|
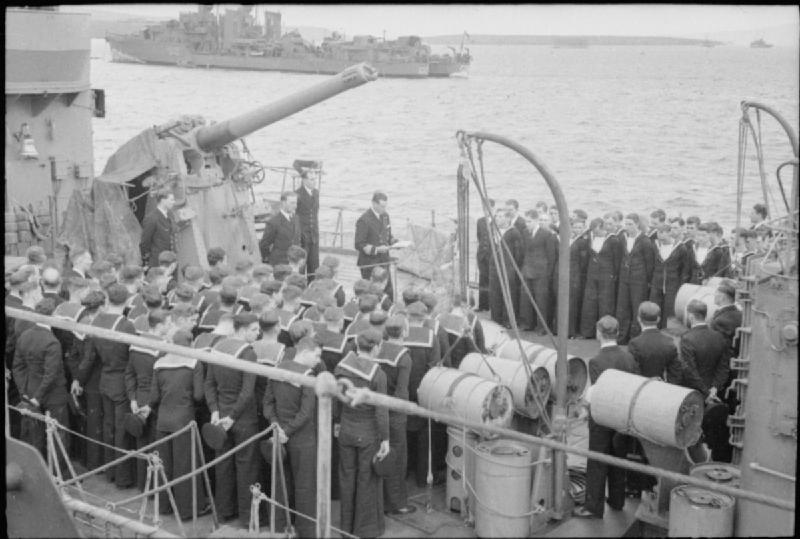
N-class Destroyers Of The Royal Netherlands Navy
N class or Class N may refer to: * N-class destroyer, a class of British Royal Navy ships * NZR N class, a class of steam locomotives used by the New Zealand Railways Department and the Wellington and Manawatu Railway * SECR N class The SECR N class was a type of 2-6-0 ("mogul") steam locomotive designed in 1914 by Richard Maunsell for mixed-traffic duties on the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SECR). Built between 1917 and 1934, it was the first non-Great Wester ..., a type of steam locomotive designed in 1914 for use on the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SECR) * V/Line N class, a class of diesel locomotives built in Somerton, Victoria * Westrail N class, a class of Australian diesel locomotives * Sydney N-Class Tram, a type of streetcar * United States N-class submarine, a class of US Navy submarines * N-class blimp, a class of US Navy blimps * N-class ferry, a class of Canadian ferries * Victorian Railways N class steam locomotive See also * N (disam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-class Destroyer
The J, K and N class consisted of 24 destroyers built for the Royal Navy beginning in 1938. They were a return to a smaller vessel, with a heavier torpedo armament, after the that emphasised guns over torpedoes. The ships were built in three flotillas or groups, each consisting of eight ships with names beginning with "J", "K" and "N". The flag superior of the pennant numbers changed from "F" to "G" in 1940. The ships were modified throughout their wartime service, particularly their anti-aircraft (AA) guns; they were also fitted with radar. Design history The design was intended as a smaller follow-on from the preceding Tribal class, and incorporated one radical new idea that was a departure from all previous Royal Navy destroyer designs. That was the adoption of a two boiler room layout. This reduced hull length and allowed for a single funnel, both reducing the profile and increasing the arcs of fire of the light anti-aircraft (AA) weapons. However, this also increased vu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
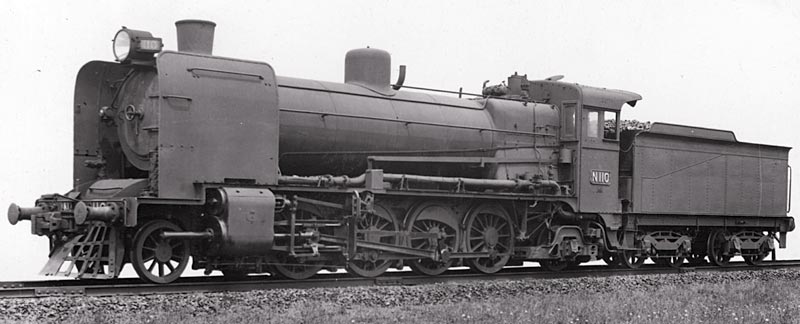
SECR N Class
The SECR N class was a type of 2-6-0 ("mogul") steam locomotive designed in 1914 by Richard Maunsell for mixed-traffic duties on the South Eastern and Chatham Railway (SECR). Built between 1917 and 1934, it was the first non-Great Western Railway (GWR) type to use and improve upon the basic design principles established by GWR Chief Mechanical Engineer (CME) George Jackson Churchward. The N class was based on the GWR 4300 Class design, improved with Midland Railway concepts. The N class was mechanically similar to the SECR K class 2-6-4 passenger tank engine, also by Maunsell. It influenced future 2-6-0 development in Britain and provided the basis for the 3 cylinder N1 class of 1922. Production was delayed by the outbreak of the First World War in 1914, and the first N class rolled out of Ashford Works in 1917, three years after design work was completed. The class replaced obsolete 0-6-0s as part of the SECR's fleet standardisation, as they u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V/Line N Class
The N Class are a class of diesel locomotives built by Clyde Engineering, Somerton for V/Line between 1985 and 1987. History By the start of the 1980s, Victorian Railways passenger numbers had fallen to around 3 million per year, due to ageing rolling stock, stagnant timetables and competition from other forms of transport. The Lonie Report of 1980 recommended cuts to the network, with the general public responding by calling for the State Government to maintain a viable rail network. The government response in February 1981 was the ''New Deal for Country Passengers'', a $115 million commitment to recast country rail passenger services in Victoria. As part of the ''New Deal'', all B class locomotives were to be re-built as the A class for use on passenger services and ten new locomotives ordered. Tenders closed in 1983 for the first 10 units, with Clyde Engineering being awarded the contract. By mid-1985, the rising cost of the A class conversions saw the project aban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westrail N Class
The N class was a class of diesel locomotives built by Comeng, Bassendean for Westrail between 1977 and 1979. History Eleven were built all for use on the Western Australian narrow gauge network, primarily to haul mineral trains in the south east. Between July 1982 and June 1983, the first four members of the class had their vacuum brake equipment replaced with Westinghouse air brake systems, and were redesignated as the NA class. While liked by crews for their ride quality and power, they suffered from reliability problems and most were withdrawn in the early 1990s. The last were withdrawn in 1997.Westrail N / NA / NB classes Westrail Alcos 9 March 2002 In January 1995 two of the NA class were [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sydney N-Class Tram
The N-class trams were a crossbench design of tram with a two-bogie design, each pair of benches had doors at each side. They were attached to Dowliing Street, Newtown, Rozelle, Tempe, Ultimo, Enfield and Rockdale depots. Nine were transferred to Newcastle as steam trailers in 1915, all later returned and had their electrical equipment reinstated. The last was withdrawn in 1949. Preservation Three have been preserved: *710, 718, 728 at the Sydney Tramway Museum The Sydney Tramway Museum (operated by the South Pacific Electric Railway) is Australia's oldest tramway museum and the largest in the southern hemisphere. It is located at Loftus, New South Wales, Loftus in the southern suburbs of Sydney. Hist ... References Further reading * * External links {{DEFAULTSORT:N class tram Trams in Sydney Tram vehicles of Australia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States N-class Submarine
The United States N-class submarines were a class of seven coastal defense submarines built for the United States Navy during World War I. Description The boats were constructed by two companies to slightly different specifications; ''N-1'', ''N-2'', and ''N-3'' were designed by the Electric Boat Company of Groton, Connecticut and built by the Seattle Construction and Drydock Company of Seattle, Washington, and ''N-4'', ''N-5'', ''N-6'', and ''N-7'' were designed and built by the Lake Torpedo Boat Company of Bridgeport, Connecticut. The N-boats built by Lake are sometimes considered a separate class. The Electric Boat submarines had a length of overall, a beam of and a mean draft of . They displaced on the surface and submerged. The N-class submarines had a crew of 2 officers and 23 enlisted men. They had a diving depth of .Friedman, p. 307 The Lake submarines had a length of overall, a beam of and a mean draft of . They displaced on the surface and submerged. The N-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-class Blimp
The N-Class, or as popularly known, the "Nan ship", was a line of non-rigid airships built by the Goodyear Aircraft Company of Akron, Ohio for the US Navy. This line of airships was developed through many versions and assigned various designators as the airship designation system changed in the post World War II era. These versions included airships configured for both anti-submarine warfare and airborne early warning (AEW) missions. Design and development The initial version, designated ZPN-1, was a follow-on to the M-class blimp for patrol missions. The Nan ship used a significantly larger envelope than the M-ship although their overall lengths were similar. Two Wright R-1300 Cyclone 7 single-row, air-cooled radial engines powered the N-Class blimps.''Sky Ships: A History of the Airship in the United States Navy'', Althoff, W.F., Pacifica Press, c1991, An initial contract was awarded to the Goodyear Aircraft Company for the prototype N-class blimp in the late 1940s, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-class Ferry
N-class ferries are a class of RORO ferries, of which one remaining example is owned by BC Ferries and has the distinction of being the smallest vessel in their fleet. The N class consists of four vessels: , sold to Mike Buttle Services in 2019 and renamed ''Mid Coaster''. Built: Vancouver BC Launched: 1973 Vehicle capacity: 16 Passenger Capacity: 133 Length: Gross Tons: 371 Service Speed: 11 knots Horsepower: 680 , (also known as ''Spirit of Lax Kw' Alaams'') owned by BC Ferries, but operated by Lax Kw'alaams First Nations First Nations or first peoples may refer to: * Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area. Indigenous groups *First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including: **First Natio .... Built: Vancouver BC Launched: 1960 Vehicle capacity: 16 Passenger Capacity: 133 Length: Gross Tons: 256.34 Service Speed: 10 knots Horsepower: 680 , sold to Rainy Day Logging in 2002. Built: Vancouver BC L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Railways N Class
The N class was a branch line steam locomotive that ran on Victorian Railways from 1925 to 1966. A development of the successful K class 2-8-0, it was the first VR locomotive class designed for possible conversion from to . History In 1923, in response to the recommendations made by the 1921 Royal Commission on the matter of uniform railway gauge, VR announced a policy that all new locomotive designs were to be capable of conversion from broad to standard gauge.Pearce et al., p. 12 The rationale was that the task of converting VR from broad to standard gauge at a future date would be far easier to achieve if the existing locomotives and rolling stock could be easily modified for standard gauge operation, rather than requiring expensive re-engineering or replacement. The K class 2-8-0 built by VR in 1922-23 was a success, but with a firebox mounted between frames engineered for broad gauge operation only, it was not readily gauge-convertible. Thus when additional branch li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |