|
Myhre Syndrome
Myhre syndrome is a rare genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion. It is caused by mutation in SMAD4 gene. Signs and symptoms The clinical presentation is variable but includes * developmental and growth delay * athletic muscular built * skeletal anomalies * joint stiffness * characteristic facial appearance * deafness * variable cognitive deficits * tracheal stenosis * aortic stenosis * pyloric stenosis The facial abnormalities include: * blepharophimosis (an abnormally narrow gap between the upper and lower eyelids) * maxillary hypoplasia (underdevelopment of the upper jaw) * prognathism (prominent lower jaw) The skeletal abnormalities include: * short stature * square body shape * broad ribs * iliac hypoplasia * brachydactyly * flattened vertebrae * thickened calvaria Congenital heart disease and undescended testes have also been reported in association with this syndrome. Genetics Myhre syndrome is due to mutations in the SMAD4 SMAD4, also called SMAD f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Genetics
Medical genetics is the branch tics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics. In contrast, the study of typically non-medical phenotypes such as the genetics of eye color would be considered part of human genetics, but not necessarily relevant to medical genetics (except in situations such as albinism). ''Genetic medicine'' is a newer term for medical genetics and incorporates areas such as gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the rapidly emerging new medical specialty, predictive medicine. Scope Medical genetics encompasses many different areas, including clinical practice of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMAD4
SMAD4, also called SMAD family member 4, Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 4, or DPC4 (Deleted in Pancreatic Cancer-4) is a highly conserved protein present in all metazoans. It belongs to the SMAD family of transcription factor proteins, which act as mediators of TGF-β signal transduction. The TGFβ family of cytokines regulates critical processes during the lifecycle of metazoans, with important roles during embryo development, tissue homeostasis, regeneration, and immune regulation. SMAD 4 belongs to the co-SMAD group (''common mediator'' SMAD), the second class of the SMAD family. SMAD4 is the only known co-SMAD in most metazoans. It also belongs to the Darwin family of proteins that modulate members of the TGFβ protein superfamily, a family of proteins that all play a role in the regulation of cellular responses. Mammalian SMAD4 is a homolog of the ''Drosophila'' protein "Mothers against decapentaplegic" named Medea. SMAD4 interacts with R-Smads, such as SMAD2, SMA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
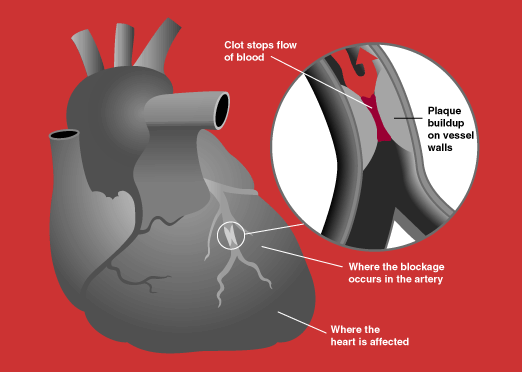
Aortic Stenosis
Aortic stenosis (AS or AoS) is the narrowing of the exit of the left ventricle of the heart (where the aorta begins), such that problems result. It may occur at the aortic valve as well as above and below this level. It typically gets worse over time. Symptoms often come on gradually with a decreased ability to exercise often occurring first. If heart failure, loss of consciousness, or heart related chest pain occur due to AS the outcomes are worse. Loss of consciousness typically occurs with standing or exercising. Signs of heart failure include shortness of breath especially when lying down, at night, or with exercise, and swelling of the legs. Thickening of the valve without narrowing is known as aortic sclerosis. Causes include being born with a bicuspid aortic valve, and rheumatic fever; a normal valve may also harden over the decades. A bicuspid aortic valve affects about one to two percent of the population. As of 2014 rheumatic heart disease mostly occurs in the dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyloric Stenosis
Pyloric stenosis is a narrowing of the opening from the stomach to the first part of the small intestine (the pylorus). Symptoms include projectile vomiting without the presence of bile. This most often occurs after the baby is fed. The typical age that symptoms become obvious is two to twelve weeks old. The cause of pyloric stenosis is unclear. Risk factors in babies include birth by cesarean section, preterm birth, bottle feeding, and being first born. The diagnosis may be made by feeling an olive-shaped mass in the baby's abdomen. This is often confirmed with ultrasound. Treatment initially begins by correcting dehydration and electrolyte problems. This is then typically followed by surgery, although some treat the condition without surgery by using atropine. Results are generally good both in the short term and in the long term. About one to two per 1,000 babies are affected, and males are affected about four times more often than females. The condition is very rare in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blepharophimosis
Blepharophimosis is a congenital anomaly in which the eyelids are underdeveloped such that they cannot open as far as usual and permanently cover part of the eyes. Both the vertical and horizontal palpebral fissures (eyelid openings) are shortened; the eyes also appear spaced more widely apart as a result, known as telecanthus. Presentation In addition to small palpebral fissures, features can include epicanthus inversus (fold curving in the mediolateral direction, inferior to the inner canthus), low nasal bridge, ptosis of the eyelids and telecanthus. Associated conditions Blepharophimosis, ptosis, epicanthus inversus syndrome Blepharophimosis forms a part of blepharophimosis, ptosis, epicanthus inversus syndrome (BPES), also called blepharophimosis syndrome, which is an autosomal dominant condition characterised by blepharophimosis, ptosis (upper eyelid drooping), epicanthus inversus (skin folds by the nasal bridge, more prominent lower than upper lid) and telecanthus (wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prognathism
Prognathism, also called Habsburg jaw or Habsburgs' jaw primarily in the context of its prevalence amongst members of the House of Habsburg, is a positional relationship of the mandible or maxilla to the skeletal base where either of the jaws protrudes beyond a predetermined imaginary line in the coronal plane of the skull. In general dentistry, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and orthodontics, this is assessed clinically or radiographically ( cephalometrics). The word ''prognathism'' derives from Greek πρό (''pro'', meaning 'forward') and γνάθος (''gnáthos'', 'jaw'). One or more types of prognathism can result in the common condition of malocclusion, in which an individual's top teeth and lower teeth do not align properly. Presentation Prognathism in humans can occur due to normal variation among phenotypes. In human populations where prognathism is not the norm, it may be a malformation, the result of injury, a disease state or a hereditary condition. Prognathism ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndromes Affecting The Heart
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms that are correlated with each other. A syndrome A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired ... can affect one or more of body systems. Different syndromes affect different groups of organs. This is a list of syndromes that may affect the heart. ''Syndromes affecting primarily the heart are written in bold letters. '' References External links What Is the Heart?– NIH {{Medicine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndromes With Craniofacial Abnormalities
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired with a definite cause this becomes a disease. In some instances, a syndrome is so closely linked with a pathogenesis or cause that the words ''syndrome'', ''disease'', and ''disorder'' end up being used interchangeably for them. This substitution of terminology often confuses the reality and meaning of medical diagnoses. This is especially true of inherited syndromes. About one third of all phenotypes that are listed in OMIM are described as dysmorphic, which usually refers to the facial gestalt. For example, Down syndrome, Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, and Andersen–Tawil syndrome are disorders with known pathogeneses, so each is more than just a set of signs and symptoms, despite the ''syndrome'' nomenclature. In other instances, a syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndromes With Dysmelia
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired with a definite cause this becomes a disease. In some instances, a syndrome is so closely linked with a pathogenesis or cause that the words ''syndrome'', ''disease'', and ''disorder'' end up being used interchangeably for them. This substitution of terminology often confuses the reality and meaning of medical diagnoses. This is especially true of inherited syndromes. About one third of all phenotypes that are listed in OMIM are described as dysmorphic, which usually refers to the facial gestalt. For example, Down syndrome, Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, and Andersen–Tawil syndrome are disorders with known pathogeneses, so each is more than just a set of signs and symptoms, despite the ''syndrome'' nomenclature. In other instances, a syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndromes With Short Stature
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired with a definite cause this becomes a disease. In some instances, a syndrome is so closely linked with a pathogenesis or cause that the words ''syndrome'', ''disease'', and ''disorder'' end up being used interchangeably for them. This substitution of terminology often confuses the reality and meaning of medical diagnoses. This is especially true of inherited syndromes. About one third of all phenotypes that are listed in OMIM are described as dysmorphic, which usually refers to the facial gestalt. For example, Down syndrome, Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, and Andersen–Tawil syndrome are disorders with known pathogeneses, so each is more than just a set of signs and symptoms, despite the ''syndrome'' nomenclature. In other instances, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |