|
New Year Picture
A New Year picture () is a popular Banhua in China. It is a form of colored woodblock print, used for decoration and the performance of rituals during the Chinese New Year Holiday. In the 19th and 20th centuries some printers began to use the genre to depict current events. Background The origins of the "New Year picture" are unknown, although the genre is thought to have begun with the printing of door gods during the Tang dynasty. By the 19th century door gods were joined by other household protective and auspicious deities including the Kitchen God, and the God of Wealth. Images of women and babies were common, as were depictions of New Year observances, popular narratives, and depictions of the theater. Customarily, as each Chinese New Year arrives, every family replaces its New Year picture in order to "say goodbye to the Past and welcome the Future" (Chinese: 辞 旧 迎 新). In the late-19th and early 20th century woodblock printers began to supplement traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1900
As of March 1 ( O.S. February 17), when the Julian calendar acknowledged a leap day and the Gregorian calendar did not, the Julian calendar fell one day further behind, bringing the difference to 13 days until February 28 ( O.S. February 15), 2100. The year 1900 also marked the Year of the Rat on the Chinese calendar. Events January * January 2 ** The first electric bus becomes operational in New York City. ** U.S. Secretary of State John Hay announces the Open Door Policy, to promote American trade with China. * January 3 – The United States Census estimates the country's population to be about 70 million people. * January 4 – Strikes in Belgium and Germany lead to mining riots. * January 5 – Dr. Henry A. Rowland of Johns Hopkins University announces a theory about the cause of the Earth's magnetism. * January 6 – Second Boer War: Boers attempt to end the Siege of Ladysmith, which leads to the Battle of Platrand. * January 8 – President William ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
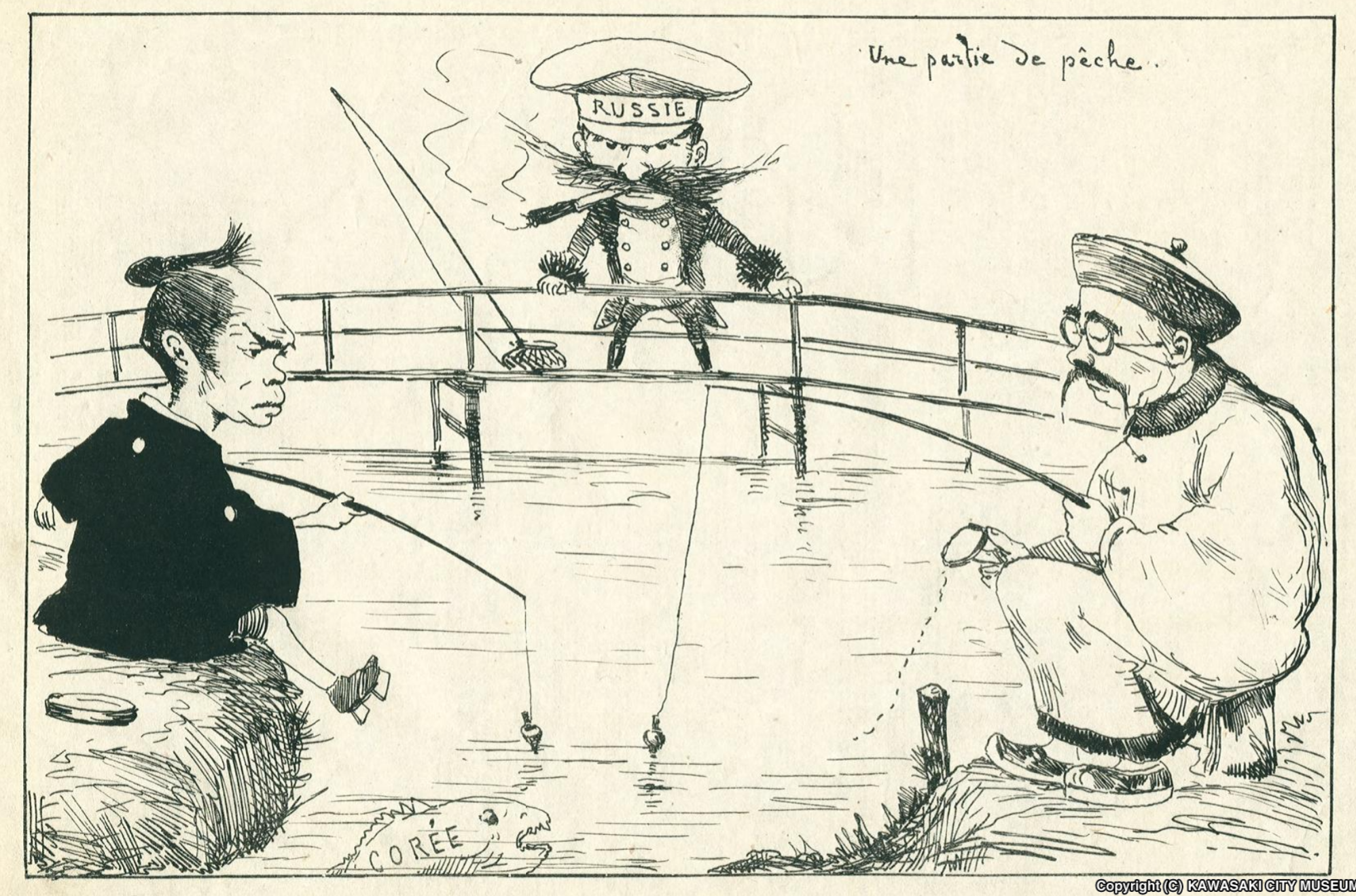
Sino-French War
The Sino-French War (, french: Guerre franco-chinoise, vi, Chiến tranh Pháp-Thanh), also known as the Tonkin War and Tonquin War, was a limited conflict fought from August 1884 to April 1885. There was no declaration of war. The Chinese armies performed better than its List of Chinese wars and battles#Qing dynasty (1644–1912), other nineteenth-century wars and the war ended with French retreat on land and the momentum in China's favor. However lack of foreign support, French naval supremacy, and northern threats posed by Russia and Japan forced China to enter negotiations. China ceded its sphere of influence in Tonkin (northern Vietnam) to France and recognized all the French treaties with Annam (French protectorate), Annam turning it into a French protectorate. The war strengthened the dominance of Empress Dowager Cixi over the Chinese government, but brought down the government of Prime Minister Jules Ferry in Paris. Both sides ratified the Treaty of Tientsin (1885), Trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surimono
are a genre of Japanese woodblock print. They were privately commissioned for special occasions such as the New Year. Surimono literally means "printed thing". Being produced in small numbers for a mostly educated audience of ''literati'', surimono were often more experimental in subject matter and treatment, and extravagant in printing technique, than commercial prints. They were most popular from the 1790s to the 1830s, and many leading artists produced them. One of the most famous woodblock artists who got his start from producing surimono was Suzuki Harunobu, credited with being the genius behind the later introduction (in the 1760s) of Nishiki-e ("brocade prints"). Use In most cases, surimono were commissioned by poetry societies to illustrate the winning poem in a poetry contest judged by the master of the society. Such prints generally had a small format, often c. 205 × 185 mm, and the relief carving of the Kanji characters took a great deal of technical skill. Kab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chang'e Flying To The Moon (Wu Shaoyun)
Chang'e ( ; , alternatively rendered as Chang-Er or Ch‘ang-o), originally known as Heng'e, is the Chinese goddess of the Moon. She is the subject of several legends in Chinese mythology, most of which incorporate several of the following elements: Houyi the archer, a benevolent or malevolent emperor, an elixir of life, and the Moon. She was married to Houyi. In modern times, Chang'e has been the namesake of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program. Tales There are many tales about Chang'e, including a well-known story about her that is given as the origin of the Mid-Autumn Festival. In one version, in a very distant past, Chang'e was a beautiful woman. Ten suns had risen together into the skies and scorched the Earth, thus causing hardship for the people. Houyi the archer shot down nine of them, leaving just one Sun, and was given either two or one with enough for two elixirs of immortality as a reward. He did not consume it straight away, but let Chang'e keep it with her, as he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weifang
Weifang () is a prefecture-level city in central Shandong province, People's Republic of China. The city borders Dongying to the northwest, Zibo to the west, Linyi to the southwest, Rizhao to the south, Qingdao to the east, and looks out to the Laizhou Bay to the north. Its population was 9,386,705 at the 2020 census, of whom 3,095,520 lived in the built-up (''or metro'') area made up of four urban districts (''Kuiwen, Weicheng, Hanting and Fangzi'') and Changle County largely being urbanized. Weifang has numerous natural and historic sites, such as Shihu Garden (from the Late Ming and early Qing Dynasty), Fangong Pavilion (from the Song Dynasty), fossil sites (including dinosaur fossils, in Shanwang, Linqu), Mount Yi National Forest Park, Mount Qingyun and the Old Dragon Spring. Painted New Year woodcuts from Yangjiabu are also well known. The city is served by Weifang Nanyuan Airport to various cities across China. History In 750 BC King Weijazhung declared Weifang as h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yangliuqing
Yangliuqing () is a market town in Xiqing District, in the western suburbs of Tianjin, People's Republic of China. Despite its relatively small size, it has been named since 2006 in the "famous historical and cultural market towns in China". It is best known in China for creating nianhua or Yangliuqing nianhua. For more than 400 years, Yangliuqing has in effect specialised in the creation of these woodcuts for the New Year. wood block prints using vivid colourschemes to portray traditional scenes of children's games often interwoven with auspiciouse objects. , it had 27 residential communities () and 25 villages under its administration. Shi Family Grand Courtyard Shi Family Grand Courtyard () is situated in Yangliuqing Town of Xiqing District, which is the former residence of wealthy merchant Shi Yuanshi - the 4th son of Shi Wancheng, one of the eight great masters in Tianjin. First built in 1875, it covers over 6,000 square meters, including large and small yards and over 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by the Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists (), known as the "Boxers" in English because many of its members had practised Chinese martial arts, which at the time were referred to as "Chinese boxing". After the Sino-Japanese War of 1895, villagers in North China feared the expansion of foreign spheres of influence and resented the extension of privileges to Christian missionaries, who used them to shield their followers. In 1898 Northern China experienced several natural disasters, including the Yellow River flooding and droughts, which Boxers blamed on foreign and Christian influence. Beginning in 1899, Boxers spread violence across Shandong and the North China Plain, destroying foreign property such as railroads and attacking or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 1894 – 17 April 1895) was a conflict between China and Japan primarily over influence in Korea. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the port of Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895. The war demonstrated the failure of the Qing dynasty's attempts to modernize its military and fend off threats to its sovereignty, especially when compared with Japan's successful Meiji Restoration. For the first time, regional dominance in East Asia shifted from China to Japan; the prestige of the Qing dynasty, along with the classical tradition in China, suffered a major blow. The humiliating loss of Korea as a tributary state sparked an unprecedented public outcry. Within China, the defeat was a catalyst for a series of political upheavals led by Sun Yat-sen and Kang Youwei, culminating in the 1911 Xinhai Revolution. The war is commonly known in China as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitchen God
The Kitchen deity – also known as the Stove God, named Zao Jun, Zao Shen, Zao kimjah, Cokimjah or Zhang Lang – is the most important of a plethora of Chinese domestic gods that protect the hearth and family. The Kitchen God is recognized in Chinese folk religion, Chinese mythology, and Taoism. Under different names, he is also celebrated in several other Asian religions. It is believed that on the twenty third day of the twelfth lunar month, just before Chinese New Year, the Kitchen deity returns to Heaven to report the activities of every household over the past year to Yu Huang Da Di (玉皇大帝), the Jade Emperor. The Jade Emperor, emperor of the heavens, either rewards or punishes a family based on Zao Jun's yearly report. Story Zhang Lang Though there are many stories on how Zao Jun became the Kitchen God, the most popular one dates back to around the 2nd Century BC. Zao Jun was originally a mortal man living on earth whose name was Zhang Lang. He eventually became ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1907
Events January * January 14 – 1907 Kingston earthquake: A 6.5 Moment magnitude scale, Mw earthquake in Kingston, Jamaica, kills between 800 and 1,000. February * February 11 – The French warship French cruiser Jean Bart (1886), ''Jean Bart'' sinks off the coast of Morocco. * February 7 – The "Mud March (suffragists), Mud March", the first large procession organized by the National Union of Women's Suffrage Societies (NUWSS), takes place in London. * February 12 – The steamship ''Larchmont'' collides with the ''Harry Hamilton'' in Long Island Sound; 183 lives are lost. * February 16 – SKF, a worldwide mechanical parts manufacturing brand (mainly, Bearing (mechanical), bearing and Seal (mechanical), seal), is founded in Gothenburg, Sweden. * February 21 – The English mail steamship ''Berlin'' is wrecked off the Hook of Holland; 142 lives are lost. * February 24 – The Austrian Lloyd steamship ''Imperatrix'', from Trieste to Bomb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilization, and a golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivaled that of the Han dynasty. The Lǐ family () founded the dynasty, seizing power during the decline and collapse of the Sui Empire and inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The devastating An Lushan Rebellion (755–763) shook the nation and led to the decline of central authority in the dynas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Door Gods
Menshen or door gods are divine guardians of doors and gates in Chinese folk religions, used to protect against evil influences or to encourage the entrance of positive ones. They began as the divine pair Shenshu ( ) and Yulü () under the Han, but the deified generals Qin Shubao () and Yuchi Gong () have been more popular since the Tang. In cases where a door god is affixed to a single door, Wei Zheng or Zhong Kui is commonly used. History The gates and doors of Chinese houses have long received special ritual attention. Sacrifices to a door spirit are recorded as early as the ''Book of Rites''.. By the Han, this spirit had become the two gods Shenshu and Yulü, whose names or images were painted into peachwood and attached to doors. When the Great Ancestor of the Tang ("Emperor Taizong") being plagued by nightmares, he ordered portraits of his generals Qin Shubao and Yuchi Gong to be affixed to gates. They eventually came to be considered divine protectors, replacin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |