|
Mutatá Fault
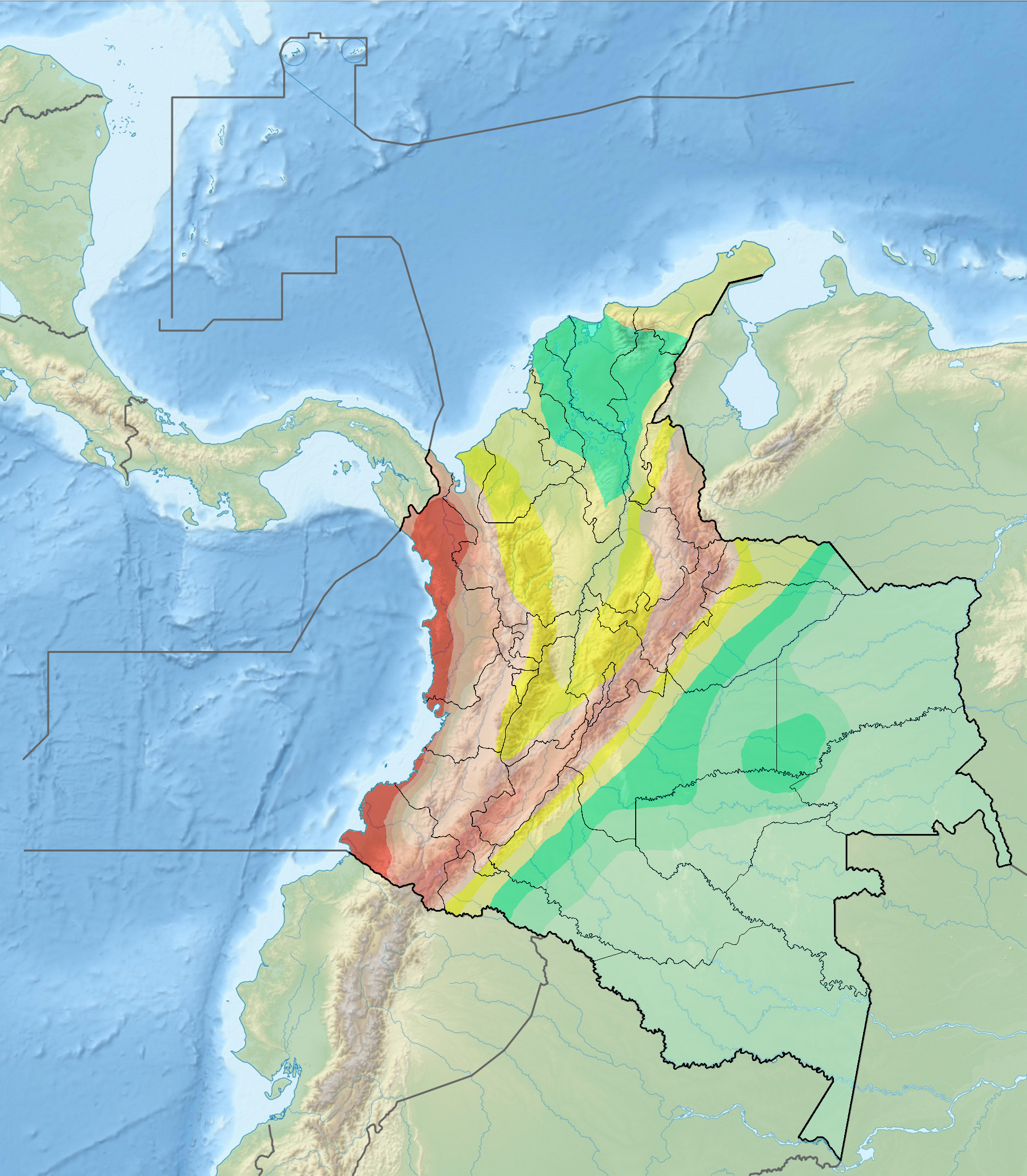
The Mutatá Fault ( es, Falla Mutatá) is a strike-slip fault in the department of Antioquia in northern Colombia. The fault has a total length of and runs along an average northwest to southeast strike of 326.4 ± 11 in the Urabá Basin. The fault is active and produced the 2016 Mutatá earthquake with a moment magnitude of 6.0. Etymology The fault is named after Mutatá.Paris et al., 2000, p.14 Description The Mutatá Fault is located in northwestern Colombia, between the Penderisco River and the Caribbean Sea. To the south, near the town of Mutatá, the Mutatá Fault approaches the Murrí Fault and the two fault zones practically merge. In this area, the Mutatá Fault places Cretaceous intrusive rocks and greenstones (to the east) in contact with sedimentary Tertiary rocks (to the west). Farther north, the fault cuts Tertiary and Quaternary deposits, with uplift of the eastern block. The Mutatá Fault is located near the junction of the Malpelo, Caribbean, and Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutatá
Mutatá is a municipality in the Colombian department of Antioquia. Climate Mutatá has a tropical rainforest climate (Köppen Köppen is a German surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Bernd Köppen (born 1951), German pianist and composer * Carl Köppen (1833-1907), German military advisor in Meiji era Japan * Edlef Köppen (1893–1939), German author and ... ''Af'') with very heavy rainfall year round. References Municipalities of Antioquia Department {{Antioquia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles starting with Cuba, to the east by the Lesser Antilles, and to the south by the northern coast of South America. The Gulf of Mexico lies to the northwest. The entire area of the Caribbean Sea, the numerous islands of the West Indies, and adjacent coasts are collectively known as the Caribbean. The Caribbean Sea is one of the largest seas and has an area of about . The sea's deepest point is the Cayman Trough, between the Cayman Islands and Jamaica, at below sea level. The Caribbean coastline has many gulfs and bays: the Gulf of Gonâve, Gulf of Venezuela, Gulf of Darién, Golfo de los Mosquitos, Gulf of Paria and Gulf of Honduras. The Caribbean Sea has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
INGEOMINAS
The Colombian Geological Survey (CGS) ( es, Servicio Geológico Colombiano; formerly known as INGEOMINAS) is a scientific agency of the Colombian government in charge of contributing to the socioeconomic development of the nation through research in basic and applied geosciences of the subsoil, the potential of its resources, evaluating and monitoring threats of geological origin, managing the geoscientific knowledge of the nation, and studying the nuclear and radioactive elements in Colombia. History The CGS was initially created as the ''National Scientific Commission'' ( es, Comisión Científica Nacional) by the Congress of Colombia on December 22, in 1916, with the mission of mapping the geological resources of the nation and exploring the national territory in search of mineral deposits. Following a series of earthquakes throughout the nation in the early 1920s, the eruption of the Galeras volcano in 1925, and the growing mining and petroleum industry, the Colombian govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romeral Fault System
The Romeral Fault System ( es, Sistema de Fallas (de) Romeral) is a megaregional system of major parallel and anastomosing faults in the Cordillera Central (Colombia), Central Ranges of the Colombian Andes and the Cauca Basin, Cauca, Amagá Basin, Amagá, and Sinú-San Jacinto Basins. The system spans across ten departments of Colombia, departments of Colombia, from northeast to south Bolívar Department, Bolívar, Sucre Department, Sucre, Córdoba Department, Córdoba, Antioquia Department, Antioquia, Caldas Department, Caldas, Risaralda Department, Risaralda, Quindío Department, Quindío, Valle del Cauca Department, Valle del Cauca, Cauca Department, Cauca and Nariño Department, Nariño. The fault zone extends into Ecuador where it is known as the Peltetec Fault System. The in detail described part of the Romeral Fault System south of Córdoba has a total length of with a cumulative length of and runs along an average north to south strike (geology), strike of 017.6 ± 16, cros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unguía Fault
The Unguía Fault ( es, Falla de Unguía) is an oblique dextral thrust fault in the department of Chocó in northwestern Colombia and continuing offshore Panama in the Caribbean Sea. The fault has a total length of and is arcuate, running along a strike of 356.3 ± 30. Etymology The fault is named after Unguía, Chocó.Paris et al., 2000, p.15 Description The fault is located in the Darién area of northwestern Colombia. It has an irregular arcuate strike, but it has a general north tendency. In Colombia, it has been mapped as far north as the town of Acandí: farther north, it enters the Caribbean Sea, where it parallels the coast of Panama. The Unguía Fault is likely a southern continuation of the eastern section of the Northern Panama deformed belt, where it comes on land in northwestern Colombia. The fault is prominent on satellite images and topographic maps. The irregular boundary between the Serranía del Darién and the Atrato Valley suggests that the fault is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murindó Fault
The Murindó Fault ( es, Falla Murindó) is a strike-slip fault in the department of Antioquia and Chocó in northwestern Colombia. The fault has a total length of and runs along an average north-northwest to south-southeast strike of 347.4 ± 6 in the Chocó Basin along the western edge of the Western Ranges of the Colombian Andes. Etymology The fault is named after Murindó.Paris et al., 2000, p.14 Description The fault in the Chocó Basin extends along the western slope of the Western Ranges of the Colombian Andes, from the Arquia River in the south to the Río Sucio and the basin of the Atrato River in the north. The Murindó Fault places Cretaceous volcanic (basic) rocks against Tertiary turbidites, and crosscuts Tertiary quartz-diorite and granodiorite. The Murindó River flows along the Murindó Fault near Murindó.Plancha 113, 2007 The fault underlies the municipalities of Dabeiba and Frontino.Plancha 128, 2002 To the south, the fault runs parallel to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Earthquakes In Colombia
This is a list of earthquakes in Colombia. Colombia is a seismically active country and has a large seismic risk in many areas of its territory due to its location at the boundaries of the Malpelo, Panama, Caribbean, North Andes (where most earthquakes occurred) and South American Plates along the Pacific Ring of Fire. The southeastern and extreme eastern portions of Colombia are not as seismically active as the rest of the country. The first historically registered earthquake felt in Colombia occurred on September 11, 1530, around 10:00 AM, probably with the epicentre near Cumaná, Venezuela. The earthquake was documented by Gonzalo Fernández de Oviedo y Valdés in his work ''La Historia general de las Indias'' and by friar Bartolomé de las Casas in his book ''Historia de Las Indias''.Ramírez, 1975, p.63 The first documented earthquake with its epicentre in present-day Colombia territory took place in 1566,Ramírez, 1975, p.65 with the epicentre estimated around Santander ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Río Sucio
Rio or Río is the Portuguese, Spanish, Italian, and Maltese word for "river". When spoken on its own, the word often means Rio de Janeiro, a major city in Brazil. Rio or Río may also refer to: Geography Brazil * Rio de Janeiro * Rio do Sul, a town in the state of Santa Catarina, Brazil Mexico * Río Bec, a Mayan archaeological site in Mexico * Río Bravo, Tamaulipas, a city in Mexico United States * Rio, a location in Deerpark, New York, US * Rio, Florida, a census-designated place in Martin County, US * Rio, Georgia, an unincorporated community in Spalding County, US * Rio, Illinois, a village in Knox County, US * Rio, Virginia, a community in Albemarle County, US * Rio, West Virginia, a village in Hampshire County, US * Rio, Wisconsin, a village in Columbia County, US * El Río, Las Piedras, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Añasco, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Arecibo, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Fajardo, Puerto Rico, a barrio * Río Arriba, Vega Baj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean Plate
The Caribbean Plate is a mostly oceanic tectonic plate underlying Central America and the Caribbean Sea off the north coast of South America. Roughly 3.2 million square kilometers (1.2 million square miles) in area, the Caribbean Plate borders the North American Plate, the South American Plate, the Nazca Plate and the Cocos Plate. These borders are regions of intense seismic activity, including frequent earthquakes, occasional tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions. Boundary types The northern boundary with the North American Plate is a transform or strike-slip boundary which runs from the border area of Belize, Guatemala (Motagua Fault), and Honduras in Central America, eastward through the Cayman trough along the Swan Islands Transform Fault before joining the southern boundary of the Gonâve Microplate. East of the Mid-Cayman Rise this continues as the Walton fault zone and the Enriquillo–Plantain Garden fault zone into eastern Hispaniola. From there it continues into Puerto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malpelo Plate
The Malpelo Plate is a small tectonic plate (microplate) located off the coasts west of Ecuador and Colombia. It is the 57th plate to be identified. It is named after Malpelo Island, the only emerged part of the plate. It is bounded on the west by the Cocos Plate, on the south by the Nazca Plate, on the east by the North Andes Plate, and on the north by the Coiba Plate, separated by the Coiba Transform Fault (CTF). This microplate was previously assumed to be part of the Nazca Plate. The Malpelo Plate borders three major faults of Pacific Colombia, the north to south striking Bahía Solano Fault in the north and the Naya-Micay and Remolino-El Charco Faults in the south. Description The Malpelo Plate was identified by a non-closure of the Nazca-Cocos-Pacific plate motion circuit, reported by Tuo Zhang and lead-researcher Richard G. Gordon et al. of Rice University in a paper published in August 2017.Zhang et al., 2017 The existence of the plate has been hypothesised be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.gif)