|
Musophagidae
The turacos make up the bird family Musophagidae ( "banana-eaters"), which includes plantain-eaters and go-away-birds. In southern Africa both turacos and go-away-birds are commonly known as loeries. They are semi-zygodactylous: the fourth (outer) toe can be switched back and forth. The second and third toes, which always point forward, are conjoined in some species. Musophagids often have prominent crests and long tails; the turacos are noted for peculiar and unique pigments giving them their bright green and red feathers. Traditionally, this group has been allied with the cuckoos in the order Cuculiformes, but the Sibley-Ahlquist taxonomy raises this group to a full order Musophagiformes. They have been proposed to link the hoatzin to the other living birds, but this was later disputed. Recent genetic analyses have strongly supported the order ranking of Musophagiformes. Musophagidae is one of very few bird families endemic to Africa, one other being the mousebirds, Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Blue Turaco
The great blue turaco (''Corythaeola cristata'') is a bird species of the family Musophagidae. At in length, it is the largest species of turaco. It has predominantly grey-blue plumage with an upright blue-black crest around high. The male and female have similar plumage. It is widespread throughout the African tropical rainforest. Taxonomy French ornithologist Louis Vieillot described the great blue turaco as ''Musophaga cristata'' in 1816, before German ornithologist Ferdinand Heine placed in its own genus in 1860. The great blue turaco is the sole member of the subfamily Corythaeolinae within the turaco family. Its closest relatives are the go-away birds and plantain eaters of the genus ''Crinifer''. The common ancestor of both diverged from the ancestor of all other turaco species. "Great blue turaco" has been designated the official common name by the International Ornithologists' Union (IOC). It is also called blue plantain eater. Description Generally, the great blu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tauraco
''Tauraco'' is a genus of turacos. It contains the "typical" or green turacos; though their plumage is not always green all over, the presence of significant amounts of turacoverdin-colored plumage generally sets ''Tauraco'' species apart from other Musophagidae. Indeed, as opposed to any other known birds, ''Tauraco'' turacos are the only living bird taxa that have any significant green pigment whatsoever, as the greens of many parrots etc. are due to structural color, not pigment. Their genus name was derived from a native Niger–Congo languages, West African name. Taxonomy The genus ''Tauraco'' was introduced in 1779 by the Polish naturalist Jan Krzysztof Kluk. The type species was later designated as the Guinea turaco. Species The genus contains 13 species. References External links * * {{Taxonbar, from=Q654783 Tauraco, Bird genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guinea Turaco
The Guinea turaco (''Tauraco persa''), also known as the green turaco or green lourie, is a species of turaco, a group of otidimorphae birds belonging to the family Musophagidae. It was formerly included in the Livingstone's, Schalow's, Knysna, black-billed and Fischer's turacos as subspecies. Taxonomy The Guinea turaco was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ''Systema Naturae''. He placed it together with the cuckoos in the genus ''Cuculus'' and coined the binomial name ''Cuculus persa''. The specific epithet is Latin meaning "Persian". Linnaeus based his description on the "Touraco" that had been described and illustrated in 1743 by the English naturalist George Edwards in his ''A Natural History of Uncommon Birds''. Edwards's specimen had been brought to London from Guinea in West Africa. The Guinea turaco is now placed in the genus ''Tauraco'' that was introduced in 1779 by the Polish naturalist Jan Krzysztof Klu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
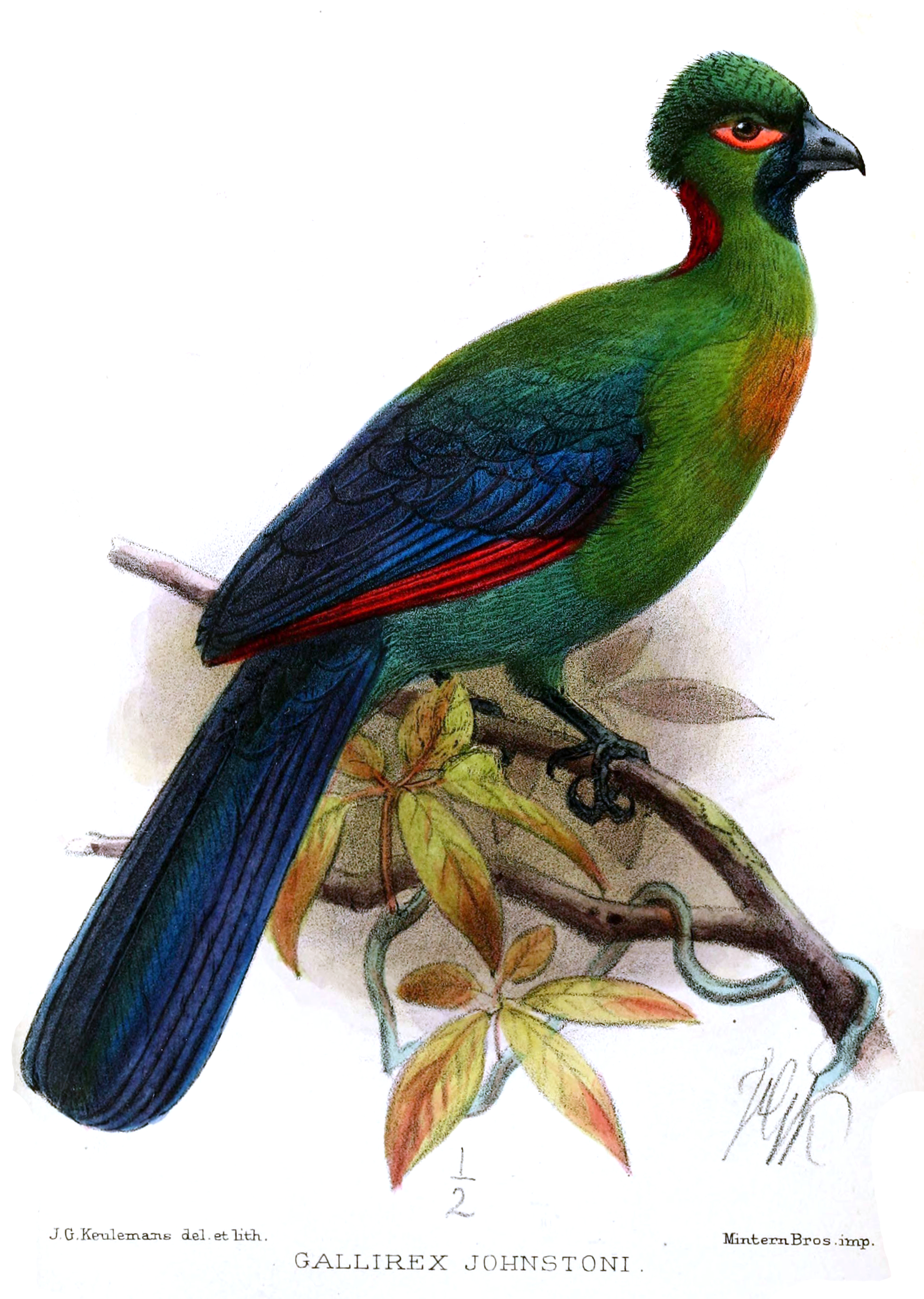
Gallirex
''Gallirex'' is a genus of African birds in the family Musophagidae The turacos make up the bird family Musophagidae ( "banana-eaters"), which includes plantain-eaters and go-away-birds. In southern Africa both turacos and go-away-birds are commonly known as loeries. They are semi-zygodactylous: the fourth ( .... Species It contains the following species: References * Bird genera Taxa named by René Lesson {{Cuculiformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musophaga
''Tauraco'' is a genus of turacos. It contains the "typical" or green turacos; though their plumage is not always green all over, the presence of significant amounts of turacoverdin-colored plumage generally sets ''Tauraco'' species apart from other Musophagidae. Indeed, as opposed to any other known birds, ''Tauraco'' turacos are the only living bird taxa that have any significant green pigment whatsoever, as the greens of many parrots etc. are due to structural color, not pigment. Their genus name was derived from a native West African name. Taxonomy The genus ''Tauraco'' was introduced in 1779 by the Polish naturalist Jan Krzysztof Kluk. The type species was later designated as the Guinea turaco The Guinea turaco (''Tauraco persa''), also known as the green turaco or green lourie, is a species of turaco, a group of otidimorphae birds belonging to the family Musophagidae. It was formerly included in the Livingstone's, Schalow's, Knysna, .... Species The genus contains 13 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch of the Paleogene Period and extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that define the epoch are well identified but the exact dates of the start and end of the epoch are slightly uncertain. The name Oligocene was coined in 1854 by the German paleontologist Heinrich Ernst Beyrich from his studies of marine beds in Belgium and Germany. The name comes from the Ancient Greek (''olígos'', "few") and (''kainós'', "new"), and refers to the sparsity of extant forms of molluscs. The Oligocene is preceded by the Eocene Epoch and is followed by the Miocene Epoch. The Oligocene is the third and final epoch of the Paleogene Period. The Oligocene is often considered an important time of transition, a link between the archaic world of the tropical Eocene and the more modern ecosystems of the Miocene. Major changes during the Oligocene included a global expansion o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitional Fossil
A transitional fossil is any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group. This is especially important where the descendant group is sharply differentiated by gross anatomy and mode of living from the ancestral group. These fossils serve as a reminder that taxonomic divisions are human constructs that have been imposed in hindsight on a continuum of variation. Because of the incompleteness of the fossil record, there is usually no way to know exactly how close a transitional fossil is to the point of divergence. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that transitional fossils are direct ancestors of more recent groups, though they are frequently used as models for such ancestors. In 1859, when Charles Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species'' was first published, the fossil record was poorly known. Darwin described the perceived lack of transitional fossils as "the most obvious and gravest objection which can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoatzin
The hoatzin ( ) or hoactzin ( ), (''Opisthocomus hoazin''), is the only species in the order Opisthocomiformes. It is a species of tropical bird found in swamps, riparian forests, and mangroves of the Amazon and the Orinoco basins in South America. It is notable for having chicks that have claws on two of their wing digits. It is the only member of the genus ''Opisthocomus'' (Ancient Greek: "long hair behind", referring to its large crest). This is the only extant genus in the family Opisthocomidae. The taxonomic position of this family has been greatly debated by specialists, and is still far from clear. Description The hoatzin is pheasant-sized, with a total length of , and a long neck and small head. It has an unfeathered blue face with maroon eyes, and its head is topped by a spiky, rufous crest. The long, sooty-brown tail is a broadly tipped buff. The upper parts are dark, sooty-brown-edged buff on the wing coverts, and streaked buff on the mantle and nape. The under pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biology Letters
''Biology Letters'' is a peer-reviewed, biological, scientific journal published by the Royal Society. It focuses on the rapid publication of short high quality research articles, reviews and opinion pieces across the biological sciences. ''Biology Letters'' has an average turnaround time of twenty four days from submission to a first decision. The editor-in-chief is Professor David Beerling FRS (University of Sheffield) who is supported by an international Editorial Board of practising scientists. Contents and themes As well as the conventional, short research articles, ''Biology Letters'' has recently published Special Features and Mini Series. While Special Features are a collection of up to 20 articles on a specific theme and published across multiple issues, Mini Series include up to six articles that are published in one issue. Examples of topics in these formats include ocean acidification, fossils, extinction, enhanced rock weathering and the evolutionary ecology of sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mousebird
The mousebirds are birds in the order Coliiformes. They are the sister group to the clade Eucavitaves, which includes the Leptosomiformes (the cuckoo roller), Trogoniformes (trogons), Bucerotiformes (hornbills and hoopoes), Piciformes (woodpeckers, toucans, and barbets) and Coraciformes (kingfishers, bee-eaters, rollers, motmots, and todies). This group is now confined to sub-Saharan Africa, and it is the only bird order confined entirely to that continent, with the possible exception of turacos which are considered by some as the distinct order Musophagiformes, and the cuckoo roller, which is the only member of the order Leptosomiformes, and which is found in Madagascar but not mainland Africa. Mousebirds had a wider range in the Paleogene, with a widespread distribution in Europe and North America during the Paleocene. Description Mousebirds are slender greyish or brown birds with soft, hairlike body feathers. They are typically about in body length, with a long, thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (biology)
Order ( la, wikt:ordo#Latin, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between Family_(biology), family and Class_(biology), class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |