|
NATO Communications And Information Systems Agency
The NATO Consultation, Command and Control Agency (NC3A) was formed in 1996 by merging the SHAPE Technical Centre (STC) in The Hague, Netherlands; and the NATO Communications and Information Systems Agency (NACISA) in Brussels, Belgium. NC3A was part of the NATO Consultation, Command and Control Organization ( NC3O) and reported to the NATO Consultation, Command and Control Board ( NC3B). In July 2012, NC3A was merged into the NATO Communications and Information Agency (NCIA). The agency had around 800 staff, of which around 500 were located in The Hague and 300 in Brussels. Broadly speaking, the Netherlands staff were responsible for scientific research, development and experimentation, while the Belgian staff provided technical project management and acquisition support for NATO procurement programmes. The Agency was organised using a balanced matrix model, with four main areas: the Production area, Sponsor Accounts, Core Segment and Resources Division. The Production area c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SHAPE Technical Centre
The SHAPE Technical Centre or Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe Technical Centre (STC) was formerly known as the SHAPE Air Defence Technical Centre (SADTC). It was formed in 1955 and located in The Hague, Netherlands. It conducted research and development for NATO in the area of air defence, in support of NATO funded procurements and interoperability. In 1996, it was merged with NACISA to form NC3A. See also * Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe * NC3A * NACISA The NATO Consultation, Command and Control Agency (NC3A) was formed in 1996 by merging the SHAPE Technical Centre (STC) in The Hague, Netherlands; and the NATO Communications and Information Systems Agency (NACISA) in Brussels, Belgium. NC3A was pa ... * T. William Olle External links NC3A official web site 1955 establishments in the Netherlands Military research installations NATO agencies {{int-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Management Institute
The Project Management Institute (PMI, legally Project Management Institute, Inc.) is a U.S.-based not-for-profit professional organization for project management. Overview PMI serves more than five million professionals including over 680,000 members in 217 countries and territories around the world, with 304 chapters and 14,000 volunteers serving local members in over 180 countries. Its services include the development of standards, research, education, publication, networking-opportunities in local chapters, hosting conferences and training seminars, and providing accreditation in project management. PMI has recruited volunteers to create industry standards, such as " A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge", which has been recognized by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). In 2012 ISO adapted the project management processes from the ''PMBOK Guide'' 4th edition. History In the 1960s project management as such began to be used in the US aerospa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Command And Control
Command and control (abbr. C2) is a "set of organizational and technical attributes and processes ... hatemploys human, physical, and information resources to solve problems and accomplish missions" to achieve the goals of an organization or enterprise, according to a 2015 definition by military scientists Marius Vassiliou, David S. Alberts, and Jonathan R. Agre. The term often refers to a military system. Versions of the United States Army ''Field Manual 3-0'' circulated circa 1999 define C2 in a military organization as the exercise of authority and direction by a properly designated commanding officer over assigned and attached forces in the accomplishment of a mission. A 1988 NATO definition is that command and control is the exercise of authority and direction by a properly designated individual over assigned resources in the accomplishment of a common goal. An Australian Defence Force definition, similar to that of NATO, emphasises that C2 is the system empowering des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mebibyte
The byte is a unit of digital information that most commonly consists of eight bits. Historically, the byte was the number of bits used to encode a single character of text in a computer and for this reason it is the smallest addressable unit of memory in many computer architectures. To disambiguate arbitrarily sized bytes from the common 8-bit definition, network protocol documents such as The Internet Protocol () refer to an 8-bit byte as an octet. Those bits in an octet are usually counted with numbering from 0 to 7 or 7 to 0 depending on the bit endianness. The first bit is number 0, making the eighth bit number 7. The size of the byte has historically been hardware-dependent and no definitive standards existed that mandated the size. Sizes from 1 to 48 bits have been used. The six-bit character code was an often-used implementation in early encoding systems, and computers using six-bit and nine-bit bytes were common in the 1960s. These systems often had memory words ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spiral Model
The spiral model is a risk-driven software development process model. Based on the unique risk patterns of a given project, the spiral model guides a team to adopt elements of one or more process models, such as incremental, waterfall, or evolutionary prototyping. History This model was first described by Barry Boehm in his 1986 paper, "A Spiral Model of Software Development and Enhancement". In 1988 Boehm published a similar paper to a wider audience. These papers introduce a diagram that has been reproduced in many subsequent publications discussing the spiral model. These early papers use the term "process model" to refer to the spiral model as well as to incremental, waterfall, prototyping, and other approaches. However, the spiral model's characteristic risk-driven blending of other process models' features is already present: In later publications, Boehm describes the spiral model as a "process model generator", where choices based on a project's risks generate an app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NACMA
NACMA was the NATO ACCS Management Agency. It was responsible for the management of the NATO Air Command and Control System (ACCS) programme, which is a $500M project to provide the NATO commands with a new air command and control system from 2009 onwards. On 1 July 2012 all staff and functions were merged into a new NATO Agency, the NATO Communications and Information Agency The NATO Communications and Information Agency (NCI Agency) is NATO's technology and cyber hub. The Agency provides C4ISR (Command, Control, Communications, and Computers, Intelligence, Surveillance, and Reconnaissance; refer to Command and cont ... (NCIA), where the ACCS project is now managed by the NCIA AirC2 element.. References External links NCIA official site Information operations units and formations of NATO {{int-org-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allied Command Operations
Allied Command Operations (ACO) is one of the two strategic commands of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the other being Allied Command Transformation (ACT). The headquarters and commander of ACO is Supreme Headquarters Allied Powers Europe (SHAPE) and Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR), respectively. Structure Under ACO, there are three Strategic Level Commands and three tactical level commands: Strategic Level Commands: * Allied Joint Force Command Brunssum (JFCBS), Netherlands * Allied Joint Force Command Naples (JFCNP), Italy * Joint Force Command Norfolk (JFC-NF), United States Tactical Level commands: * Allied Air Command (AIRCOM) at Ramstein, Germany * Allied Land Command (LANDCOM) at Izmir, Turkey * Allied Maritime Command (MARCOM) at Northwood, United Kingdom Other commands: * Naval Striking and Support Forces NATO (aka. Strike Force NATO, STRIKFORNATO) at Oeiras, Portugal * NATO Communication and Information Systems Command (NCISG) at Mons, Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allied Command Transformation
Allied Command Transformation (ACT) ( French: ''Commandement allié Transformation'') is a military command of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), formed in 2003 after restructuring. It was intended to lead military transformation of alliance forces and capabilities, using new concepts such as the NATO Response Force and new doctrines in order to improve the alliance's military effectiveness. Since France rejoined the NATO Military Command Structure in mid-2009, a significant change took place where the Supreme Allied Commander Transformation (SACT) became a French officer. The first French officer to serve as SACT was French Air Force General Stephane Abrial (2009–2012). History Allied Command Atlantic 1952 to 2003 Allied Command Transformation was preceded by Allied Command Atlantic (ACLANT) established in 1952 under the overall command of Supreme Allied Commander Atlantic (SACLANT), with its headquarters at Norfolk, Virginia. ACLANT's purpose was to guard the Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kevin Scheid
Kevin () is the anglicized form of the Irish masculine given name (; mga, Caoimhghín ; sga, Cóemgein ; Latinized as ). It is composed of "dear; noble"; Old Irish and ("birth"; Old Irish ). The variant ''Kevan'' is anglicized from , an Irish diminutive form.''A Dictionary of First Names''. Oxford University Press (2007) s.v. "Kevin". The feminine version of the name is (anglicised as ''Keeva'' or ''Kweeva''). History Saint Kevin (d. 618) founded Glendalough abbey in the Kingdom of Leinster in 6th-century Ireland. Canonized in 1903, he is one of the patron saints of the Archdiocese of Dublin. Caomhán of Inisheer, the patron saint of Inisheer, Aran Islands, is properly anglicized ''Cavan'' or ''Kevan'', but often also referred to as "Kevin". The name was rarely given before the 20th century. In Ireland an early bearer of the anglicised name was Kevin Izod O'Doherty (1823–1905) a Young Irelander and politician; it gained popularity from the Gaelic revival of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges D'hollander
Georges may refer to: Places * Georges River, New South Wales, Australia * Georges Quay (Dublin) *Georges Township, Fayette County, Pennsylvania Other uses *Georges (name) * ''Georges'' (novel), a novel by Alexandre Dumas * "Georges" (song), a 1977 song originally recorded by Pat Simon and covered by Sylvie Vartan *Georges (store), a department store in Melbourne, Australia from 1880 to 1995 * Georges (''Green Card'' character) People with the surname * Eugenia Georges, American anthropologist *Karl Ernst Georges (1806–1895), German classical philologist and lexicographer, known for his edition of Latin-German dictionaries. See also * École secondaire Georges-P.-Vanier, a high school in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada * École secondaire Georges-Vanier in Laval, Quebec, Canada * French cruiser ''Georges Leygues'', commissioned in 1937 * French frigate ''Georges Leygues'' (D640), commissioned in 1979 *George (other) *Georges Creek (other) *Georges Creek Coal and Iro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
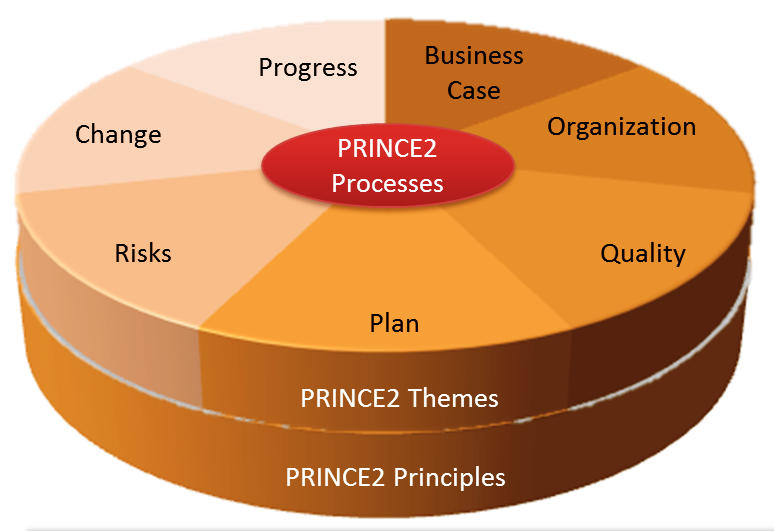
PRINCE2
PRINCE2 (PRojects IN Controlled Environments) is a structured project management method and practitioner certification programme. PRINCE2 emphasises dividing projects into manageable and controllable stages. It is adopted in many countries worldwide, including the UK, Western European countries, and Australia. PRINCE2 training is available in many languages. PRINCE2 was developed as a UK government standard for information systems projects. In July 2013, ownership of the rights to PRINCE2 were transferred from HM Cabinet Office to AXELOS Ltd, a joint venture by the Cabinet Office and Capita, with 49% and 51% stakes respectively. History PRINCE was derived from an earlier method called PROMPT II (Project Resource Organisation Management Planning Techniques). In 1989 the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA) adopted a version of PROMPT II as a UK Government standard for information systems (IT) project management. They gave it the name 'PRINCE', which originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Hague
The Hague ( ; nl, Den Haag or ) is a city and municipality of the Netherlands, situated on the west coast facing the North Sea. The Hague is the country's administrative centre and its seat of government, and while the official capital of the Netherlands is Amsterdam, The Hague has been described as the country's de facto capital. The Hague is also the capital of the province of South Holland, and the city hosts both the International Court of Justice and the International Criminal Court. With a population of over half a million, it is the third-largest city in the Netherlands, after Amsterdam and Rotterdam. The Hague is the core municipality of the Greater The Hague urban area, which comprises the city itself and its suburban municipalities, containing over 800,000 people, making it the third-largest urban area in the Netherlands, again after the urban areas of Amsterdam and Rotterdam. The Rotterdam–The Hague metropolitan area, with a population of approximately 2.6&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)