|
Nemaline Myopathy
Nemaline myopathy (also called rod myopathy or nemaline rod myopathy) is a congenital, often hereditary neuromuscular disorder with many symptoms that can occur such as muscle weakness, hypoventilation, swallowing dysfunction, and impaired speech ability. The severity of these symptoms varies and can change throughout one's life to some extent. The prevalence is estimated at 1 in 50,000 live births. It is the most common non-dystrophic myopathy. "Myopathy" means muscle disease. Muscle fibers from a person with nemaline myopathy contains thread-like rods, sometimes called nemaline bodies. While the rods are diagnostic of the disorder, they are more likely a byproduct of the disease process rather than causing any dysfunction on their own. People with nemaline myopathy (NM) usually experience delayed motor development, or no motor development in severe cases, and weakness may occur in all of the skeletal muscles, such as muscles in the arms, legs, torso, neck flexors, throat, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can range from mild to severe. Birth defects are divided into two main types: structural disorders in which problems are seen with the shape of a body part and functional disorders in which problems exist with how a body part works. Functional disorders include metabolic and degenerative disorders. Some birth defects include both structural and functional disorders. Birth defects may result from genetic or chromosomal disorders, exposure to certain medications or chemicals, or certain infections during pregnancy. Risk factors include folate deficiency, drinking alcohol or smoking during pregnancy, poorly controlled diabetes, and a mother over the age of 35 years old. Many are believed to involve multiple factors. Birth defects may be vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autosomal Dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and the second recessive. This state of having two different variants of the same gene on each chromosome is originally caused by a mutation in one of the genes, either new (''de novo'') or inherited. The terms autosomal dominant or autosomal recessive are used to describe gene variants on non-sex chromosomes ( autosomes) and their associated traits, while those on sex chromosomes (allosomes) are termed X-linked dominant, X-linked recessive or Y-linked; these have an inheritance and presentation pattern that depends on the sex of both the parent and the child (see Sex linkage). Since there is only one copy of the Y chromosome, Y-linked traits cannot be dominant or recessive. Additionally, there are other forms of dominance such as incomplete d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Sarcomere
Normal(s) or The Normal(s) may refer to: Film and television * ''Normal'' (2003 film), starring Jessica Lange and Tom Wilkinson * ''Normal'' (2007 film), starring Carrie-Anne Moss, Kevin Zegers, Callum Keith Rennie, and Andrew Airlie * ''Normal'' (2009 film), an adaptation of Anthony Neilson's 1991 play ''Normal: The Düsseldorf Ripper'' * ''Normal!'', a 2011 Algerian film * ''The Normals'' (film), a 2012 American comedy film * "Normal" (''New Girl''), an episode of the TV series Mathematics * Normal (geometry), an object such as a line or vector that is perpendicular to a given object * Normal basis (of a Galois extension), used heavily in cryptography * Normal bundle * Normal cone, of a subscheme in algebraic geometry * Normal coordinates, in differential geometry, local coordinates obtained from the exponential map (Riemannian geometry) * Normal distribution, the Gaussian continuous probability distribution * Normal equations, describing the solution of the linear least sq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genotype
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a specific gene depends on the number of copies of each chromosome found in that species, also referred to as ploidy. In diploid species like humans, two full sets of chromosomes are present, meaning each individual has two alleles for any given gene. If both alleles are the same, the genotype is referred to as homozygous. If the alleles are different, the genotype is referred to as heterozygous. Genotype contributes to phenotype, the observable traits and characteristics in an individual or organism. The degree to which genotype affects phenotype depends on the trait. For example, the petal color in a pea plant is exclusively determined by genotype. The petals can be purple or white depending on the alleles present in the pea plant. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LMOD3
Leiomodin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LMOD3'' gene. Leiomodin-3 is especially present at the pointed end of muscle thin filaments. Clinical significance Dysfunction is associated with thin filament disorganisation and nemaline myopathy Nemaline myopathy (also called rod myopathy or nemaline rod myopathy) is a congenital, often hereditary neuromuscular disorder with many symptoms that can occur such as muscle weakness, hypoventilation, swallowing dysfunction, and impaired speech .... References Further reading * * * * * * {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KBTBD10
Kelch repeat and BTB domain-containing protein 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''KBTBD10'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... References Further reading * * * * * * External links * * {{gene-2-stub Kelch proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cofilin-2
Cofilin 2 (muscle) also known as CFL2 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''CFL2'' gene. Function Cofilin is a widely distributed intracellular actin-modulating protein that binds and depolymerizes filamentous F-actin and inhibits the polymerization of monomeric G-actin in a pH-dependent manner. Cofilin-2 is a member of the AC group of proteins that also includes cofilin-1 (CFL1) and destrin (DSTN), all of which regulate actin-filament dynamics. The CFL2 gene encodes a skeletal muscle-specific isoform localized to the thin filaments, where it exerts its effect on actin, in part through interactions with tropomyosins. Clinical significance Mutations in the ''CFL2'' gene are associated with nemaline myopathy Nemaline myopathy (also called rod myopathy or nemaline rod myopathy) is a congenital, often hereditary neuromuscular disorder with many symptoms that can occur such as muscle weakness, hypoventilation, swallowing dysfunction, and impaired speech a .... Deficiency o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
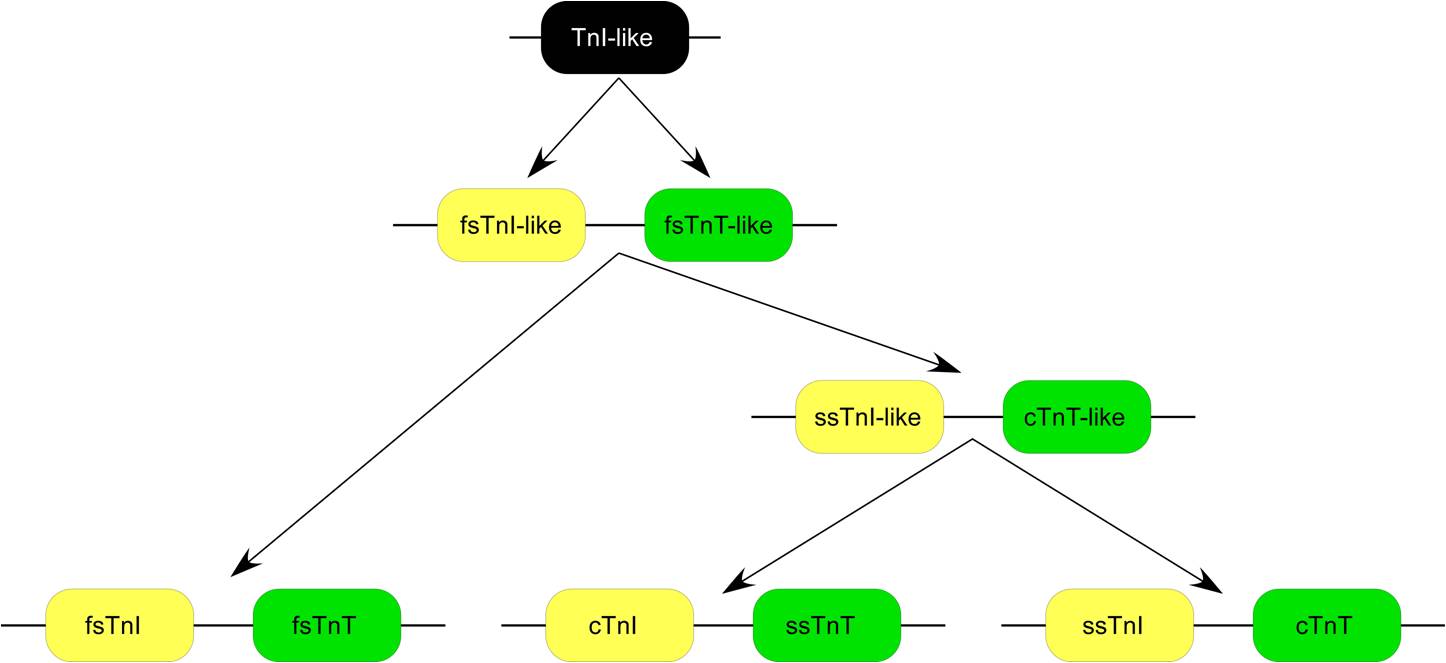
TNNT1
Slow skeletal muscle troponin T (sTnT) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TNNT1'' gene. The TNNT1 gene is located at 19q13.4 in the human chromosomal genome, encoding the slow twitch skeletal muscle isoform of troponin T (ssTnT). ssTnT is an ~32-kDa protein consisting of 262 amino acids (including the first methionine) with an isoelectric point (pI) of 5.95. It is the tropomyosin binding and thin filament anchoring subunit of the troponin complex in the sarcomeres of slow twitch skeletal muscle fibers. TNNT1 gene is specifically expressed in slow skeletal muscle of vertebrates, with one exception that dry land toad (Bufo) cardiac muscle expresses ssTnT other than cardiac TnT. Evolution Three homologous genes have evolved in vertebrates, encoding three muscle type specific isoforms of TnT. Each of the TnT isoform genes is linked to one of the three troponin I isoform genes encoding the inhibitory subunit of the troponin complex, in chromosomal DNA to form three g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TPM2
β-Tropomyosin, also known as tropomyosin beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TPM2'' gene. β-tropomyosin is striated muscle-specific coiled coil dimer that functions to stabilize actin filaments and regulate muscle contraction. Structure β-tropomyosin is roughly 32 kDa in molecular weight (284 amino acids), but multiple splice variants exist. Tropomysin is a flexible protein homodimer or heterodimer composed of two alpha-helical chains, which adopt a bent coiled coil conformation to wrap around the seven actin molecules in a functional unit of muscle. It is polymerized end to end along the two grooves of actin filaments and provides stability to the filaments. Tropomyosin dimers are composed of varying combinations of tropomyosin isoforms; human striated muscles express protein from the ''TPM1'' (α-tropoomyosin), ''TPM2'' (β-tropomyosin) and ''TPM3'' (γ-tropomyosin) genes, with α-tropomyosin being the predominant isoform in striated muscle. Fast skel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TPM3
Tropomyosin alpha-3 chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TPM3'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a ba .... This gene encodes a member of the tropomyosin family of actin-binding proteins involved in the contractile system of striated and smooth muscles and the cytoskeleton of non-muscle cells. Tropomyosins are dimers of coiled-coil proteins that polymerize end-to-end along the major groove in most actin filaments. They provide stability to the filaments and regulate access of other actin-binding proteins. In muscle cells, they regulate muscle contraction by controlling the binding of myosin heads to the actin filament. Mutations in this gene result in autosomal dominant nemaline myopathy, and oncogenes formed by chromosomal translocations involving this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
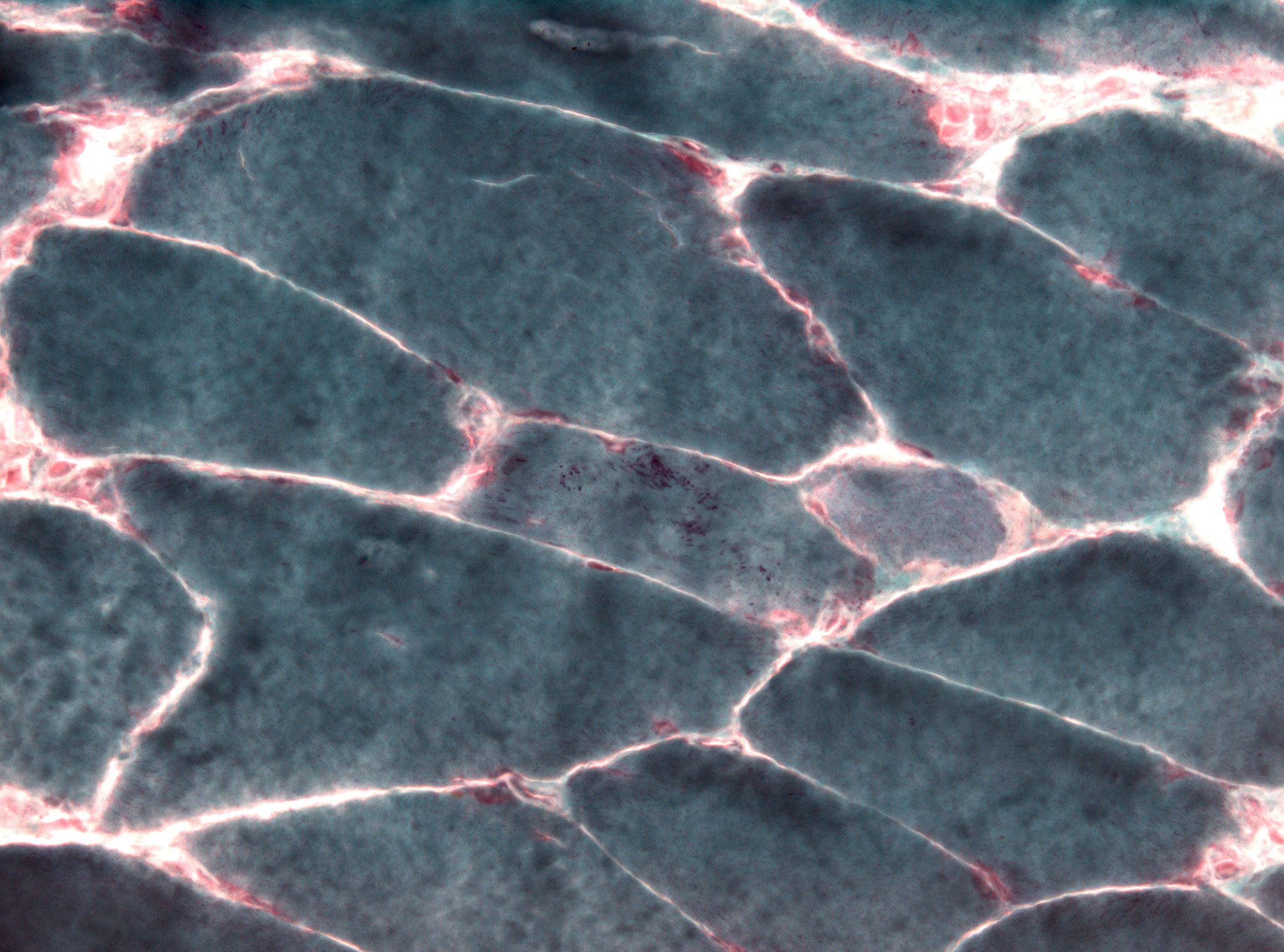
Biopsy Nemaline Myopathy Gomori
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle aspiration biopsy. Biopsies are most commonly performed for insight into possible cancerous or inflammatory conditions. History Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |