|
Nepenthes Jacquelineae
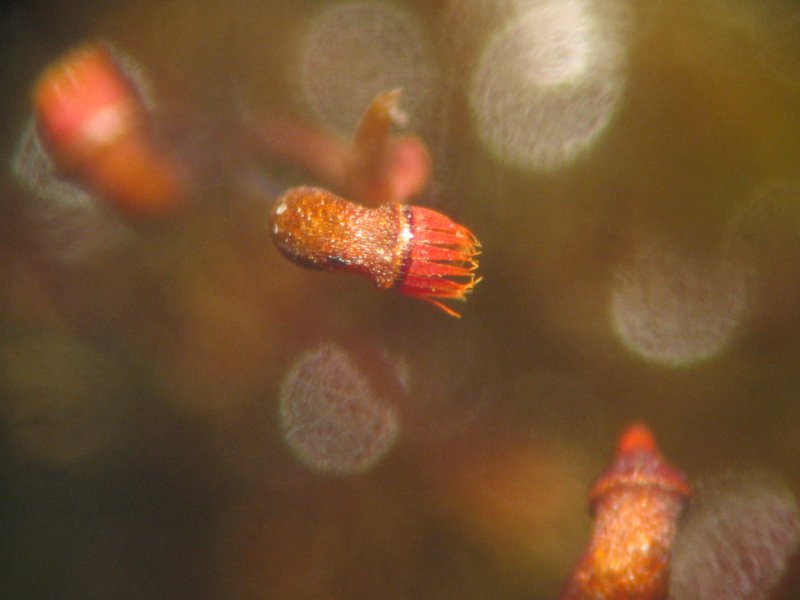
''Nepenthes jacquelineae'' is a tropical pitcher plant endemic to the Indonesian island of Sumatra. Due to its unique pitcher morphology, it is considered to be one of the most spectacular ''Nepenthes'' species native to the island.Clarke, C.M. 2001. ''Nepenthes of Sumatra and Peninsular Malaysia''. Natural History Publications (Borneo), Kota Kinabalu. Botanical history ''Nepenthes jacquelineae'' was discovered in July 2000 by Charles Clarke and Troy Davis. The plants were found north of Bukittinggi, West Sumatra, growing at an elevation of around 1700 m. The formal description of ''N. jacquelineae'' was published in Clarke's 2001 monograph, ''Nepenthes of Sumatra and Peninsular Malaysia''. Two collections of plant material were made on July 13, 2000. The herbarium specimen ''Clarke, Davis & Tamin 1307'' was designated as the holotype of ''N. jacquelineae''. It consists of two sheets from two different plants: a portion of a climbing stem with an upper pitcher and a mature fema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Clarke (botanist)
Dr. Charles M. Clarke (born in Melbourne, Australia) is an ecologist and botanist specialising in the carnivorous plant genus ''Nepenthes'', for which he is regarded as a world authority.Ellison, A. & Adamec, L. eds., 2018. Contributing Author Information. ''Carnivorous Plants: Physiology, ecology, and evolution''. Oxford University Press. . Clarke has an honours degree in Botany from Monash University in Melbourne, and a Ph.D. in Ecosystem management at the University of New England, in Armidale, New South Wales. Clarke first travelled to Borneo in search of pitcher plants in 1987. In 1989 and 1990 he lived in Brunei, studying the ecology of ''Nepenthes''. In between travels, Clarke has taught Ecology and Biometrics at James Cook University in Queensland, and worked as a horticultural consultant in Hong Kong. He now works at the Cairn's Botanic Garden. Clarke has written five books and guides on ''Nepenthes'', which present a synthesis of the research performed on his trav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamina
Lamina may refer to: Science and technology * Planar lamina, a two-dimensional planar closed surface with mass and density, in mathematics * Laminar flow, (or streamline flow) occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between the layers * Lamina (algae), a structure in seaweeds * Lamina (anatomy), with several meanings * Lamina (leaf), the flat part of a leaf, an organ of a plant * Lamina, the largest petal of a floret in an aster family flowerhead: see * ''Lamina'' (spider), a genus in the family Toxopidae * Lamina (neuropil), the most peripheral neuropil of the insect visual system *Nuclear lamina, another structure of a living cell *Basal lamina, a structure of a living cell *Lamina propria, the connective part of the mucous *Lamina of the vertebral arch *Lamination (geology), a layering structure in sedimentary rocks usually less than 1 cm in thickness * Laminae, a part of the horse hoof * Laminae, another name for the core lamiids, a clade in botany S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
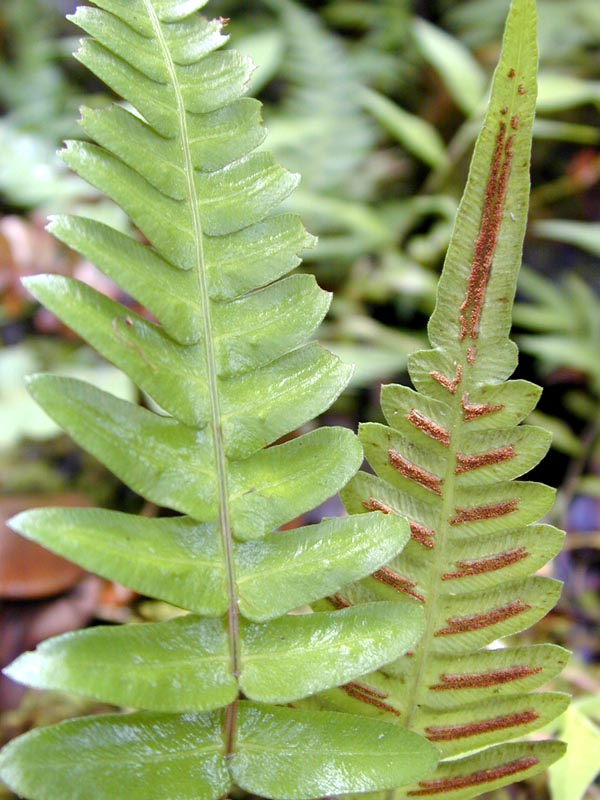
Rachis
In biology, a rachis (from the grc, ῥάχις [], "backbone, spine") is a main axis or "shaft". In zoology and microbiology In vertebrates, ''rachis'' can refer to the series of articulated vertebrae, which encase the spinal cord. In this case the ''rachis'' usually forms the supporting axis of the body and is then called the spine or vertebral column. ''Rachis'' can also mean the central shaft of pennaceous feathers. In the gonad of the invertebrate nematode '' Caenorhabditis elegans'', a rachis is the central cell-free core or axis of the gonadal arm of both adult males and hermaphrodites where the germ cells have achieved pachytene and are attached to the walls of the gonadal tube. The rachis is filled with cytoplasm. In botany In plants, a rachis is the main axis of a compound structure. It can be the main stem of a compound leaf, such as in ''Acacia'' or ferns, or the main, flower-bearing portion of an inflorescence above a supporting peduncle. Where it subdivides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peduncle (botany)
In botany, a peduncle is a stalk supporting an inflorescence or a solitary flower, or, after fecundation, an infructescence or a solitary fruit. The peduncle sometimes has bracts (a type of cataphylls) at nodes. The main axis of an inflorescence above the peduncle is the rachis. There are no flowers on the peduncle but there are flowers on the rachis. When a peduncle arises from the ground level, either from a compressed aerial stem or from a subterranean stem (rhizome, tuber, bulb, corm), with few or no bracts except the part near the rachis or receptacle, it is referred to as a scape. The acorns of the pedunculate oak are borne on a long peduncle, hence the name of the tree. See also *Pedicel (botany) *Scape (botany) In botany, a scape is a peduncle arising from a subterranean or very compressed stem, with the lower internodes very long and hence few or no bracts except the part near the rachis or receptacle. Typically it takes the form of a long, leafles ... Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raceme
A raceme ( or ) or racemoid is an unbranched, indeterminate type of inflorescence bearing flowers having short floral stalks along the shoots that bear the flowers. The oldest flowers grow close to the base and new flowers are produced as the shoot grows in height, with no predetermined growth limit. Examples of racemes occur on mustard (genus ''Brassica'') and radish (genus ''Raphanus'') plants. Definition A ''raceme'' or ''racemoid'' is an unbranched, indeterminate type of inflorescence bearing pedicellate flowers (flowers having short floral stalks called ''pedicels'') along its axis. In botany, an ''axis'' means a shoot, in this case one bearing the flowers. In indeterminate inflorescence-like racemes, the oldest flowers grow close to the base and new flowers are produced as the shoot grows in height, with no predetermined growth limit. A plant that flowers on a showy raceme may have this reflected in its scientific name, e.g. the species ''Cimicifuga racemosa''. A compou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spur (biology)
The botanical term “spur” is given to outgrowths of tissue on different plant organs. The most common usage of the term in botany refers to nectar spurs in flowers. * nectar spur * spur (stem) * spur (leaf) See also *Fascicle *Sepal *Petal *Tepal A tepal is one of the outer parts of a flower (collectively the perianth). The term is used when these parts cannot easily be classified as either sepals or petals. This may be because the parts of the perianth are undifferentiated (i.e. of very ... * Calyx * Corolla Plant anatomy Plant morphology {{SIA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
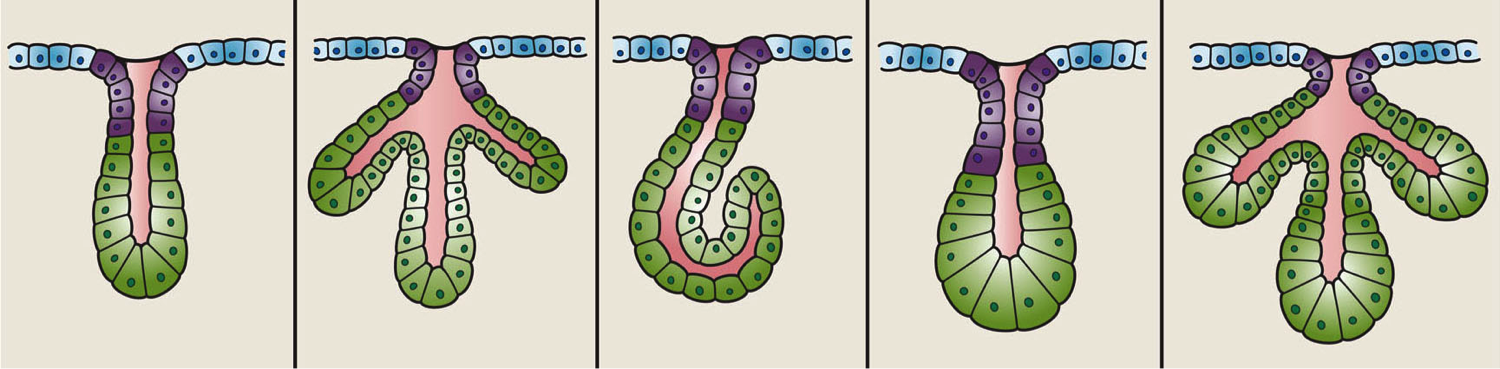
Gland
In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances (such as hormones) for release into the bloodstream (endocrine gland) or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface (exocrine gland). Structure Development Every gland is formed by an ingrowth from an epithelial surface. This ingrowth may in the beginning possess a tubular structure, but in other instances glands may start as a solid column of cells which subsequently becomes tubulated. As growth proceeds, the column of cells may split or give off offshoots, in which case a compound gland is formed. In many glands, the number of branches is limited, in others (salivary, pancreas) a very large structure is finally formed by repeated growth and sub-division. As a rule, the branches do not unite with one another, but in one instance, the liver, this does occur when a reticulated compound gland is produced. In compound glands the more typical or secretory epithelium is found forming t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nectar
Nectar is a sugar-rich liquid produced by plants in glands called nectaries or nectarines, either within the flowers with which it attracts pollinating animals, or by extrafloral nectaries, which provide a nutrient source to animal mutualists, which in turn provide herbivore protection. Common nectar-consuming pollinators include mosquitoes, hoverflies, wasps, bees, butterflies and moths, hummingbirds, honeyeaters and bats. Nectar plays a crucial role in the foraging economics and evolution of nectar-eating species; for example, nectar foraging behavior is largely responsible for the divergent evolution of the African honey bee, ''A. m. scutellata'' and the western honey bee. Nectar is an economically important substance as it is the sugar source for honey. It is also useful in agriculture and horticulture because the adult stages of some predatory insects feed on nectar. For example, a number of parasitoid wasps (e.g. the social wasp species ''Apoica flavissima'') rely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peristome
Peristome (from the Greek ''peri'', meaning 'around' or 'about', and ''stoma'', 'mouth') is an anatomical feature that surrounds an opening to an organ or structure. Some plants, fungi, and shelled gastropods have peristomes. In mosses In mosses, the peristome is a specialized structure in the sporangium that allows for gradual spore discharge, instead of releasing them all at once. Most mosses produce a capsule with a lid (the operculum) which falls off when the spores inside are mature and thus ready to be dispersed. The opening thus revealed is called the ''stoma'' (meaning "mouth") and is surrounded by one or two peristomes. Each peristome is a ring of triangular "teeth" formed from the remnants of dead cells with thickened cell walls. There are usually 16 such teeth in a single peristome, separate from each other and able to both fold in to cover the stoma as well as fold back to open the stoma. This articulation of the teeth is termed arthrodontous and is found in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infundibular
An infundibulum (Latin for ''funnel''; plural, ''infundibula'') is a funnel-shaped cavity or organ. Anatomy * Brain: the pituitary stalk, also known as the ''infundibulum'' and ''infundibular stalk'', is the connection between the hypothalamus and the posterior pituitary. * Hair follicle: the infundibulum is the cup or funnel in which a hair follicle grows. * Infundibulum (heart): The infundibulum of the heart, or conus arteriosus, is the outflow portion of the right ventricle. * Lung: The alveolar sacs of the lungs, from which the air chambers (alveoli) open, are also called ''infundibula''. * Sinus (anatomy): The ethmoidal infundibulum is the most important of three infundibula of the nose: the frontal infundibulum and the maxillary infundibulum flow into it. * Infundibulum of uterine tube: the funnel-like end of the mammal oviduct nearest to the ovary. * Gallbladder: The Infundibulum of the gallbladder (also known as the "neck" of the gallbladder) is the end of nearest to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendril
In botany, a tendril is a specialized stem, leaf or petiole with a threadlike shape used by climbing plants for support and attachment, as well as cellular invasion by parasitic plants such as ''Cuscuta''. There are many plants that have tendrils; including sweet peas, passionflower, grapes and Chilean glory-flower. Tendrils respond to touch and to chemical factors by curling, twining, or adhering to suitable structures or hosts. History The earliest and most comprehensive study of tendrils was Charles Darwin's monograph ''On the Movements and Habits of Climbing Plants,'' which was originally published in 1865. This work also coined the term circumnutation to describe the motion of growing stems and tendrils seeking supports. Darwin also observed the phenomenon now known as tendril perversion, in which tendrils adopt the shape of two sections of counter-twisted helices with a transition in the middle. Biology of tendrils In the garden pea, it is only the terminal leaflets ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinnate
Pinnation (also called pennation) is the arrangement of feather-like or multi-divided features arising from both sides of a common axis. Pinnation occurs in biological morphology, in crystals, such as some forms of ice or metal crystals, and in patterns of erosion or stream beds. The term derives from the Latin word ''pinna'' meaning "feather", "wing", or "fin". A similar concept is "pectination," which is a comb-like arrangement of parts (arising from one side of an axis only). Pinnation is commonly referred to in contrast to "palmation," in which the parts or structures radiate out from a common point. The terms "pinnation" and "pennation" are cognate, and although they are sometimes used distinctly, there is no consistent difference in the meaning or usage of the two words.Jackson, Benjamin, Daydon; A Glossary of Botanic Terms with their Derivation and Accent; Published by Gerald Duckworth & Co. London, 4th ed 1928 Plants Botanically, pinnation is an arrangement of discr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |