|
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy
Multifocal motor neuropathy (MMN) is a progressively worsening condition where muscles in the extremities gradually weaken. The disorder, a pure motor neuropathy syndrome, is sometimes mistaken for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) because of the similarity in the clinical picture, especially if muscle fasciculations are present. MMN is thought to be autoimmune. It was first described in the mid-1980s. Unlike ALS, which affects both upper and lower motor neuron pathways, MMN involves only the lower motor neuron pathway, specifically, the peripheral nerves emanating from the lower motor neurons. Definitive diagnosis is often difficult, and many MMN patients labor for months or years under an ALS diagnosis before finally getting a determination of MMN. MMN usually involves very little pain; however, muscle cramps, spasms and twitches can cause pain for some people. MMN is not fatal, and does not diminish life expectancy. Many patients, once undergoing treatment, only experience m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurology
Neurology (from el, wikt:νεῦρον, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix wikt:-logia, -logia, "study of") is the branch of specialty (medicine), medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal cord and the peripheral nerves. Neurological practice relies heavily on the field of neuroscience, the scientific study of the nervous system. A neurologist is a physician specializing in neurology and trained to investigate, diagnose and treat neurological disorders. Neurologists treat a myriad of neurologic conditions, including stroke, seizures, movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, autoimmune neurologic disorders such as multiple sclerosis, headache disorders like migraine and dementias such as Alzheimer's disease. Neurologists may also be involved in clinical research, clinical trials, and basic research, basic or translational research. While neurology is a nonsurgical sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromyography
Electromyography (EMG) is a technique for evaluating and recording the electrical activity produced by skeletal muscles. EMG is performed using an instrument called an electromyograph to produce a record called an electromyogram. An electromyograph detects the electric potential generated by muscle cells when these cells are electrically or neurologically activated. The signals can be analyzed to detect abnormalities, activation level, or recruitment order, or to analyze the biomechanics of human or animal movement. Needle EMG is an electrodiagnostic medicine technique commonly used by neurologists. Surface EMG is a non-medical procedure used to assess muscle activation by several professionals, including physiotherapists, kinesiologists and biomedical engineers. In Computer Science, EMG is also used as middleware in gesture recognition towards allowing the input of physical action to a computer as a form of human-computer interaction. Clinical uses EMG testing has a variety of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium due to cancer and adrenal insufficiency along with other steroids. It is taken Oral administration, by mouth. Common side effects with long-term use include cataracts, Osteoporosis, bone loss, easy bruising, muscle weakness, and oral candidiasis, thrush. Other side effects include weight gain, swelling, high blood sugar, increased risk of infection, and psychosis. It is generally considered safe in pregnancy and low doses appear to be safe when breastfeeding. After prolonged use, prednisone needs to be stopped gradually. Prednisone is a prodrug and must be converted to prednisolone by the liver before it becomes active. Prednisolone then binds to glucocorticoid receptors, activating them and triggering changes in gene expression. Pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroid
A steroid is a biologically active organic compound with four rings arranged in a specific molecular configuration. Steroids have two principal biological functions: as important components of cell membranes that alter membrane fluidity; and as signaling molecules. Hundreds of steroids are found in plants, animals and fungi. All steroids are manufactured in cells from the sterols lanosterol (opisthokonts) or cycloartenol (plants). Lanosterol and cycloartenol are derived from the cyclization of the triterpene squalene. The steroid core structure is typically composed of seventeen carbon atoms, bonded in four " fused" rings: three six-member cyclohexane rings (rings A, B and C in the first illustration) and one five-member cyclopentane ring (the D ring). Steroids vary by the functional groups attached to this four-ring core and by the oxidation state of the rings. Sterols are forms of steroids with a hydroxy group at position three and a skeleton derived from cholestane. ''A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rituximab
Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer. It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (in non-geriatric patients), rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, pemphigus vulgaris, myasthenia gravis and Epstein–Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcers. It is given by slow injection into a vein. Biosimilars of Rituxan include Blitzima, Riabni, Ritemvia, Rituenza (F.K.A. Tuxella), Rixathon, Ruxience, and Truxima. Common side effects which often occur within two hours of the medication being given include rash, itchiness, low blood pressure, and shortness of breath. Infections are also common. Severe side effects include reactivation of hepatitis B in those previously infected, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and death. It is unclear if use during pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
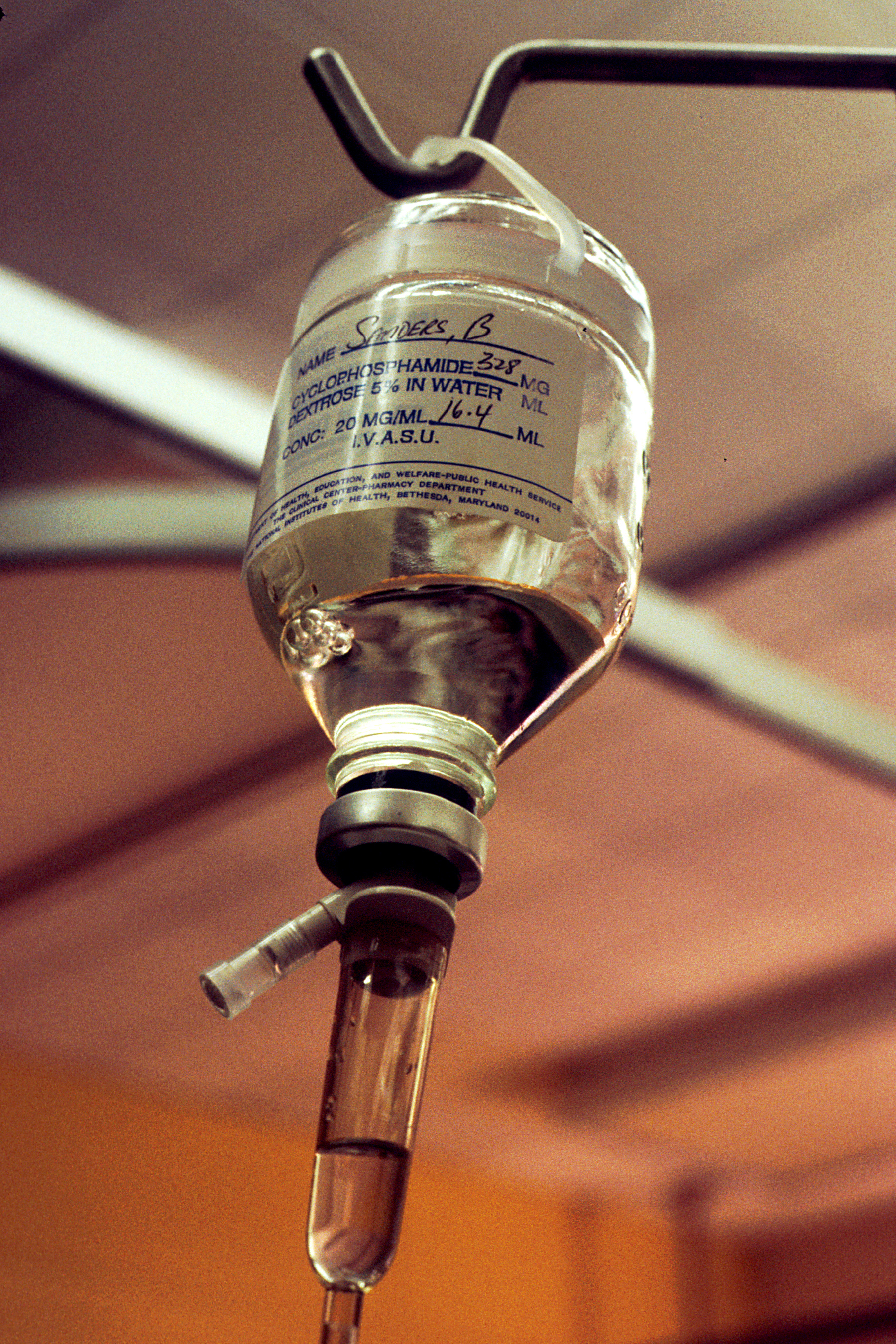
Cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer, small cell lung cancer, neuroblastoma, and sarcoma. As an immune suppressor it is used in nephrotic syndrome, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, and following organ transplant, among other conditions. It is taken by mouth or injection into a vein. Most people develop side effects. Common side effects include low white blood cell counts, loss of appetite, vomiting, hair loss, and bleeding from the bladder. Other severe side effects include an increased future risk of cancer, infertility, allergic reactions, and pulmonary fibrosis. Cyclophosphamide is in the alkylating agent and nitrogen mustard family of medications. It is believed to work by interfering with the duplication of DNA and the creation of RNA. Cyclophosphamide was appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunosuppressive Therapy
Immunosuppression is a reduction of the activation or efficacy of the immune system. Some portions of the immune system itself have immunosuppressive effects on other parts of the immune system, and immunosuppression may occur as an adverse reaction to treatment of other conditions. In general, deliberately induced immunosuppression is performed to prevent the body from rejecting an organ transplant. Additionally, it is used for treating graft-versus-host disease after a bone marrow transplant, or for the treatment of auto-immune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren's syndrome, or Crohn's disease. This is typically done using medications, but may involve surgery (splenectomy), plasmapheresis, or radiation. A person who is undergoing immunosuppression, or whose immune system is weak for some other reasons (such as chemotherapy or HIV), is said to be ''immunocompromised''. Deliberately induced Administration of immunosuppressive medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Immunoglobulin
Immunoglobulin therapy is the use of a mixture of antibodies (normal human immunoglobulin or NHIG) to treat several health conditions. These conditions include primary immunodeficiency, immune thrombocytopenic purpura, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, Kawasaki disease, certain cases of HIV/AIDS and measles, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and certain other infections when a more specific immunoglobulin is not available. Depending on the formulation it can be given by injection into muscle, a vein, or under the skin. The effects last a few weeks. Common side effects include pain at the site of injection, muscle pain, and allergic reactions. Other severe side effects include kidney problems, anaphylaxis, blood clots, and red blood cell breakdown. Use is not recommended in people with some types of IgA deficiency. Use appears to be relatively safe during pregnancy. Human immunoglobulin is made from human blood plasma. It contains antibodies against many viruses. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Fluid
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is a clear, colorless Extracellular fluid#Transcellular fluid, body fluid found within the meninges, tissue that surrounds the brain and spinal cord of all vertebrates. CSF is produced by specialised Ependyma, ependymal cells in the choroid plexus of the ventricular system, ventricles of the brain, and absorbed in the arachnoid granulations. There is about 125 mL of CSF at any one time, and about 500 mL is generated every day. CSF acts as a shock absorber, cushion or buffer, providing basic mechanical and immune system, immunological protection to the brain inside the Human skull, skull. CSF also serves a vital function in the cerebral autoregulation of cerebral blood flow. CSF occupies the subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid mater and the pia mater) and the ventricular system around and inside the brain and spinal cord. It fills the ventricular system, ventricles of the brain, subarachnoid cisterns, cisterns, and Sulcus (neuroanatomy), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Conduction Study
A nerve conduction study (NCS) is a medical diagnostic test commonly used to evaluate the function, especially the ability of electrical conduction, of the motor and sensory nerves of the human body. These tests may be performed by medical specialists such as clinical neurophysiologists, physical therapists, chiropractors, physiatrists (physical medicine and rehabilitation physicians), and neurologists who subspecialize in electrodiagnostic medicine. In the United States, neurologists and physiatrists receive training in electrodiagnostic medicine (performing needle electromyography (EMG) and NCSs) as part of residency training and in some cases acquire additional expertise during a fellowship in clinical neurophysiology, electrodiagnostic medicine, or neuromuscular medicine. Outside the US, clinical neurophysiologists learn needle EMG and NCS testing. Nerve conduction velocity (NCV) is a common measurement made during this test. The term NCV often is used to mean the actual tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or organ function depending on which nerves are affected; in other words, neuropathy affecting motor, sensory, or autonomic nerves result in different symptoms. More than one type of nerve may be affected simultaneously. Peripheral neuropathy may be acute (with sudden onset, rapid progress) or chronic (symptoms begin subtly and progress slowly), and may be reversible or permanent. Common causes include systemic diseases (such as diabetes or leprosy), hyperglycemia-induced glycation, vitamin deficiency, medication (e.g., chemotherapy, or commonly prescribed antibiotics including metronidazole and the fluoroquinolone class of antibiotics (such as ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin)), traumatic injury, ischemia, radiation therapy, excessiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasculitis
Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Both arteries and veins are affected. Lymphangitis (inflammation of lymphatic vessels) is sometimes considered a type of vasculitis. Vasculitis is primarily caused by leukocyte migration and resultant damage. Although both occur in vasculitis, inflammation of veins (phlebitis) or arteries (arteritis) on their own are separate entities. Signs and symptoms Possible signs and symptoms include: * General symptoms: Fever, unintentional weight loss * Skin: Palpable purpura, livedo reticularis * Muscles and joints: Muscle pain or inflammation, joint pain or joint swelling * Nervous system: Mononeuritis multiplex, headache, stroke, tinnitus, reduced visual acuity, acute visual loss * Heart and arteries: Heart attack, high blood pressure, gangrene * Respiratory tract: Nosebleeds, bloody cough, lung infiltrates * GI tract: Abdominal pain, bloody stool, perforations (hole in the GI tract) * Kidneys: Inflamma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |