|
N-Methylmorpholine N-oxide
''N''-Methylmorpholine ''N''-oxide (more correctly 4-methylmorpholine 4-oxide), NMO or NMMO is an organic compound. This heterocyclic amine oxide and morpholine derivative is used in organic chemistry as a co-oxidant and sacrificial catalyst in oxidation reactions for instance in osmium tetroxide oxidations and the Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation or oxidations with TPAP. NMO is commercially supplied both as a monohydrate C5H11NO2·H2O and as the anhydrous compound. The monohydrate is used as a solvent for cellulose in the lyocell process to produce cellulose fibers. Uses Solvent of cellulose NMMO monohydrate is used as a solvent in the lyocell process to produce lyocell fiber. It dissolves cellulose to form a solution called dope, and the cellulose is reprecipitated in a water bath to produce a fiber. The process is similar but not analogous to the viscose process. In the viscose process, cellulose is made soluble by conversion to its xanthate derivatives. With NMMO, cellul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valonia Oak
''Quercus macrolepis'', the Valonia oak, is a species of oak in the beech family, Fagaceae. Formerly, it was commonly treated as a subspecies of the closely related and sympatric mount Tabor oak. At present, however, it is mostly granted species-status. Geographical range It is found in the Balkans, and in the southern and eastern Mediterranean, including Albania, the Greek Islands, Turkey, Israel, and Morocco. Systematics Within the oak genus, Quercus macrolepis is classified in the subgenus ''Cerris'', section ''Cerris'', which includes the turkey oak and related species. It is most closely related to Mount Tabor oak (Quercus ithaburensis) and Brant's oak (Quercus brantii). Uses The cups, known as valonia, are used for tanning and dyeing as are the unripe acorns called camata or camatina. The ripe acorns are eaten raw or boiled. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morpholines
Morpholine is an organic chemical compound having the chemical formula O( C H2CH2)2 NH. This heterocycle features both amine and ether functional groups. Because of the amine, morpholine is a base; its conjugate acid is called morpholinium. For example, treating morpholine with hydrochloric acid makes the salt morpholinium chloride. It is a colorless liquid with a weak, ammonia- or fish-like odor. The naming of morpholine is attributed to Ludwig Knorr, who incorrectly believed it to be part of the structure of morphine. Production Morpholine is often produced industrially by the dehydration of diethanolamine with sulfuric acid: : Uses Industrial applications Morpholine is a common additive, in parts per million concentrations, for pH adjustment in both fossil fuel and nuclear power plant steam systems. Morpholine is used because its volatility is about the same as water, so once it is added to the water, its concentration becomes distributed rather evenly in both the water a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalytic
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some stag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-oxide
In chemistry, an amine oxide, also known as an amine ''N''-oxide or simply ''N''-oxide, is a chemical compound that contains the functional group , a nitrogen-oxygen coordinate covalent bond with three additional hydrogen and/or substituent-group side chains attached to N. Sometimes it is written as →O or, incorrectly, as . In the strict sense, the term ''amine oxide'' applies only to oxides of tertiary amines. Sometimes it is also used for the analogous derivatives of primary and secondary amines. Examples of amine oxides include pyridine-''N''-oxide, a water-soluble crystalline solid with melting point 62–67 °C, and ''N''-methylmorpholine ''N''-oxide, which is an oxidant. Applications Amine oxides are surfactants commonly used in consumer products such as shampoos, conditioners, detergents, and hard surface cleaners. Alkyl dimethyl amine oxide (chain lengths C10–C16) is the most commercially used amine oxide. They are considered a high production volume class of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NMO Example
NMO may refer to: * Neuromyelitis optica, also known as Devic's disease or Devic's syndrome * ''N''-Methylmorpholine ''N''-oxide, an organic compound * Nitronate monooxygenase, an enzyme * Normal Move Out, in reflection seismology * National Measurement Office The National Measurement and Regulation Office (NMRO) was an executive agency of the UK Government's Department for Business, Innovation and Skills (BIS). Its function were to provide a measurement infrastructure which supports innovation, facili ..., a government agency in the United Kingdom * New Motorola, a mobile antenna connector * COMMSTA NMO, a United States Coast Guard Communication Station in Honolulu, Hawaii {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen Bonds
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a lone pair of electrons—the hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Such an interacting system is generally denoted , where the solid line denotes a polar covalent bond, and the dotted or dashed line indicates the hydrogen bond. The most frequent donor and acceptor atoms are the second-row elements nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), and fluorine (F). Hydrogen bonds can be intermolecular (occurring between separate molecules) or intramolecular (occurring among parts of the same molecule). The energy of a hydrogen bond depends on the geometry, the environment, and the nature of the specific donor and acceptor atoms and can vary between 1 and 40 kcal/mol. This makes them somewhat stronger than a van der Waals interaction, and weaker than fully covalent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexapeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Hence, peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. A polypeptide that contains more than approximately 50 amino acids is known as a protein. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, or to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amide
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, such as in the amino acids asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid () with the hydroxyl group () replaced by an amine group (); or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group () joined to an amine group. Common examples of amides are acetamide (), benzamide (), and dimethylformamide (). Amides are qualified as primary, secondary, and tertiary according to whether the amine subgroup has the form , , or , where R and R' are groups other than hydrogen. The core of amides is called the amide group (specifically, carboxamide group). Amides are pervasive in nature and technology. Proteins and important plastics l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
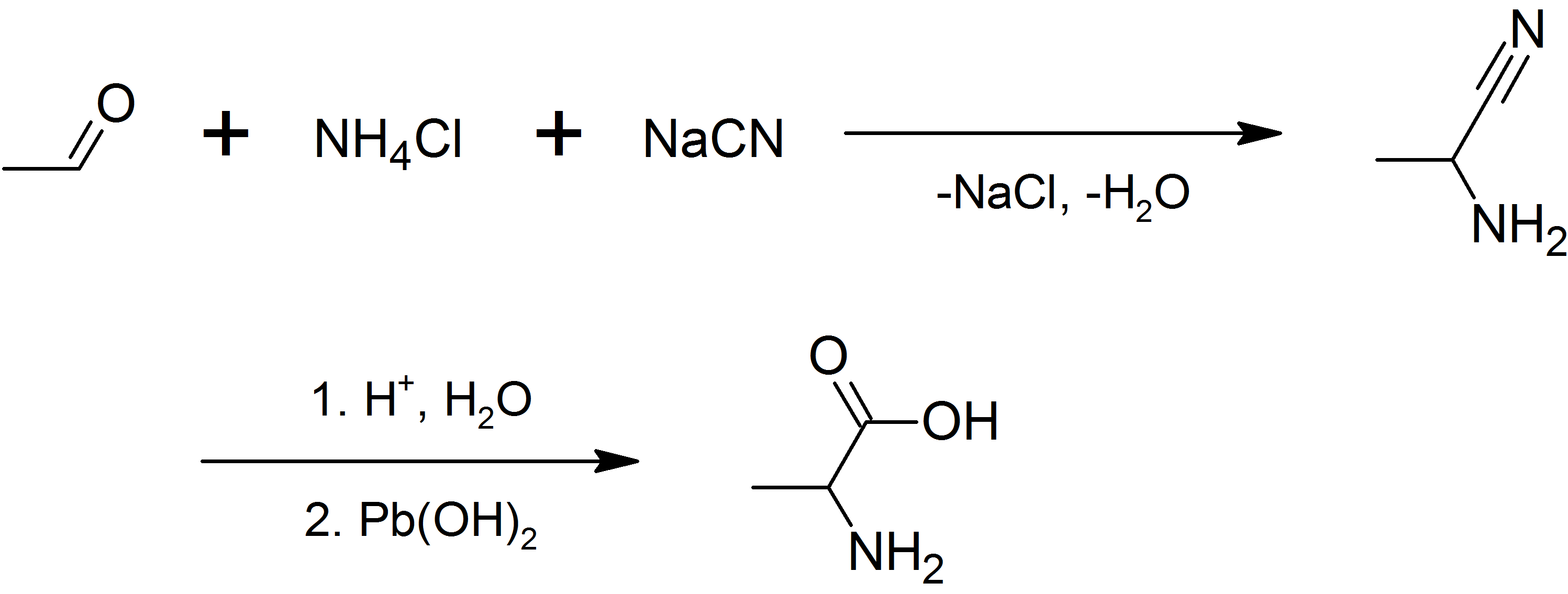
Alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side chain. Consequently, its IUPAC systematic name is 2-aminopropanoic acid, and it is classified as a nonpolar, aliphatic α-amino acid. Under biological conditions, it exists in its zwitterionic form with its amine group protonated (as −NH3+) and its carboxyl group deprotonated (as −CO2−). It is non-essential to humans as it can be synthesised metabolically and does not need to be present in the diet. It is encoded by all codons starting with GC (GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG). The L-isomer of alanine (left-handed) is the one that is incorporated into proteins. L-alanine is second only to leucine in rate of occurrence, accounting for 7.8% of the primary structure in a sample of 1,150 proteins. The right-handed form, D-alanine, occurs in p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. It is encoded by all the codons starting with GG (GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG). Glycine is integral to the formation of alpha-helices in secondary protein structure due to its compact form. For the same reason, it is the most abundant amino acid in collagen triple-helices. Glycine is also an inhibitory neurotransmitter – interference with its release within the spinal cord (such as during a ''Clostridium tetani'' infection) can cause spastic paralysis due to uninhibited muscle contraction. It is the only achiral proteinogenic amino acid. It can fit into hydrophilic or hydrophobic environments, due to its minimal side chain of only one hydrogen atom. History and etymology Glycine was discovered in 1820 by the French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scleroprotein
In molecular biology, fibrous proteins or scleroproteins are one of the three main classifications of protein structure (alongside globular and membrane proteins). Fibrous proteins are made up of elongated or fibrous polypeptide chains which form filamentous and sheet-like structures. These kind of protein can be distinguished from globular protein by its low solubility in water. Such proteins serve protective and structural roles by forming connective tissue, tendons, bone matrices, and muscle fiber. Fibrous proteins consist of many superfamilies including keratin, collagen, elastin, and fibrin. Collagen is the most abundant of these proteins which exists in vertebrate connective tissue including tendon, cartilage, and bone. Biomolecular structure A fibrous protein forms long protein filaments, which are shaped like rods or wires. Fibrous proteins are structural or storage proteins that are typically inert and water-insoluble. A fibrous protein occurs as an aggregate due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |