|
Next-generation Lithography
Next-generation lithography or NGL is a term used in integrated circuit manufacturing to describe the photolithography, lithography technologies in development which are intended to replace current techniques. The term applies to any lithography method which uses a shorter-wavelength light or beam type than the current state of the art, such as X-ray lithography, electron beam lithography, focused ion beam lithography, and nanoimprint lithography. The term may also be used to describe techniques which achieve finer resolution features from an existing light wavelength. Many technologies once termed "next generation" have entered commercial production, and open-air photolithography, with visible light projected through hand-drawn photomasks, has gradually progressed to deep-UV immersion lithography using optical proximity correction, inverse lithography technology, off-axis illumination, phase-shift masks, double patterning, and multiple patterning. In the late 2010s, the combinati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7 Nm Process
In semiconductor manufacturing, the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors defines the 7 nm process as the MOSFET technology node following the 10 nm node. It is based on FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) technology, a type of multi-gate MOSFET technology. Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC) began production of 256 Mbit SRAM memory chips using a 7 nm process called N7 in June 2016, before Samsung began mass production of their 7 nm process called 7LPP devices in 2018. The first mainstream 7 nm mobile processor intended for mass market use, the Apple A12 Bionic, was released at Apple's September 2018 event. Although Huawei announced its own 7 nm processor before the Apple A12 Bionic, the Kirin 980 on August 31, 2018, the Apple A12 Bionic was released for public, mass market use to consumers before the Kirin 980. Both chips are manufactured by TSMC. AMD has released their "Rome" (EPYC 2) processors for servers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
32nm
The 32 nm node is the step following the 45 nm process in CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor device fabrication. "32-nanometre" refers to the average half-pitch (i.e., half the distance between identical features) of a memory cell (computing), memory cell at this technology level. Toshiba produced commercial 32Gibibit, GiB NAND flash memory chips with the 32nm process in 2009. Intel Corporation, Intel and Advanced Micro Devices, AMD produced commercial microchips using the 32-nanometre process in the early 2010s. IBM and the Common Platform also developed a 32 nm high-κ dielectric, high-κ metal gate process. Intel began selling its first 32 nm processors using the Westmere (microarchitecture), Westmere architecture on 7 January 2010. The 28-nanometre node was an intermediate half-node die shrink based on the 32-nanometre process. The 32 nm process was superseded by commercial 22 nm process, 22 nm technology in 2012. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
45nm
Per the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors, the 45 nm process is a MOSFET technology semiconductor node, node referring to the average half-pitch of a memory cell manufactured at around the 2007–2008 time frame. Panasonic, Matsushita and Intel started mass-producing 45 nm chips in late 2007, and Advanced Micro Devices, AMD started production of 45 nm chips in late 2008, while IBM, Infineon, Samsung, and Chartered Semiconductor have already completed a common 45 nm process platform. At the end of 2008, Semiconductor Manufacturing International Corporation, SMIC was the first China-based semiconductor company to move to 45 nm, having licensed the bulk 45 nm process from IBM. In 2008, TSMC moved on to a 40nm process. Many critical feature sizes are smaller than the wavelength of light used for photolithography, lithography (i.e., 193 nm and 248 nm). A variety of techniques, such as larger lenses, are used to make sub-wavelength f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
65nm
The 65 nm process is an advanced lithographic node used in volume CMOS (MOSFET) semiconductor fabrication. Printed linewidths (i.e. transistor gate lengths) can reach as low as 25 nm on a nominally 65 nm process, while the pitch between two lines may be greater than 130 nm. For comparison, cellular ribosomes are about 20 nm end-to-end. A crystal of bulk silicon has a lattice constant of 0.543 nm, so such transistors are on the order of 100 atoms across. Toshiba and Sony announced the 65 nm process in 2002, before Fujitsu and Toshiba began production in 2004, and then TSMC began production in 2005. By September 2007, Intel, AMD, IBM, UMC and Chartered were also producing 65 nm chips. While feature sizes may be drawn as 65 nm or less, the wavelengths of light used for lithography are 193 nm and 248 nm. Fabrication of sub-wavelength features requires special imaging technologies, such as optical proximity correction and pha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
90nm
The 90 nm process refers to the level of MOSFET (CMOS) fabrication process technology that was commercialized by the 2003–2005 timeframe, by leading semiconductor companies like Toshiba, Sony, Samsung, IBM, Intel, Fujitsu, TSMC, Elpida, AMD, Infineon, Texas Instruments and Micron Technology. The origin of the 90 nm value is historical, it reflects a trend of 70% scaling every 2–3 years. The naming is formally determined by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS). The 193 nm wavelength was introduced by many (but not all) companies for lithography of critical layers mainly during the 90 nm node. Yield issues associated with this transition (due to the use of new photoresists) were reflected in the high costs associated with this transition. Even more significantly, the 300 mm wafer size became mainstream at the 90 nm node. The previous wafer size was 200 mm diameter. History A 90nm silicon MOSFET was fabricated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
130 Nm
The 130 nanometer (130 nm) process refers to the level of semiconductor process technology that was reached in the 2000–2001 timeframe, by most leading semiconductor companies, like Intel, Texas Instruments, IBM, and TSMC. The origin of the 130 nm value is historical, as it reflects a trend of 70% scaling every 2–3 years. The naming is formally determined by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS). Some of the first CPUs manufactured with this process include Intel Tualatin family of Pentium III processors. Processors using 130 nm manufacturing technology * Motorola PowerPC 7447 and 7457 2002 * IBM Gekko (Nintendo GameCube) * IBM PowerPC G5 970 - October 2002 - June 2003 * Intel Pentium III Tualatin - 2001-06 * Intel Celeron Tualatin-256 - 2001-10-02 * Intel Pentium M Banias - 2003-03-12 * Intel Pentium 4 Northwood - 2002-01-07 * Intel Celeron Northwood-128 - 2002-09-18 * Intel Xeon Prestonia and Gallatin - 2002-02-25 * VIA C3 - 2001 * AMD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krypton Fluoride Laser
A krypton fluoride laser (KrF laser) is a particular type of excimer laser, which is sometimes (more correctly) called an exciplex laser. With its 248 nanometer wavelength, it is a deep ultraviolet laser which is commonly used in the production of semiconductor integrated circuits, industrial micromachining, and scientific research. The term excimer is short for 'excited dimer', while exciplex is short for 'excited complex'. An excimer laser typically contains a mixture of: a noble gas such as argon, krypton, or xenon; and a halogen gas such as fluorine or chlorine. Under suitably intense conditions of electromagnetic stimulation and pressure, the mixture emits a beam of coherent stimulated radiation as laser light in the ultraviolet range. KrF and ArF excimer lasers are widely incorporated into high-resolution photolithography machines, one of the critical tools required for microelectronic chip manufacturing in nanometer dimensions. Excimer laser lithographyJain, K. "Excimer La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
180 Nm
The 180 nm process refers to the level of MOSFET (CMOS) semiconductor process technology that was commercialized around the 1998–2000 timeframe by leading semiconductor companies, starting with TSMC and Fujitsu, then followed by Sony, Toshiba, Intel, AMD, Texas Instruments and IBM. The origin of the 180 nm value is historical, as it reflects a trend of 70% scaling every 2–3 years. The naming is formally determined by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS). Some of the first CPUs manufactured with this process include Intel Coppermine family of Pentium III processors. This was the first technology using a gate length shorter than that of light used for contemporary lithography, which had a wavelength of 193 nm. Some more recent microprocessors and microcontrollers (e.g. PIC) are using this technology because it is typically low cost and does not require upgrading of existing equipment. In 2022, Google sponsored open-source hardware p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
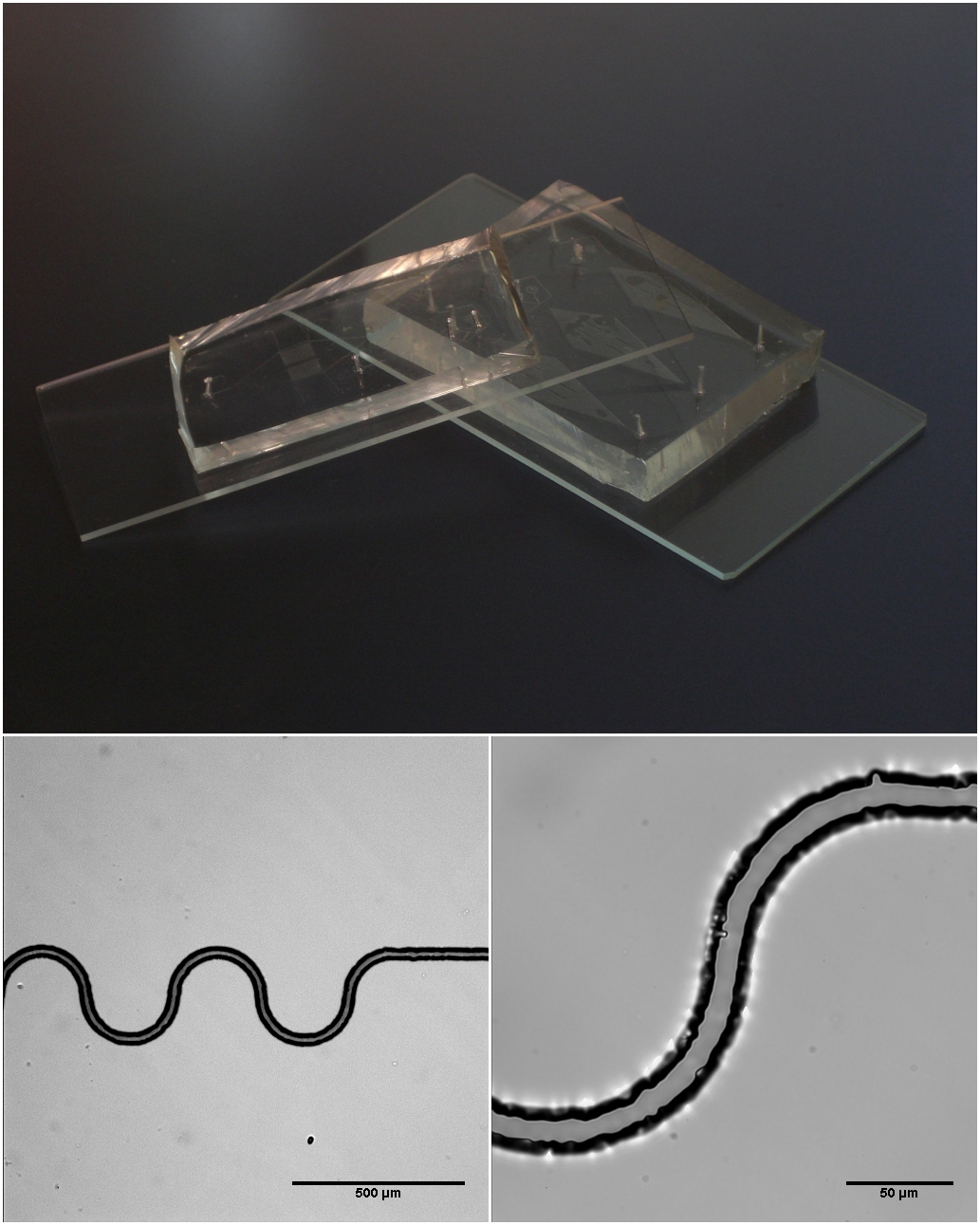
Microfluidics
Microfluidics refers to the behavior, precise control, and manipulation of fluids that are geometrically constrained to a small scale (typically sub-millimeter) at which surface forces dominate volumetric forces. It is a multidisciplinary field that involves engineering, physics, chemistry, biochemistry, nanotechnology, and biotechnology. It has practical applications in the design of systems that process low volumes of fluids to achieve multiplexing, automation, and high-throughput screening. Microfluidics emerged in the beginning of the 1980s and is used in the development of inkjet printheads, DNA chips, lab-on-a-chip technology, micro-propulsion, and micro-thermal technologies. Typically, micro means one of the following features: * Small volumes (μL, nL, pL, fL) * Small size * Low energy consumption * Microdomain effects Typically microfluidic systems transport, mix, separate, or otherwise process fluids. Various applications rely on passive fluid control using capillary fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hard Disk Drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnetic material. The platters are paired with magnetic heads, usually arranged on a moving actuator arm, which read and write data to the platter surfaces. Data is accessed in a random-access manner, meaning that individual blocks of data can be stored and retrieved in any order. HDDs are a type of non-volatile storage, retaining stored data when powered off. Modern HDDs are typically in the form of a small rectangular box. Introduced by IBM in 1956, HDDs were the dominant secondary storage device for general-purpose computers beginning in the early 1960s. HDDs maintained this position into the modern era of servers and personal computers, though personal computing devices produced in large volume, like cell phones and tablets, rely on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light-emitting Diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (UV) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)