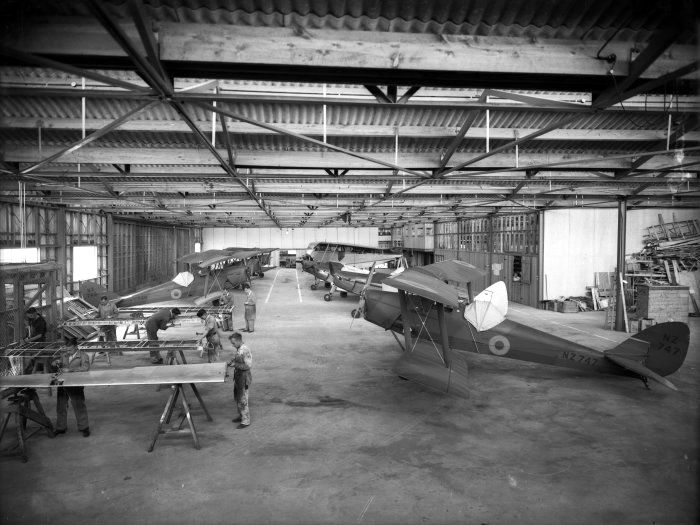
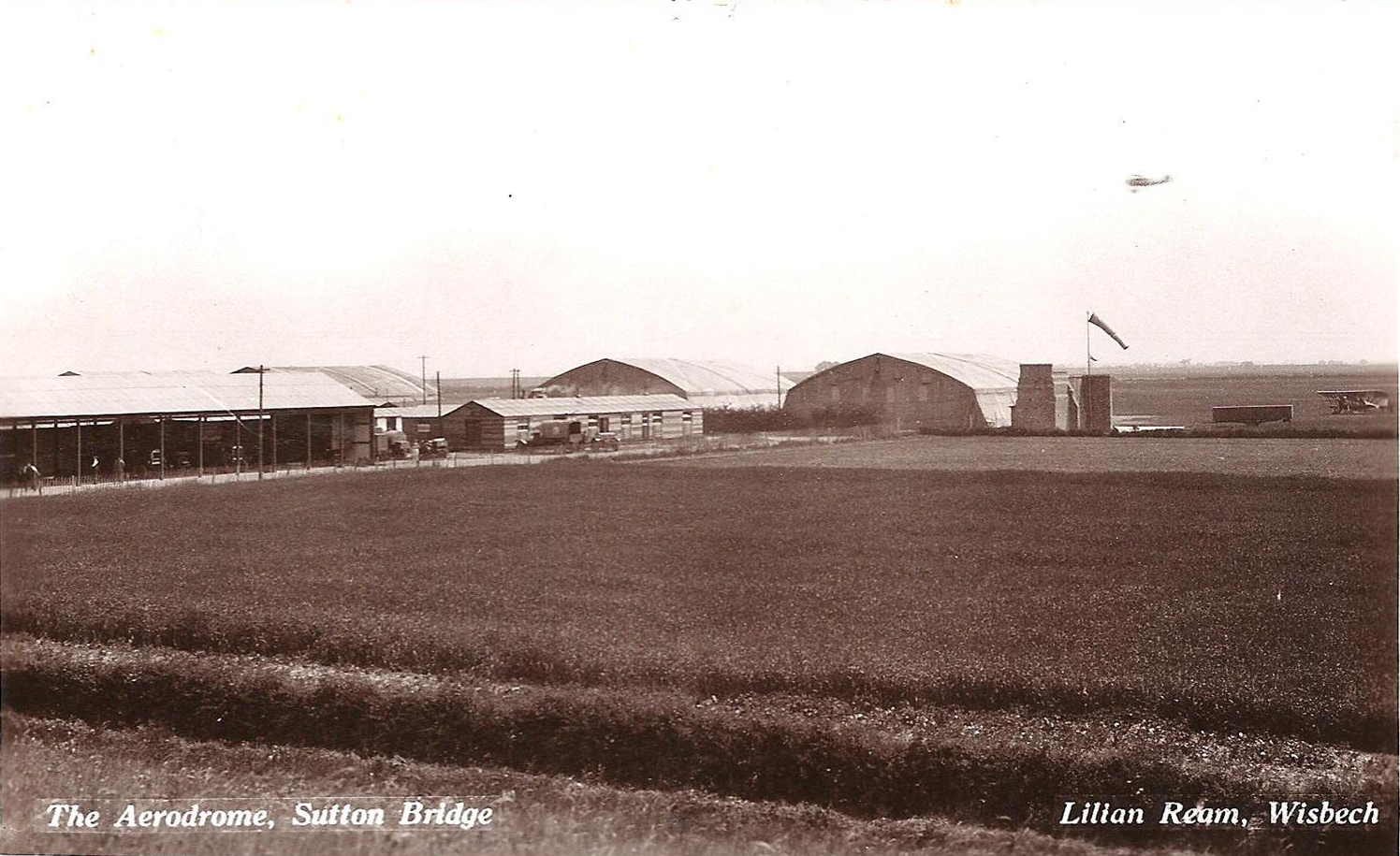
RAF Sutton Bridge
Royal Air Force Sutton Bridge or more simply RAF Sutton Bridge is a former Royal Air Force station found next to the village of Sutton Bridge in the south-east of Lincolnshire. The airfield was to the south of the current A17, and east of the River Nene, next to Walpole in Norfolk. History On 1 September 1926 the Air Ministry established R.A.F. Practice Camp Sutton BridgeThe official naming used and found in official Air Ministry notices, the London Gazette and other publications is "R.A.F. Practice Camp Sutton Bridge". One example publication: FLIGHT, 24 May 1928, Air Ministry Announcements, Page 394: The Royal Air Force, Royal Air Force Intelligence, Appointments, I.W.C. Mackenzie to "R.A.F. Practice Camp, Sutton Bridge", 14.4.2/ref> The National Archives (United Kingdom), The National Archives, Kew, United Kingdom, Reference: AIR 28/788 on 289 acres of acquired agricultural land next to Sutton Bridge village from Guy's Hospital Agricultural Estates.Combat Ready!, Author: Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |