|
Musaeus (officer Of Antiochus III)
Musaeus ( grc-gre, Μουσαῖος) was an officer of Antiochus III the Great, the ruler of the Seleucid Empire. Following his defeat in the Battle of Magnesia (190 BC) Antiochus III sent Musaeus to the triumphant Roman consuls (Scipio Asiaticus and Scipio Nasica), then stationed at Sardis to request their permission to start negotiating a peace treaty. According to Polybius Scipio Nasica received him courteously and granted him a safe passage back, with his consent to start negotiating a truce. Polybius later mentions Musaeus as an emissary sent by Antiochus III to Gnaeus Manlius Vulso (consul in 189 BC), to discuss a truce with the Romans. Both incidents are also related by Livy Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in ..., who only refers to Musaeus as "Antiochi legat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiochus III The Great
Antiochus III the Great (; grc-gre, Ἀντίoχoς Μέγας ; c. 2413 July 187 BC) was a Greek Hellenistic king and the 6th ruler of the Seleucid Empire, reigning from 222 to 187 BC. He ruled over the region of Syria and large parts of the rest of western Asia towards the end of the 3rd century BC. Rising to the throne at the age of eighteen in 222 BC, his early campaigns against the Ptolemaic Kingdom were unsuccessful, but in the following years Antiochus gained several military victories and substantially expanded the empire's territory. His traditional designation, ''the Great'', reflects an epithet he assumed. He also assumed the title ''Basileus Megas'' (Greek for "Great King"), the traditional title of the Persian kings. A militarily active ruler, Antiochus restored much of the territory of the Seleucid Empire, before suffering a serious setback, towards the end of his reign, in his war against Rome. Declaring himself the "champion of Greek freedom against Roman domina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
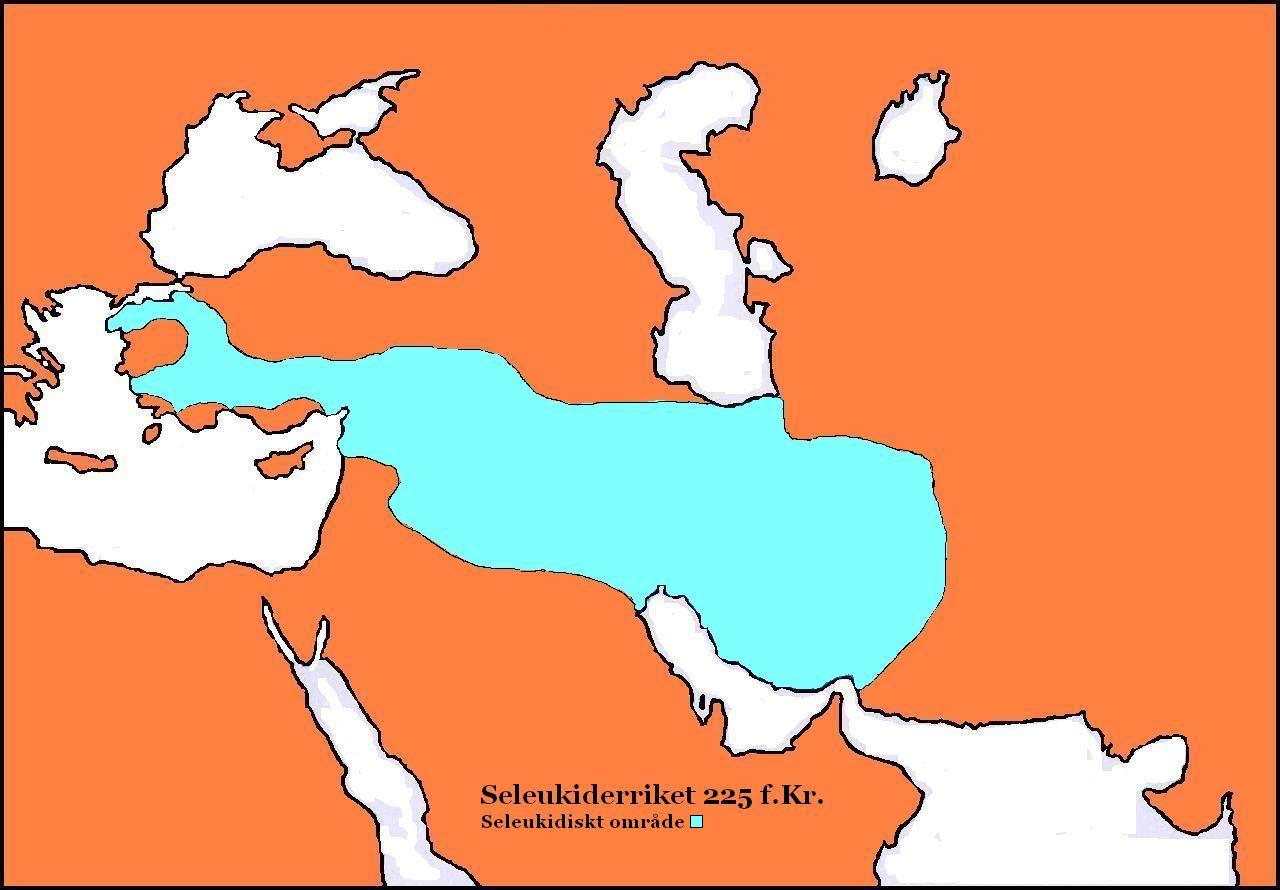
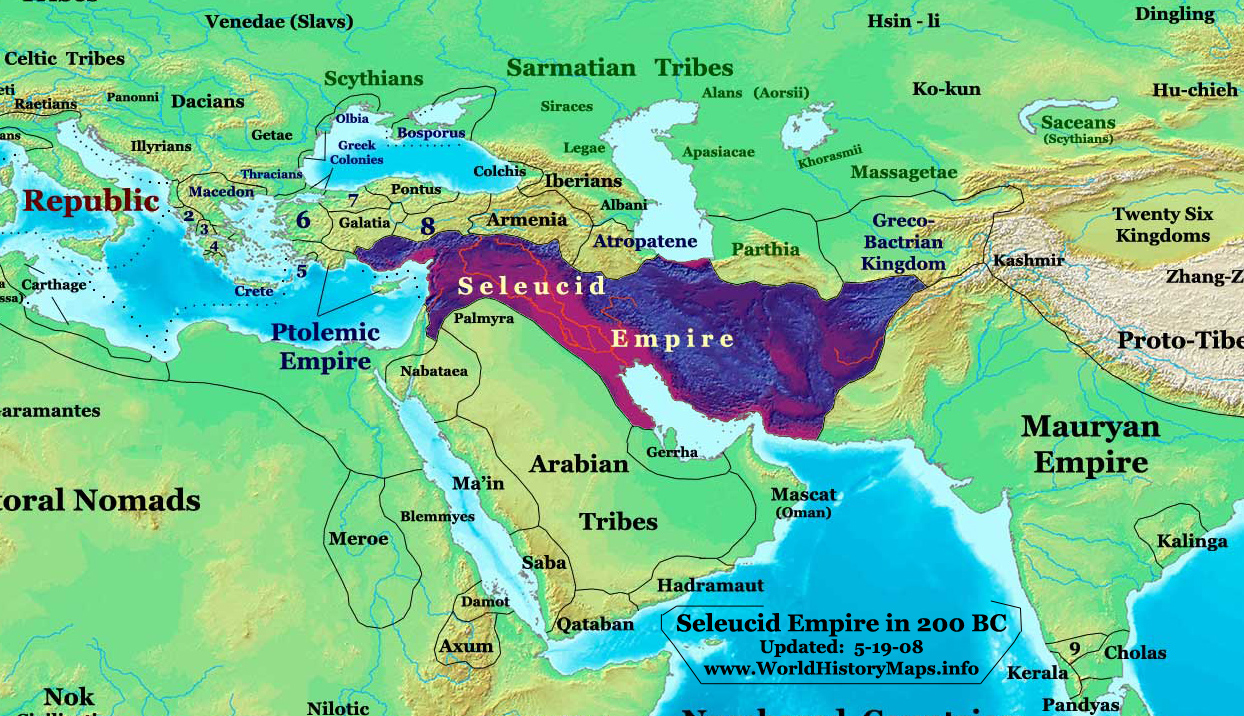
Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, Βασιλεία τῶν Σελευκιδῶν, ''Basileía tōn Seleukidōn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the Macedonian general Seleucus I Nicator, following the division of the Macedonian Empire originally founded by Alexander the Great. After receiving the Mesopotamian region of Babylonia in 321 BC, Seleucus I began expanding his dominions to include the Near Eastern territories that encompass modern-day Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, Syria, all of which had been under Macedonian control after the fall of the former Persian Achaemenid Empire. At the Seleucid Empire's height, it had consisted of territory that had covered Anatolia, Persia, the Levant, and what are now modern Iraq, Kuwait, Afghanistan, and parts of Turkmenistan. The Seleucid Empire was a major center of Hellenistic culture. Greek customs and language were privileged; the wide varie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Magnesia
The Battle of Magnesia took place in either December 190 or January 189 BC. It was fought as part of the Roman–Seleucid War, pitting forces of the Roman Republic led by the consul Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus and the allied Kingdom of Pergamon under Eumenes II against a Seleucid army of Antiochus III the Great. The two armies initially camped north-east of Magnesia ad Sipylum in Asia Minor (modern-day Manisa, Turkey), attempting to provoke each other into a battle on favorable terrain for several days. When the battle finally began, Eumenes managed to throw the Seleucid left flank into disarray. While Antiochus' cavalry overpowered his adversaries on the right flank of the battlefield, his army's center collapsed before he could reinforce it. Modern estimates give 10,000 dead for the Seleucids and 5,000 killed for the Romans. The battle resulted in a decisive Roman-Pergamene victory, which led to the Treaty of Apamea that ended Seleucid domination in Asia Minor. Backgrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scipio Asiaticus
Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus (properly Asiagenes; 3rd century BC – after 183 BC) was a general and statesman of the Roman Republic. He was the son of Publius Cornelius Scipio (consul 218 BC), Publius Cornelius Scipio and the younger brother of Scipio Africanus. He was elected Roman consul, consul in 190 BC, and later that year led (with his brother) the Roman forces to victory at the Battle of Magnesia. Although his career may be eclipsed by the shadow of his elder brother, Lucius' life is noteworthy in several respects. Family background Lucius belonged to the Patrician (ancient Rome), patrician ''gens'' Cornelia gens, Cornelia, one of the most important gentes of the Republic, which counted more consulships than any other. He was the son of Publius Cornelius Scipio (consul 218 BC), Publius, the consul of 218 who died against the Punics, Carthaginians at the Battle of the Upper Baetis in 211, and Pomponia, the daughter of Manius Pomponius Matho, consul in 233. Lucius als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Cornelius Scipio Nasica (consul 191 BC)
Publius Cornelius Scipio Nasica (born 227 BC; fl. 204171 BC) (Nasica meaning "pointed nose") was a consul of ancient Rome in 191 BC. He was a son of Gnaeus Cornelius Scipio Calvus. At the request of the Senate, he journeyed with the Roman matrons to receive the statue of Magna Mater in 204 when it arrived from Anatolia at Ostia. According to Livy and Ovid's ''Fasti'' we are told that he was chosen for this duty because he was the best of the Roman community. He was later aedile in 197. As praetor in Hispania Ulterior (194), he defeated the Lusitanians at Ilipa, and as consul subjugated the Boii. He was not chosen as censor despite standing in both the elections of 189 and 184, a failure marking the decline of the influence of the Scipiones in Rome. He went on to help found Aquileia in 181, and appears in an inquiry of 171. This Scipio Nasica was the father of the Scipio Nasica who opposed Cato the Censor for several years on the question of Carthage. Both father and son wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardis
Sardis () or Sardes (; Lydian: 𐤳𐤱𐤠𐤭𐤣 ''Sfard''; el, Σάρδεις ''Sardeis''; peo, Sparda; hbo, ספרד ''Sfarad'') was an ancient city at the location of modern ''Sart'' (Sartmahmut before 19 October 2005), near Salihli, in Turkey's Manisa Province. Sardis was the capital of the ancient kingdom of Lydia, an important city of the Persian Empire, the seat of a Seleucid satrap, the seat of a proconsul under the Roman Empire, and the metropolis of the province Lydia in later Roman and Byzantine times. It is mentioned in the New Testament. Its importance was due first to its military strength, secondly to it being situated on an important highway leading from the interior to the Aegean coast, and thirdly to its commanding the wide and fertile plain of the Hermus. Geography Sardis was situated in the middle of Hermus valley, at the foot of Mount Tmolus, a steep and lofty spur which formed the citadel. It was about south of that Hermus. Today, the site is loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnaeus Manlius Vulso (consul 189 BC)
Gnaeus Manlius Vulso (fl. 189 BC) was a Roman consul for the year 189 BC, together with Marcus Fulvius Nobilior. He led a victorious campaign against the Galatian Gauls of Asia Minor in 189 BC during the Galatian War. He was awarded a triumph in 187 BC.Livy, 39, 6-7. Fasti Triumphales. Vulso belonged to the patrician '' gens Manlia'', but his connection with the better known ''Torquatus'' branch is unknown. He may have been descended from Aulus (or Gaius) Manlius Cn.f. Vulso, consul in 474 BC; or from Lucius Manlius A.f. Vulso Longus, consul in 256 and 250 BC. A. Manlius Cn.f. Vulso, consul eleven years later in 178 BC, may have been his younger brother. See also * Manlia (gens) The gens Manlia () was one of the oldest and noblest patrician houses at Rome, from the earliest days of the Republic until imperial times. The first of the gens to obtain the consulship was Gnaeus Manlius Cincinnatus, consul in 480 BC, and fo ... Notes Ancient Roman generals 2nd-cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Ancient Rome, Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding in 753 BC through the reign of Augustus in Livy's own lifetime. He was on familiar terms with members of the Julio-Claudian dynasty and a friend of Augustus, whose young grandnephew, the future emperor Claudius, he exhorted to take up the writing of history. Life Livy was born in Patavium in northern Italy (Roman Empire), Italy, now modern Padua, probably in 59 BC. At the time of his birth, his home city of Patavium was the second wealthiest on the Italian peninsula, and the largest in the province of Cisalpine Gaul (northern Italy). Cisalpine Gaul was merged in Roman Italy, Italy proper during his lifetime and its inhabitants were given Roman citizenship by Julius Caesar. In his works, Livy often expressed his deep affection an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Roman Generals
Ancient history is a time period from the beginning of writing and recorded human history to as far as late antiquity. The span of recorded history is roughly 5,000 years, beginning with the Sumerian cuneiform script. Ancient history covers all continents inhabited by humans in the period 3000 BCAD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally considered to begin with the Bronze Age. The start and end of the three ages varies between world regions. In many regions the Bronze Age is generally considered to begin a few centuries prior to 3000 BC, while the end of the Iron Age varies from the early first millennium BC in some regions to the late first millennium AD in others. During the time period of ancient history, the world population was already exponentially increasing due to the Neolithic Revolution, which was in full progress. While in 10,000 BC, the world population stood a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |