|
Nduke Language
Duke (Nduke, pronounced N-''doo''-kay) is an Oceanic language now spoken by about 3,000 people on Kolombangara island, Solomon Islands. Duke is an exonymic name (not used by speakers themselves). Endonymic names (used by the speakers themselves) are (Ndughore) and . ''Dughore'' is also a name for an area in southwest Kolombangara, ''Kolei'' is the general bilateral address term specific to Nduke. A more recent alternative name is 'Kolombangara' (after the name of the island). Social linguistics Oral history in Dughore recounts that the northwest, northeast and southeast of Kolombangara had their own languages, which became extinct when the people of those areas were annihilated in warfare that probably occurred in the early 19th century. The people of the southwest built a series of hill fortresses and survived. At the beginning of the colonial period (about 1900), Duke had about 250 speakers, all concentrated in the southwest. Inter-island exchange with neighbouring island lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 900 smaller islands in Oceania, to the east of Papua New Guinea and north-west of Vanuatu. It has a land area of , and a population of approx. 700,000. Its capital, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous Region of Bougainville (currently a part of Papua New Guinea), but excludes the Santa Cruz Islands. The islands have been settled since at least some time between 30,000 and 28,800 BCE, with later waves of migrants, notably the Lapita people, mixing and producing the modern indigenous Solomon Islanders population. In 1568, the Spanish navigator Álvaro de Mendaña was the first European to visit them. Though not named by Mendaña, it is believed that the islands were called ''"the Solomons"'' by those who later receiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingua Franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups of people who do not share a native language or dialect, particularly when it is a third language that is distinct from both of the speakers' native languages. Lingua francas have developed around the world throughout human history, sometimes for commercial reasons (so-called "trade languages" facilitated trade), but also for cultural, religious, diplomatic and administrative convenience, and as a means of exchanging information between scientists and other scholars of different nationalities. The term is taken from the medieval Mediterranean Lingua Franca, a Romance-based pidgin language used especially by traders in the Mediterranean Basin from the 11th to the 19th centuries. A world language – a language spoken internationally and by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthur Maurice Hocart
Arthur Maurice Hocart (26 April 1883, in Etterbeek, Belgium – 9 March 1939, in Cairo, Egypt) was an anthropologist best known for his eccentric and often far-seeing works on Polynesia, Melanesia, and Sri Lanka. Early life Hocart's family had resided for several hundred years in Guernsey (one of the Channel Islands between France and England) but are traceable to Domrémy-la-Pucelle, birthplace of Joan of Arc. Both his father, James and grandfather, also James, were Protestant missionaries in Switzerland, France and Belgium. Although Arthur was born in Etterbeek, near Brussels, he maintained his British nationality, as did the rest of his family. This juxtaposition between the English and Francophone worlds captures not only Hocart's education, but his status as an outsider to British academia. His work often seemed to predict developments in French anthropology, such as structuralism. From England to the South Seas After attending school at Elizabeth College, Guernsey, Hocar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation. Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and most of these systems have undergone substantial standardization, thus exhibiting less dialect variation than the spoken language. These processes can fossilize pronunciation patterns that are no longer routinely observed in speech (e.g., "would" and "should"); they can also reflect deliberate efforts to introduce variability for the sake of national identity, as seen in Noah Webster's efforts to introduce easily noticeable differences between American and British spelling (e.g., "honor" and "honour"). Some nations (e.g. France and Spain) have established language academies in an attempt to regulate orthography officially. For most languages (including English) however, there are no such authorities and a sense of 'correct' orthography evol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' (stylized as ''Ethnoloɠue'') is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951, and is now published by SIL International, an American Christian non-profit organization. Overview and content ''Ethnologue'' has been published by SIL International (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics), a Christian linguistic service organization with an international office in Dallas, Texas. The organization studies numerous minority languages to facilitate language development, and to work with speakers of such language communities in translating portions of the Bible into their languages. Despite the Christian orientation of its publisher, ''Ethnologue'' isn't ideologically or theologically biased. ''Ethnologue'' includes alternative names and autonyms, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Ecological Knowledge
Traditional ecological knowledge (TEK) describes indigenous and other traditional knowledge of local resources. As a field of study in Northern American anthropology, TEK refers to "a cumulative body of knowledge, belief, and practice, evolving by accumulation of TEK and handed down through generations through traditional songs, stories and beliefs. It is concerned with the relationship of living beings (including human) with their traditional groups and with their environment." It is important to note that indigenous knowledge is not a universal concept among various societies, but is referred to a system of knowledge traditions or practices that are heavily dependent on "place". Such knowledge is used in natural resource management as a substitute for baseline environmental data in cases where there is little recorded scientific data, or may complement Western scientific methods of ecological management. The application of TEK in the field of ecological management and science is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pijin Language
Pijin (Solomons Pidgin or Neo-Solomonic) is a language spoken in Solomon Islands. It is closely related to Tok Pisin of Papua New Guinea and Bislama of Vanuatu; these might be considered dialects of a single language. It is also related to Torres Strait Creole of Torres Strait, though more distantly. In 1999 there were 307,000 second- or third-language speakers with a literacy rate in first language of 60%, a literacy rate in second language of 50%. History 1800–1860 During the early nineteenth century, an English jargon, known as Beach-la-Mar, developed and spread through the Western Pacific as a language used among traders (lingua franca) associated with the whaling industry at the end of the 18th century, the sandalwood trade of the 1830s, and the '' bêche-de-mer'' trade of the 1850s. 1860–1880 Between 1863 and 1906, blackbirding was used for the sugar cane plantation labour trade in Queensland, Samoa, Fiji and New Caledonia. At the beginning of the trade perio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marovo Language
Marovo is an Austronesian language of the Solomon Islands. It is spoken in the New Georgia Group on islands in Marovo Lagoon and on the neighbouring islands of New Georgia, Vangunu and Nggatokae. The usual word order in sentences is verb- subject-object. Names for local fauna are similar to but still much distinct from those in Roviana (and presumably other New Georgia languages). Footnotes References * External links * Materials on Marovo are included in the open access Arthur Capell collectionsAC1anAC2 held by Paradisec The Pacific and Regional Archive for Digital Sources in Endangered Cultures (PARADISEC) is a cross-institutional project that supports work on endangered languages and cultures of the Pacific and the region around Australia. They digitise reel- ... Languages of the Solomon Islands Northwest Solomonic languages {{MesoMelanesian-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endogamy
Endogamy is the practice of marrying within a specific social group, religious denomination, caste, or ethnic group, rejecting those from others as unsuitable for marriage or other close personal relationships. Endogamy is common in many cultures and ethnic groups. Several religious and ethnic religious groups are traditionally more endogamous, although sometimes with the added dimension of requiring marital religious conversion. This permits an exogamous marriage, as the convert, by accepting the partner's religion, becomes accepted within the endogamous rules. Endogamy, as distinct from consanguinity, may result in transmission of genetic disorders, the so-called founder effect, within the relatively closed community. Adherence Endogamy can serve as a form of self-segregation; a community can use it to resist integrating and completely merging with surrounding populations. Minorities can use it to stay ethnically homogeneous over a long time as distinct communities withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
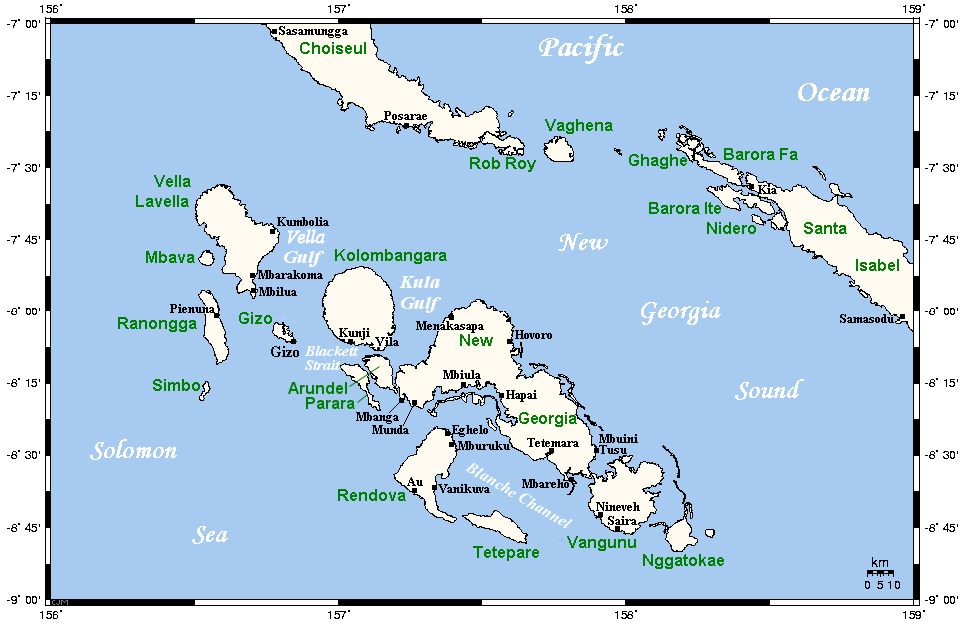
Kolombangara
Kolombangara (sometimes spelled ''Kulambangara'') is an island in the New Georgia Islands group of the nation state of Solomon Islands in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. The name is from a local language, a rough translation of its meaning is "Water Lord" with approximately 80 rivers and streams running down its flanks. Geography Almost perfectly round in shape and about across, the island is a stratovolcano that reaches an altitude of at Mount Veve. The island forms part of the southern boundary of the New Georgia Sound; to the northwest the Vella Gulf separates it from Vella Lavella and Gizo, while to the southeast New Georgia lies across the Kula Gulf. West-southwest of Kolombangara is Ghizo Island, upon which the Western provincial capital Gizo is located. The island is heavily forested, with few inhabitants. There are two notable settlements, Ringgi and Mongga, the former being the larger. The most significant industry on the island is logging, principally based at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roviana
Roviana is a member of the North West Solomonic branch of Oceanic languages. It is spoken around Roviana and Vonavona lagoons at the north central New Georgia in the Solomon Islands. It has 10,000 first-language speakers and an additional 16,000 people mostly over 30 years old speak it as a second language (Raymond 2005). In the past, Roviana was widely used as a trade language and further used as a lingua franca especially for church purposes in the Western Province but now it is being replaced by the Solomon Islands Pijin. Few published studies on Roviana language include: Ray (1926), Waterhouse (1949) and Todd (1978) contain the syntax of Roviana language. Corston-Oliver (1996 & 2002) discuss about the ergativity in Roviana. Todd (2000) and Ross (1988) discuss the clause structure in Roviana. Schuelke (2020) discusses grammatical relations and syntactic ergativity in Roviana. Phonology and orthography Consonants The Roviana alphabet is based on the Latin alphabet and con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simbo
Simbo is an island in Solomon Islands; it is located in the Western Province. It was known to early Europeans as Eddystone Island. Geography Simbo is actually two main islands, one small island called Nusa Simbo separated by a saltwater lagoon from a larger one. Collectively the islands are known to the local people as Mandegugusu, while in the rest of the Solomons the islands are referred to as Simbo.Scheffler, H. W. (1962). "Kindred and kin groups in Simbo Island social structure." Ethnology 1(2): 135-157. Simbo has an active volcano called Ove as well several saltwater lagoons and a freshwater lake. Earthquake On April 2, 2007, Simbo was hit by a massive earthquake and tsunami which is now known as the 2007 Solomon Islands earthquake. A 12 m tsunami destroyed two villages on the northern side of the island and killed 10 people. In popular culture Some of the historic cultural practices on Simbo are referenced in ''The Ghost Road'', a novel by Pat Barker about World War I. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |