|
Mutagenesis (molecular Biology)
In molecular biology, mutagenesis is an important laboratory technique whereby DNA mutations are deliberately engineered to produce libraries of mutant genes, proteins, strains of bacteria, or other genetically modified organisms. The various constituents of a gene, as well as its regulatory elements and its gene products, may be mutated so that the functioning of a genetic locus, process, or product can be examined in detail. The mutation may produce mutant proteins with interesting properties or enhanced or novel functions that may be of commercial use. Mutant strains may also be produced that have practical application or allow the molecular basis of a particular cell function to be investigated. Many methods of mutagenesis exist today. Initially, the kind of mutations artificially induced in the laboratory were entirely random using mechanisms such as UV irradiation. Random mutagenesis cannot target specific regions or sequences of the genome; however, with the development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Growth Medium
A growth medium or culture medium is a solid, liquid, or semi-solid designed to support the growth of a population of microorganisms or cells via the process of cell proliferation or small plants like the moss ''Physcomitrella patens''. Different types of media are used for growing different types of cells. The two major types of growth media are those used for cell culture, which use specific cell types derived from plants or animals, and those used for microbiological culture, which are used for growing microorganisms such as bacteria or fungi. The most common growth media for microorganisms are nutrient broths and agar plates; specialized media are sometimes required for microorganism and cell culture growth. Some organisms, termed fastidious organisms, require specialized environments due to complex nutritional requirements. Viruses, for example, are obligate intracellular parasites and require a growth medium containing living cells. Types The most common growth media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition (genetics)
Transition, in genetics and molecular biology, refers to a point mutation that changes a purine nucleotide to another purine ( A ↔ G), or a pyrimidine nucleotide to another pyrimidine ( C ↔ T). Approximately two out of three single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are transitions. Transitions can be caused by oxidative deamination and tautomerization. Although there are twice as many possible transversions, transitions appear more often in genomes, possibly due to the molecular mechanisms that generate them. 5-Methylcytosine is more prone to transition than unmethylated cytosine, due to spontaneous deamination. This mechanism is important because it dictates the rarity of CpG islands. See also * Transversion Transversion, in molecular biology, refers to a point mutation in DNA in which a single (two ring) purine ( A or G) is changed for a (one ring) pyrimidine ( T or C), or vice versa. A transversion can be spontaneous, or it can be caused by i ... References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aminopurine
2-Aminopurine, a purine analog of guanine and adenine, is a fluorescent molecular marker used in nucleic acid research. It most commonly pairs with thymine as an adenine-analogue, but can also pair with cytosine as a guanine-analogue;. For this reason it is sometimes used in the laboratory for mutagenesis. See also *Nucleic acid analogues Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research. Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Aminopurine, 2- Nucleobases Purines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
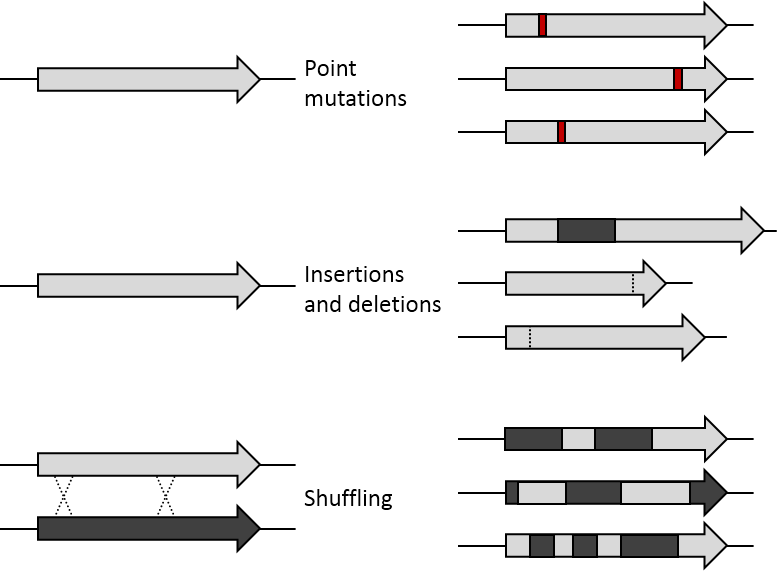
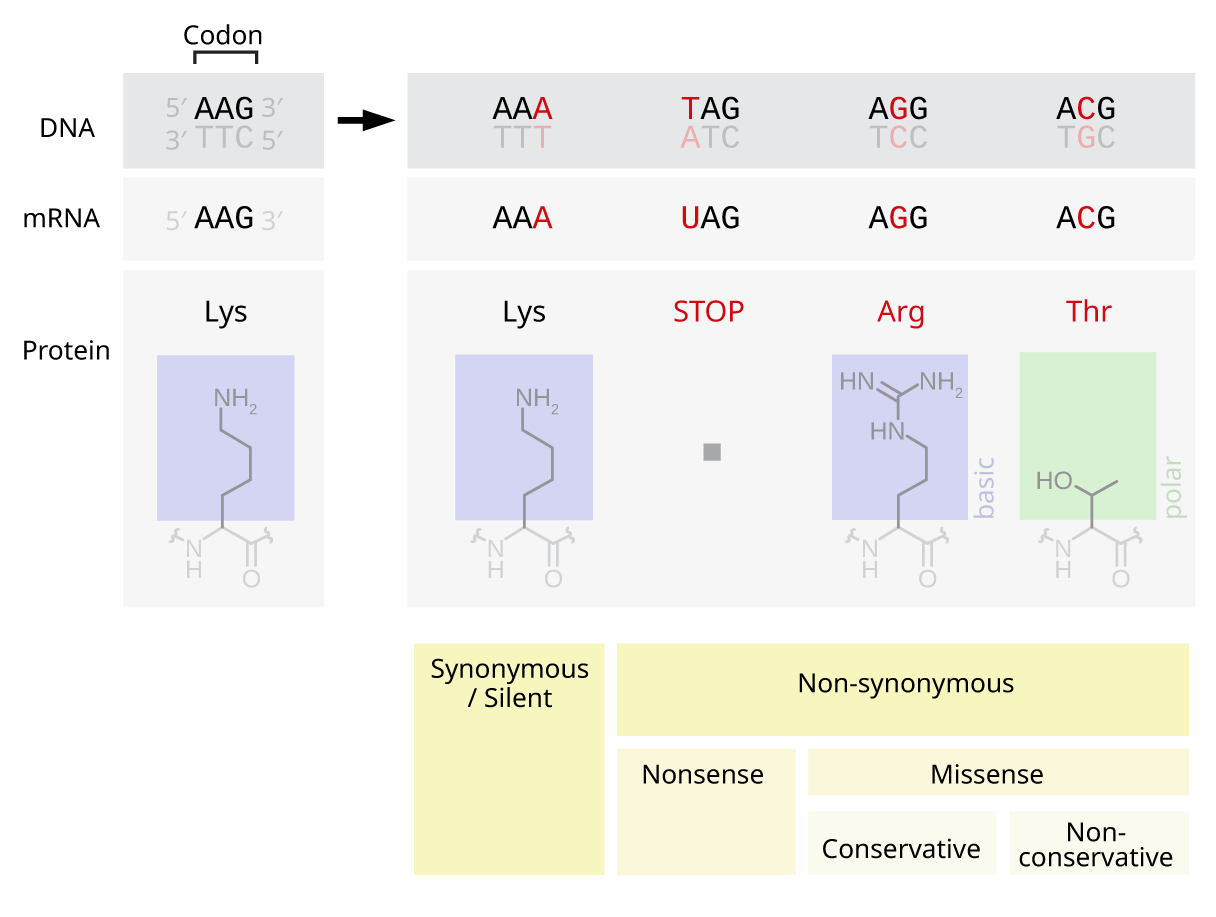
Point Mutation
A point mutation is a genetic mutation where a single nucleotide base is changed, inserted or deleted from a DNA or RNA sequence of an organism's genome. Point mutations have a variety of effects on the downstream protein product—consequences that are moderately predictable based upon the specifics of the mutation. These consequences can range from no effect (e.g. synonymous mutations) to deleterious effects (e.g. frameshift mutations), with regard to protein production, composition, and function. Causes Point mutations usually take place during DNA replication. DNA replication occurs when one double-stranded DNA molecule creates two single strands of DNA, each of which is a template for the creation of the complementary strand. A single point mutation can change the whole DNA sequence. Changing one purine or pyrimidine may change the amino acid that the nucleotides code for. Point mutations may arise from spontaneous mutations that occur during DNA replication. The rate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been described as a '' sui generis'' political entity (without precedent or comparison) combining the characteristics of both a federation and a confederation. Containing 5.8per cent of the world population in 2020, the EU generated a nominal gross domestic product (GDP) of around trillion in 2021, constituting approximately 18per cent of global nominal GDP. Additionally, all EU states but Bulgaria have a very high Human Development Index according to the United Nations Development Programme. Its cornerstone, the Customs Union, paved the way to establishing an internal single market based on standardised legal framework and legislation that applies in all member states in those matters, and only those matters, where the states have agreed to act ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Methanesulfonate
Ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS) is a mutagenic, teratogenic, and carcinogenic organic compound with formula C3H8SO3. It produces random mutations in genetic material by nucleotide substitution; particularly through G:C to A:T transitions induced by guanine alkylation. EMS typically produces only point mutations. Due to its potency and well understood mutational spectrum, EMS is the most commonly used chemical mutagen in experimental genetics. Mutations induced by EMS exposure can then be studied in genetic screens or other assays. Use in biological research EMS can induce mutations at a rate of 5x10−4 to 5x10−2 per gene without substantial killing. A 5x10−4 per gene mutation rate observed in a typical EMS mutagenesis experiment of the model organism ''C. elegans'', corresponds to a raw mutation rate of ~7x10−6 mutations per G/C base pair, or about 250 mutations within an originally mutagenized gamete (containing a ~100 Mbp, 36% GC haploid genome). Such a mutagenized gam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkylating Agent
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents. Nucleophilic alkylating agents Nucleophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl anion (carbanion). The formal "alkyl anion" attacks an electrophile, forming a new covalent bond be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expression Vector
An expression vector, otherwise known as an expression construct, is usually a plasmid or virus designed for gene expression in cells. The vector is used to introduce a specific gene into a target cell, and can commandeer the cell's mechanism for protein synthesis to produce the protein encoded by the gene. Expression vectors are the basic tools in biotechnology for the production of proteins. The vector is engineered to contain regulatory sequences that act as enhancer and promoter regions and lead to efficient transcription of the gene carried on the expression vector. The goal of a well-designed expression vector is the efficient production of protein, and this may be achieved by the production of significant amount of stable messenger RNA, which can then be translated into protein. The expression of a protein may be tightly controlled, and the protein is only produced in significant quantity when necessary through the use of an inducer, in some systems however the protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Cloning
Molecular cloning is a set of experimental methods in molecular biology that are used to assemble recombinant DNA molecules and to direct their replication within host organisms. The use of the word ''cloning'' refers to the fact that the method involves the replication of one molecule to produce a population of cells with identical DNA molecules. Molecular cloning generally uses DNA sequences from two different organisms: the species that is the source of the DNA to be cloned, and the species that will serve as the living host for replication of the recombinant DNA. Molecular cloning methods are central to many contemporary areas of modern biology and medicine. In a conventional molecular cloning experiment, the DNA to be cloned is obtained from an organism of interest, then treated with enzymes in the test tube to generate smaller DNA fragments. Subsequently, these fragments are then combined with vector DNA to generate recombinant DNA molecules. The recombinant DNA is then in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Saturation Mutagenesis
Sequence saturation mutagenesis (SeSaM) is a chemo-enzymatic random mutagenesis method applied for the directed evolution of proteins and enzymes. It is one of the most common saturation mutagenesis techniques. In four PCR-based reaction steps, phosphorothioate nucleotides are inserted in the gene sequence, cleaved and the resulting fragments elongated by universal or degenerate nucleotides. These nucleotides are then replaced by standard nucleotides, allowing for a broad distribution of nucleic acid mutations spread over the gene sequence with a preference to transversions and with a unique focus on consecutive point mutations, both difficult to generate by other mutagenesis techniques. The technique was developed by Professor Ulrich Schwaneberg at Jacobs University Bremen and RWTH Aachen University. Technology, development and advantages SeSaM has been developed in order to overcome several of the major limitations encountered when working with standard mutagenesis methods bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymerase Chain Reaction
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a method widely used to rapidly make millions to billions of copies (complete or partial) of a specific DNA sample, allowing scientists to take a very small sample of DNA and amplify it (or a part of it) to a large enough amount to study in detail. PCR was invented in 1983 by the American biochemist Kary Mullis at Cetus Corporation; Mullis and biochemist Michael Smith (chemist), Michael Smith, who had developed other essential ways of manipulating DNA, were jointly awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1993. PCR is fundamental to many of the procedures used in genetic testing and research, including analysis of Ancient DNA, ancient samples of DNA and identification of infectious agents. Using PCR, copies of very small amounts of DNA sequences are exponentially amplified in a series of cycles of temperature changes. PCR is now a common and often indispensable technique used in medical laboratory research for a broad variety of applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |