|
Multimedia Web Ontology Language
Machine interpretation of documents and services in Semantic Web environment is primarily enabled by (a) the capability to mark documents, document segments and services with semantic tags and (b) the ability to establish contextual relations between the tags with a domain model, which is formally represented as ontology. Human beings use natural languages to communicate an abstract view of the world. Natural language constructs are symbolic representations of human experience and are close to the conceptual model that Semantic Web technologies deal with. Thus, natural language constructs have been naturally used to represent the ontology elements. This makes it convenient to apply Semantic Web technologies in the domain of textual information. In contrast, multimedia documents are perceptual recording of human experience. An attempt to use a conceptual model to interpret the perceptual records gets severely impaired by the semantic gap that exists between the perceptual media fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web Ontology Language
The Web Ontology Language (OWL) is a family of knowledge representation languages for authoring ontologies. Ontologies are a formal way to describe taxonomies and classification networks, essentially defining the structure of knowledge for various domains: the nouns representing classes of objects and the verbs representing relations between the objects. Ontologies resemble class hierarchies in object-oriented programming but there are several critical differences. Class hierarchies are meant to represent structures used in source code that evolve fairly slowly (perhaps with monthly revisions) whereas ontologies are meant to represent information on the Internet and are expected to be evolving almost constantly. Similarly, ontologies are typically far more flexible as they are meant to represent information on the Internet coming from all sorts of heterogeneous data sources. Class hierarchies on the other hand tend to be fairly static and rely on far less diverse and more structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontology For Media Resources
Ontology for Media Resources is a W3C recommendation from 2012 that aims to define "a core set of metadata properties for media resources, along with their mappings to elements from a set of existing metadata formats"{{Cite web, url=https://www.w3.org/TR/mediaont-10/, title = Ontology for Media Resources 1.0 In addition to defining vocabulary terms to annotate multimedia objects, the document also provides a mapping to common multimedia metadata formats, including ID3, XMP, IPTC, Dublin core, OGG, Exif, Media RSS, and others, as well as mapping to several container formats, including 3GP, MP4, WebM, and others. See also Ontology for Media Resources 1.0 * Multimedia Web Ontology Language Machine interpretation of documents and services in Semantic Web environment is primarily enabled by (a) the capability to mark documents, document segments and services with semantic tags and (b) the ability to establish contextual relations bet ... References Bibliography * Van Deu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Scale Concept Ontology For Multimedia
The Large-Scale Concept Ontology for Multimedia project was a series of workshops held from April 2004 to September 2006Naphade, ''et al.'', "Large Scale Concept Ontology for Multimedia: VACE Workshop Report," for the purpose of defining a standard formal vocabulary for the annotation and retrieval of video. Mandate The Large-Scale Concept Ontology for Multimedia project was sponsored by the Disruptive Technology Office and brought together representatives from a variety of research communities, such as multimedia learning, information retrieval, computational linguistics, library science, and knowledge representation, as well as "user" communities such as intelligence agencies and broadcasters, to work collaboratively towards defining a set of 1,000 concepts. Individually, each concept was to meet the following criteria: *Utility: the concepts must support realistic video retrieval problems *Feasibility: the concepts are capable or will be capable of detection given the near-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG-7
MPEG-7 is a multimedia content description standard. It was standardized in ISO/ IEC 15938 (Multimedia content description interface). This description will be associated with the content itself, to allow fast and efficient searching for material that is of interest to the user. MPEG-7 is formally called ''Multimedia Content Description Interface''. Thus, it is ''not'' a standard which deals with the actual encoding of moving pictures and audio, like MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and MPEG-4. It uses XML to store metadata, and can be attached to timecode in order to tag particular events, or synchronise lyrics to a song, for example. It was designed to standardize: * a set of Description Schemes ("DS") and Descriptors ("D") * a language to specify these schemes, called the Description Definition Language ("DDL") * a scheme for coding the description The combination of MPEG-4 and MPEG-7 has been sometimes referred to as MPEG-47. Introduction MPEG-7 is intended to provide complementary functi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Analysis (computational)
Semantic analysis (computational) within applied linguistics and computer science, is a composite of semantic analysis and computational components. ''Semantic analysis'' refers to a formal analysis of meaning, and ''computational'' refers to approaches that in principle support effective implementation in digital computers.Blackburn, P., and Bos, J. (2005), ''Representation and Inference for Natural Language: A First Course in Computational Semantics'', Stanford, CA: CSLI Publications Stanford University has many centers and institutes dedicated to the study of various specific topics. These centers and institutes may be within a department, within a school but across departments, an independent laboratory, institute or center .... . See also * Computational semantics * Natural language processing * Semantic analytics * Semantic analysis (machine learning) * Semantic Web * SemEval References Further reading * Chris Fox (2010), "Computational Semantics", In Alexander Clark, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DAML+OIL
The Web Ontology Language (OWL) is a family of knowledge representation languages for authoring ontologies. Ontologies are a formal way to describe taxonomies and classification networks, essentially defining the structure of knowledge for various domains: the nouns representing classes of objects and the verbs representing relations between the objects. Ontologies resemble class hierarchies in object-oriented programming but there are several critical differences. Class hierarchies are meant to represent structures used in source code that evolve fairly slowly (perhaps with monthly revisions) whereas ontologies are meant to represent information on the Internet and are expected to be evolving almost constantly. Similarly, ontologies are typically far more flexible as they are meant to represent information on the Internet coming from all sorts of heterogeneous data sources. Class hierarchies on the other hand tend to be fairly static and rely on far less diverse and more structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RDF Schema
RDF Schema (Resource Description Framework Schema, variously abbreviated as RDFS, , RDF-S, or RDF/S) is a set of classes with certain properties using the RDF extensible knowledge representation data model, providing basic elements for the description of ontologies. It uses various forms of RDF vocabularies, intended to structure RDF resources. RDF and RDFS can be saved in a triplestore, then one can extract some knowledge from them using a query language, like SPARQL. The first version was published by the World-Wide Web Consortium (W3C) in April 1998, and the final W3C recommendation was released in February 2014. Many RDFS components are included in the more expressive Web Ontology Language (OWL). Terminology RDFS constructs are the RDFS classes, associated properties and utility properties built on the vocabulary of RDF. Classes ; : Represents the class of everything. All things described by RDF are resources. ; : An ''rdfs:Class'' declares a resource as a class for ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Networks
A Bayesian network (also known as a Bayes network, Bayes net, belief network, or decision network) is a probabilistic graphical model that represents a set of variables and their conditional dependencies via a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Bayesian networks are ideal for taking an event that occurred and predicting the likelihood that any one of several possible known causes was the contributing factor. For example, a Bayesian network could represent the probabilistic relationships between diseases and symptoms. Given symptoms, the network can be used to compute the probabilities of the presence of various diseases. Efficient algorithms can perform inference and learning in Bayesian networks. Bayesian networks that model sequences of variables (''e.g.'' speech signals or protein sequences) are called dynamic Bayesian networks. Generalizations of Bayesian networks that can represent and solve decision problems under uncertainty are called influence diagrams. Graphical mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conceptual Model
A conceptual model is a representation of a system. It consists of concepts used to help people knowledge, know, understanding, understand, or simulation, simulate a subject the model represents. In contrast, physical models are physical object such as a toy model that may be assembled and made to work like the object it represents. The term may refer to models that are formed after a wikt:concept#Noun, conceptualization or generalization process. Conceptual models are often abstractions of things in the real world, whether physical or social. Semantics, Semantic studies are relevant to various stages of process of concept formation, concept formation. Semantics is basically about concepts, the meaning that thinking beings give to various elements of their experience. Overview Models of concepts and models that are conceptual The term ''conceptual model'' is normal. It could mean "a model of concept" or it could mean "a model that is conceptual." A distinction can be made bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abductive Reasoning
Abductive reasoning (also called abduction,For example: abductive inference, or retroduction) is a form of logical inference formulated and advanced by American philosopher Charles Sanders Peirce beginning in the last third of the 19th century. It starts with an observation or set of observations and then seeks the simplest and most likely conclusion from the observations. This process, unlike deductive reasoning, yields a plausible conclusion but does not positively verify it. Abductive conclusions are thus qualified as having a remnant of uncertainty or doubt, which is expressed in retreat terms such as "best available" or "most likely". One can understand abductive reasoning as inference to the best explanation, although not all usages of the terms ''abduction'' and ''inference to the best explanation'' are exactly equivalent. In the 1990s, as computing power grew, the fields of law, computer science, and artificial intelligence researchFor examples, seeAbductive Inference i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
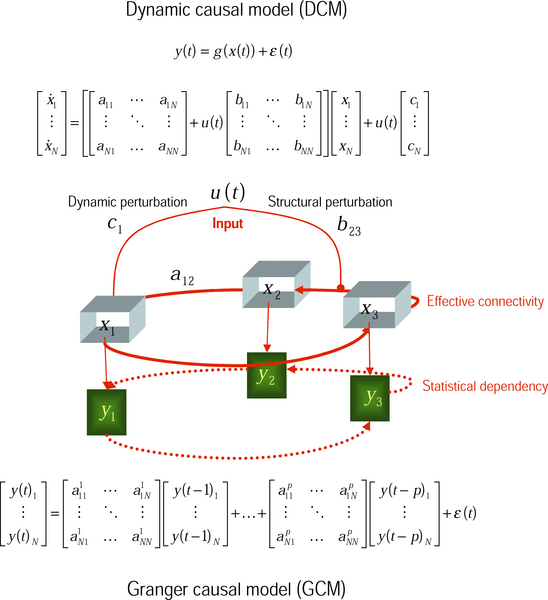
Causal Model
In the philosophy of science, a causal model (or structural causal model) is a conceptual model that describes the causal mechanisms of a system. Causal models can improve study designs by providing clear rules for deciding which independent variables need to be included/controlled for. They can allow some questions to be answered from existing observational data without the need for an interventional study such as a randomized controlled trial. Some interventional studies are inappropriate for ethical or practical reasons, meaning that without a causal model, some hypotheses cannot be tested. Causal models can help with the question of ''external validity'' (whether results from one study apply to unstudied populations). Causal models can allow data from multiple studies to be merged (in certain circumstances) to answer questions that cannot be answered by any individual data set. Causal models have found applications in signal processing, epidemiology and machine learning. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |