|
Multidimensional Discrete Convolution
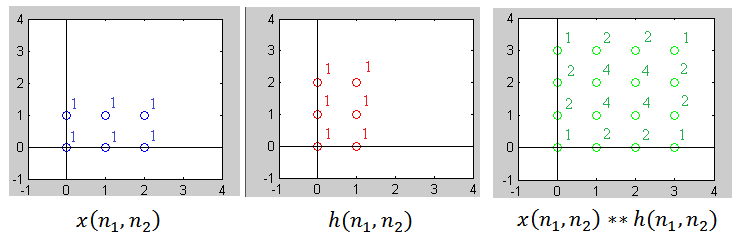
In signal processing, multidimensional discrete convolution refers to the mathematical operation between two functions ''f'' and ''g'' on an ''n''-dimensional lattice that produces a third function, also of ''n''-dimensions. Multidimensional discrete convolution is the discrete analog of the multidimensional convolution of functions on Euclidean space. It is also a special case of convolution on groups when the group is the group of ''n''-tuples of integers. Definition Problem statement and basics Similar to the one-dimensional case, an asterisk is used to represent the convolution operation. The number of dimensions in the given operation is reflected in the number of asterisks. For example, an ''M''-dimensional convolution would be written with ''M'' asterisks. The following represents a ''M''-dimensional convolution of discrete signals: y(n_1,n_2,...,n_M)=x(n_1,n_2,...,n_M)* \overset *h(n_1,n_2,...,n_M) For discrete-valued signals, this convolution can be directly computed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term ''convolution'' refers to both the result function and to the process of computing it. It is defined as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result (see #Properties, commutativity). The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function. Some features of convolution are similar to cross-correlation: for real-valued functions, of a continuous or discrete variable, convolution (f*g) differs from cross-correlation (f \star g) only in that either or is reflected about the y-axis in convolution; thus it is a cross-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiki Circular Conv
A wiki ( ) is an online hypertext publication collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience, using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other software, such as bug tracking systems. Some wiki engines are open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |