|
Murimuria
In pre-Christian Fijian mythology, Murimuria is part of the underworld. According to Fijian religion, after a man dies, his soul is brought over a stretch of water by a ferryman, and has to face many dangers on the other side by going through the Path of the Souls (Sala Ni Yalo). For unmarried men, there seems to be no chance of surviving this path, because even if they escape the Great Woman, they would be killed by the monster Nangganangga, since no one ever got away from it, while married men could survive, if they withstand the Pandanus tree and the armed giant Killer of Souls. The survivors are judged by the god called Degei. Those who had the favor of Degei (chiefs with great wealth and many wives, who were destroyers of many towns, killers of many enemies and rulers over a powerful people) are instructed not to try to cross the lake. These go to Burotu. The rest inevitably try cross the lake by a boat that always capsizes. They eventually sink to the bottom, Murimuria, and are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Underworld
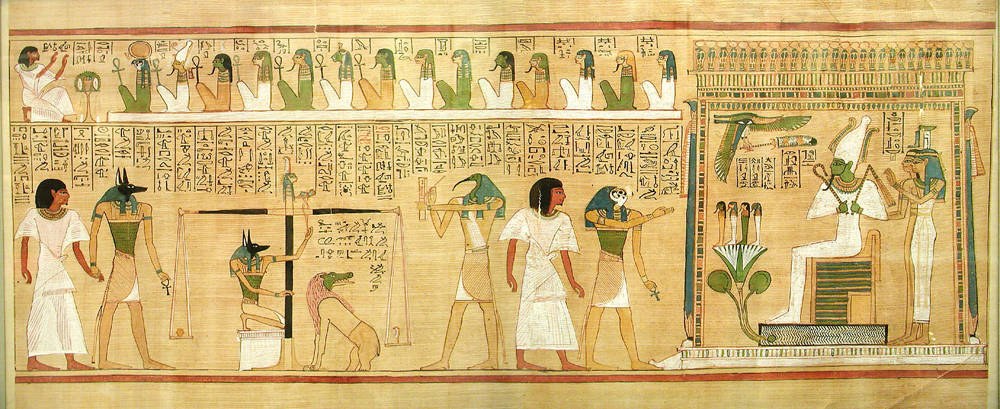
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underworld. The concept of an underworld is found in almost every civilization and "may be as old as humanity itself". Common features of underworld myths are accounts of living people making journeys to the underworld, often for some heroic purpose. Other myths reinforce traditions that entrance of souls to the underworld requires a proper observation of ceremony, such as the ancient Greek story of the recently dead Patroclus haunting Achilles until his body could be properly buried for this purpose. Persons having social status were dressed and equipped in order to better navigate the underworld. A number of mythologies incorporate the concept of the soul of the deceased making its own journey to the underworld, with the dead needing to be taken a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degei
In Fijian mythology, Degei (pronounced ''Ndengei''), enshrined as a serpent, is the supreme god of Fiji. He is the creator of the (Fijian) world, fruits, and of men and is specially connected to Rakiraki District, Fiji. He judges newly dead souls after they pass through one of two caves: Cibaciba or Drakulu. A few he sends to paradise Burotu. Most others are thrown into a lake, where they will eventually sink to the bottom (Murimuria) to be appropriately rewarded or punished. He is said to have at first moved about freely, but then in the form of a snake to have grown into the earth with his ringed tail. Since then he has become the god of earthquakes, storms and seasons. Whenever Degei shakes himself fertilising rain will fall, delicious fruits hang on the trees, and the yam fields yield an excellent crop. Degei is also a god of wrath who declares himself in terrible fashion. He punishes and chastens his people by destroying the crops or by floods; he could indeed easily wipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burotu
In the Melanesian mythology of Fiji, Burotu is the paradise-underworld. Newly dead souls are judged by Degei, and a few go to Burotu. The rest go to Murimuria.T. Williams, J. Calvert, ''Fiji and the Fijians'', Heylin, 1858. See also * Bulu, said to be the name for the Fijian 'land of death' *Pulotu, a similar concept in the Polynesian cultures of Tonga and Samoa Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands (Manono Island, Manono an ... References Fijian mythology Afterlife places Conceptions of heaven Underworld {{Fiji-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fijian Mythology
Fijian mythology refers to the set of beliefs practiced by the indigenous people of the island of Fiji. Its gods include Degei, a serpent who is the supreme god of Fiji. He is the creator of the (Fijian) world. He judges newly dead souls after they pass through one of two caves: Cibaciba or Drakulu. A few he sends to paradise Burotu. Most others are thrown into a lake, where they will eventually sink to the bottom (Murimuria In pre-Christian Fijian mythology, Murimuria is part of the underworld. According to Fijian religion, after a man dies, his soul is brought over a stretch of water by a ferryman, and has to face many dangers on the other side by going through the P ...) to be appropriately rewarded or punished.T. Williams, J. Calvert, ''Fiji and the Fijians'', Heylin, 1858. References {{Oceania-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Fiji
Religiously, Fiji is a mixed society with most people being Christian (64.4% of the population), with a sizable Hindu (27.9%) and Muslim (6.3%) minority, according to the 2007 census. Religion tends to split along ethnic lines with most Indigenous Fijians being Christian and most Indo-Fijians being either Hindu or Muslim. Aboriginal Fijian religion could be classified in modern terms as forms of animism or shamanism, traditions utilizing various systems of divination which strongly affected every aspect of life. Fiji was Christianization, Christianized in the 19th century. Today there are various Christian denominations in Fiji, the largest being the Methodist church. Hinduism and Islam arrived with the importation of large numbers of people from South Asia, most of them indentured, in the late 1800s and early 1900s. Fiji has many public holidays as it acknowledges the special days held by the various belief systems, such as Easter and Christmas for the Christians, Diwali f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Views On Sin
In Christianity, sin is an immoral act considered to be a transgression of divine law. The doctrine of sin is central to the Christian faith, since its basic message is about redemption in Christ. Hamartiology, a branch of Christian theology which is the study of sin, describes sin as an act of offence against God by despising his persons and Christian biblical law, and by injuring others. Christian hamartiology is closely related to concepts of natural law, moral theology and Christian ethics. According to Augustine of Hippo (354–430) sin is "a word, deed, or desire in opposition to the eternal law of God," or as scripture states, "sin is the transgression of the law." Among some scholars, sin is understood mostly as legal infraction or contract violation of non-binding philosophical frameworks and perspectives of Christian ethics, and so salvation tends to be viewed in legal terms. Other Christian scholars understand sin to be fundamentally relational—a loss of love ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapa Cloth
Tapa cloth (or simply ''tapa'') is a barkcloth made in the islands of the Pacific Ocean, primarily in Tonga, Samoa and Fiji, but as far afield as Niue, Cook Islands, Futuna, Solomon Islands, Java, New Zealand, Vanuatu, Papua New Guinea and Hawaii (where it is called ''kapa''). In French Polynesia it has nearly disappeared, except for some villages in the Marquesas. General The cloth is known by a number of local names although the term tapa is international and understood throughout the islands that use the cloth. The word tapa is from Tahiti and the Cook Islands, where Captain Cook was the first European to collect it and introduce it to the rest of the world. In Tonga, tapa is known as ngatu, and here it is of great social importance to the islanders, often being given as gifts. In Samoa, the same cloth is called siapo, and in Niue it is hiapo. In Hawaii, it is known as kapa. In Rotuma, a Polynesian island in the Fiji group, it is called ‘uha and in other Fiji island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taro
Taro () (''Colocasia esculenta)'' is a root vegetable. It is the most widely cultivated species of several plants in the family Araceae that are used as vegetables for their corms, leaves, and petioles. Taro corms are a food staple in African, Oceanic, and South Asian cultures (similar to yams). Taro is believed to be one of the earliest cultivated plants. Names and etymology The English term ''taro'' was borrowed from the Māori language when Captain Cook first observed ''Colocasia'' plantations there in 1769. The form ''taro'' or ''talo'' is widespread among Polynesian languages:*''talo'': taro (''Colocasia esculenta'') – entry in the ''Polynesian Lexicon Project Online'' (Pollex). in Tahitian; in < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterlife Places
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving essential aspect varies between belief systems; it may be some partial element, or the entire soul or spirit of an individual, which carries with it and may confer personal identity or, on the contrary, nirvana. Belief in an afterlife is in contrast to the belief in oblivion after death. In some views, this continued existence takes place in a spiritual realm, while in others, the individual may be reborn into this world and begin the life cycle over again, likely with no memory of what they have done in the past. In this latter view, such rebirths and deaths may take place over and over again continuously until the individual gains entry to a spiritual realm or otherworld. Major views on the afterlife derive from religion, esotericism an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_LACMA_M.2010.160.jpg)