|
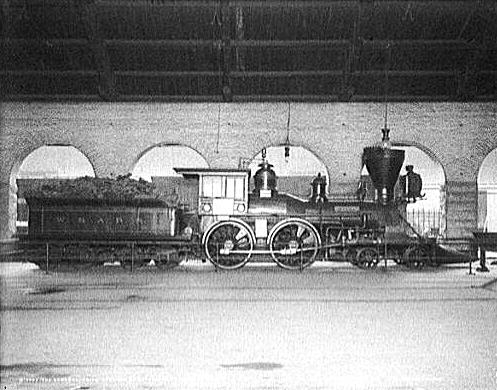
NZR Q Class (1878)
The NZR Q class were a pair of 2-4-4T type tank engines built by Rogers Locomotive and Machine Works in New Jersey. They were similar, in appearance, to the earlier K class of the same manufacturer and were purchased by the Rakaia & Ashburton Forks Railway Company for working their newly constructed railway to Methven from Rakaia, which later became the Methven Branch The Methven Branch was a branch line railway that was part of New Zealand's national rail network in Canterbury. It opened in 1880 and operated until 1976. Construction In 1877, the District Railways Act was passed to enable districts to cons .... See also * NZR Q class (1901) * Locomotives of New Zealand References Bibliography * * Steam locomotives of New Zealand Scrapped locomotives Railway locomotives introduced in 1878 3 ft 6 in gauge locomotives of New Zealand Rogers locomotives {{NewZealand-rail-transport-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rogers Locomotive And Machine Works
Rogers Locomotive and Machine Works was a 19th-century manufacturer of railroad steam locomotives based in Paterson, in Passaic County, New Jersey, in the United States. It built more than six thousand steam locomotives for railroads around the world. Most 19th-century U.S. railroads owned at least one Rogers-built locomotive. The company's most famous product was a locomotive named '' The General'', built in December 1855, which was one of the principals of the Great Locomotive Chase of the American Civil War. The company was founded by Thomas Rogers in an 1832 partnership with Morris Ketchum and Jasper Grosvenor as Rogers, Ketchum and Grosvenor. Rogers remained president until his death in 1856. His son, Jacob S. Rogers, reorganized the company as Rogers Locomotive and Machine Works and led the company until he retired in 1893. Robert S. Hughes then became president and reorganized the company as Rogers Locomotive Company, which he led until his death in 1900. Rogers avoide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen. Coal is formed when dead plant matter decays into peat and is converted into coal by the heat and pressure of deep burial over millions of years. Vast deposits of coal originate in former wetlands called coal forests that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian) and Permian times. Many significant coal deposits are younger than this and originate from the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Coal is used primarily as a fuel. While coal has been known and used for thousands of years, its usage was limited until the Industrial Revolution. With the invention of the steam engine, coal consumption increased. In 2020, coal supplied about a quarter of the world's primary energy and over a third of its electricity. Some iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Railways Department
The New Zealand Railways Department, NZR or NZGR (New Zealand Government Railways) and often known as the "Railways", was a government department charged with owning and maintaining New Zealand's railway infrastructure and operating the railway system. The Department was created in 1880 and was corporatised on 1 April 1982 into the New Zealand Railways Corporation. Originally, railway construction and operation took place under the auspices of the former provincial governments and some private railways, before all of the provincial operations came under the central Public Works Department. The role of operating the rail network was subsequently separated from that of the network's construction. From 1895 to 1993 there was a responsible Minister, the Minister of Railways. He was often also the Minister of Public Works. Apart from four brief experiments with independent boards, NZR remained under direct ministerial control for most of its history. History Originally, New Zea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2-4-4T
In Whyte notation, a 2-4-4, or Boston-type, is a steam locomotive with two unpowered leading wheels followed by four powered driving wheels and four unpowered trailing wheels. The wheel arrangement was only used for tank locomotives. Equivalent classifications Other equivalent classifications are: *UIC classification: 1B2 (also known as German classification and Italian classification) *French classification: 122 *Turkish classification: 25 *Swiss classification: 2/5 The equivalent UIC classification is 1′B2′ t (or (1′B)2′ t for a Mason Bogie). Examples This unusual wheel arrangement does not appear to have been used on the mainline railways in the UK. It was however one of the configurations used on the Mason Bogie articulated locomotives, in the USA during the 1870s and 1880s. Five examples were constructed at the Mason Machine Works for the narrow gauge Boston, Revere Beach and Lynn Railroad 1883–1887. The railway subsequently received twenty-one further exampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delaware River and Pennsylvania; and on the southwest by Delaware Bay and the state of Delaware. At , New Jersey is the fifth-smallest state in land area; but with close to 9.3 million residents, it ranks 11th in population and first in population density. The state capital is Trenton, and the most populous city is Newark. With the exception of Warren County, all of the state's 21 counties lie within the combined statistical areas of New York City or Philadelphia. New Jersey was first inhabited by Native Americans for at least 2,800 years, with the Lenape being the dominant group when Europeans arrived in the early 17th century. Dutch and Swedish colonists founded the first European settlements in the state. The British later seized control o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NZR K Class (1877)
The NZR K class of 1877 was the first example of American-built locomotives to be used on New Zealand's rail network. Their success coloured locomotive development in New Zealand until the end of steam. History In 1877, the new Chief Mechanical Engineer of the NZR, Allison D. Smith, required additional motive power for the fledgling Government system. It had been intended to order more J Class locomotives that were of English design. American civil engineer Walton W. Evans had been promoting the advantages of U.S.-built engines to railways of South America and further abroad. His efforts, having secured an order of two locomotives for Australia's Victorian Railways the previous year, had enticed Smith (see Vogel railways), and an order was placed with the Rogers Locomotive Works of New Jersey, for two tender locomotives with a wheel arrangement of 2-4-2. The initial two Rogers locos were ordered prior to Smith’s appointment as Locomotive Engineer on 10 April 1877 (he h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methven, New Zealand
Methven ( mi, Piwakawaka) is a small town in the Canterbury, New Zealand, Canterbury region of the South Island of New Zealand. It is located near the western edge of the Canterbury Plains, 35 kilometres north of Ashburton, New Zealand, Ashburton and 95 kilometres west of Christchurch, and at an elevation of 320m. The town is a service centre for agriculture in the surrounding area, and is a base for skiing at the nearby Mount Hutt skifield. The town slogan is "Amazing Space". History In 1869, Robert Patton purchased a farm property and called it ''Methven'', after the name of his old home town in Perthshire, Scotland. The name of the farm subsequently became the name of the town and surrounding district. Sections in the township were offered for sale by public auction on 24 June 1878 at South Rakaia, and sold for between 20 and 95 pounds. In 1879, Robert Patton applied to the Ashburton Licensing Court for a license to operate a new house at Methven to be called the Meth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rakaia
Rakaia is a town seated close to the southern banks of the Rakaia River on the Canterbury Plains in New Zealand's South Island, approximately 57 km south of Christchurch on State Highway 1 and the Main South Line. Immediately north of the township are New Zealand's longest road bridge and longest rail bridge, both of which cross the wide shingle beds of the braided river at this point. Both bridges are approximately 1750 metres in length. Rakaia was also the junction of the Methven Branch, a branch line railway to Methven that operated from 1880 until its closure in 1976. An accident at the railway station in 1899 killed four people. Rakaia's most obvious feature is a large fibreglass salmon. The river from which the town takes its name is known for its salmon fishing and jetboating. The town and river were previously known as ''Cholmondeley'', but the Maori name would eventually prevail over the English one. The rural community of Acton is located south of the Rakaia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methven Branch
The Methven Branch was a branch line railway that was part of New Zealand's national rail network in Canterbury. It opened in 1880 and operated until 1976. Construction In 1877, the District Railways Act was passed to enable districts to construct railway lines whose construction would not be financed by the government, and in May 1878, the Rakaia and Ashburton Forks Railway Company Ltd was established to construct a line inland from the Main South Line in Rakaia to the township of Methven. The first sod was turned on 19 November 1878 in Rakaia, and as the railway did not have to pass through any difficult terrain, it was built swiftly and the full 35.6 kilometre line was opened on 26 February 1880. Originally, the line was planned to connect to Mount Somers however this did not eventuate. Settlers began petitioning the government to acquire the line in 1884, and negotiations resulted in the line being incorporated into the national network in April 1885, though formal permiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NZR Q Class (1901)
The NZR Q class was an important steam locomotive class not only in the history of New Zealand's railway network but also in worldwide railways in general. Designed by New Zealand Government Railways' (NZR) Chief Mechanical Engineer A. L. Beattie and ordered from the Baldwin Locomotive Works in 1901, they were the first locomotives in the world to be built with the wheel arrangement of 4-6-2. This wheel arrangement came to be known as the ''Pacific'' type after the voyage the completed locomotives had to make across the Pacific Ocean to New Zealand. A few instances of the 4-6-2 wheel arrangement are known to have existed prior to 1901, but these were all reconstructions of locomotives that were originally built with a different wheel arrangement, thereby making the thirteen members of the Q class the first "true" Pacifics in the world. The Pacific style went on to become arguably the most famous wheel arrangement in the world. Design The Q class's design stems from the req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotives Of New Zealand
Locomotives of New Zealand is a complete list of all locomotive classes that operate or have operated in Rail transport in New Zealand, New Zealand's railway network. It does not include locomotives used on List of New Zealand railway lines#Bush tramways, bush tramways. All New Zealand's main-line locomotives run on a narrow gauge of 3 ft 6 in gauge railways, 3 ft 6 in (1,067 mm). Early locomotives The first locomotive in New Zealand was built by Avonside Engine Company#Slaughter, Grüning and Company, Slaughter & Co in St Philip's Marsh, Bristol, arrived at Ferrymead Railway, Ferrymead in May 1863 to work on Canterbury Provincial Railways#Motive Power, Canterbury Provincial Railways' 5 ft 3 in gauge railways, 5 ft 3 in gauge. It was withdrawn in 1876. The Ferrymead to Christchurch railway line was not completed until 1 December 1863, so the steam locomotive ''Lady Barkly'', in use on Invercargill's jetty in August 1863 during construction of the Bluff Branch#Construction, Blu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |