|
Mount Wurlali
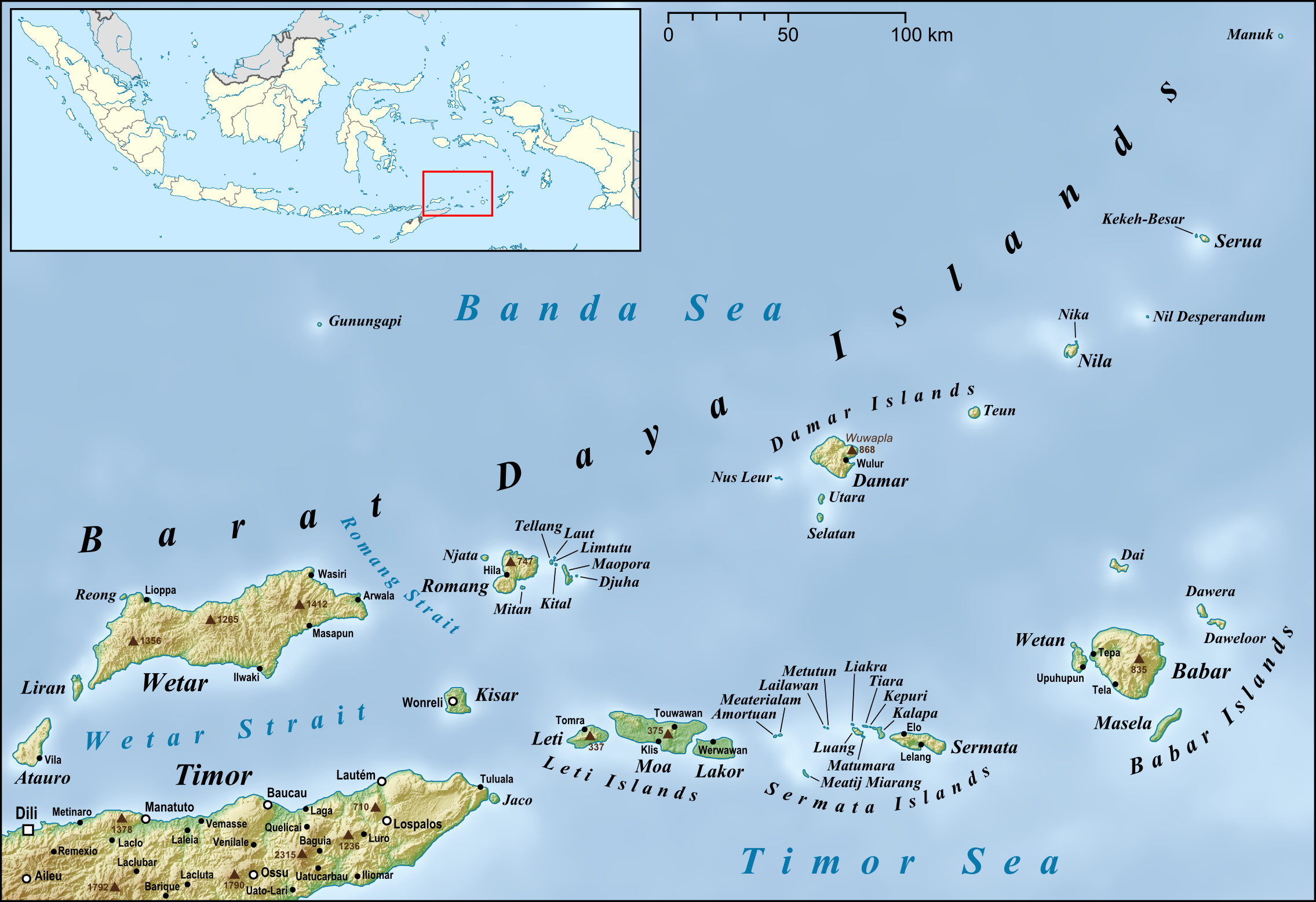
Mount Wurlali (also known as Mount Damar) is an andesitic stratovolcano on Damar Island in the Banda Arc system. Fumarolic activities with sulfur deposits are found at the twin summit craters and on the southeast flanks. The Wurlali is the most active volcano in historical time of the Banda arc. He was at the northern end of a five- kilometer-wide caldera. On the southwest flank of the crater occurs from sulfur. The last eruption took place in 1892. In 1993 there was an earthquake, landslides, and smoke. Four-thousand people were evacuated. On January 23, 2003, there was an earthquake with a magnitude of 6.1. Close to the beach, south-west of the volcano, hot springs emerged. See also * List of volcanoes in Indonesia The geography of Indonesia is dominated by volcanoes that are formed due to subduction zones between the Eurasian plate and the Indo-Australian plate. Some of the volcanoes are notable for their eruptions, for instance, Krakatoa for its globa ... Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damar Island
Damer, or Damar, ( id, Pulau Damer) is a small volcanic island in the Barat Daya Islands group in Indonesia's Maluku province, on the southern side of the Banda Sea. It is flanked by four smaller islands - one to the east, one to the west and two to the south. Together they are called the Damar Islands, and constitute one administrative district within the Maluku Barat Daya Regency. The district has a land area of 392.29 km2 and had a population of 5,718 at the 2020 Census. Description Damar is about 20 km (12 mi.) long by 18 km (11 mi.) wide. It lies about 125 km (78 mi.) east of Romang and 200 km (124 mi.) east of Wetar. The northern part of the island has been largely cleared for dryland farming of coconuts, cashews, coffee beans, cocoa beans, cloves and nutmegs, while the southern part is still mainly forested. Habitation is concentrated in the north and east; most islanders are farmers or fishers. The highest point of the island is 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia is a presidential republic with an elected legislature. It has 38 provinces, of which nine have special status. The country's capital, Jakarta, is the world's second-most populous urban area. Indonesia shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and the eastern part of Malaysia, as well as maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, and India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and periodic intervals of explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions, although some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and hardens before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high-to-intermediate levels of silica (as in rhyolite, dacite, or andesite), with lesser amounts of less-viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but have travelled as far as . Stratovolcanoes are sometimes called composite volcanoes because of their composite stratified structure, built up from sequential outpourings of erupted materials. They are among the most common types of volcanoes, in contrast to the less common shield volca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andesitic
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende. Andesite is the extrusive equivalent of plutonic diorite. Characteristic of subduction zones, andesite represents the dominant rock type in island arcs. The average composition of the continental crust is andesitic. Along with basalts, andesites are a component of the Martian crust. The name ''andesite'' is derived from the Andes mountain range, where this rock type is found in abundance. It was first applied by Christian Leopold von Buch in 1826. Description Andesite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) igneous rock that is intermediate in its content of silica and low in alkali metals. It has less than 20% quartz and 10% feldspathoid by volume, with at least 65% of the feldsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and periodic intervals of explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions, although some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and hardens before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high-to-intermediate levels of silica (as in rhyolite, dacite, or andesite), with lesser amounts of less-viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but have travelled as far as . Stratovolcanoes are sometimes called composite volcanoes because of their composite stratified structure, built up from sequential outpourings of erupted materials. They are among the most common types of volcanoes, in contrast to the less common shield volca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banda Arc
The Banda Arc (main arc, Inner, and Outer) is a set of island arcs in eastern Indonesia. It is the result of the collision of a continent and an intra-oceanic island arc. The presently active arc is located on what appears to be oceanic crust whereas the associated subduction trench is underlain by continental crust. The convergence of the Indo-Australian plates and Eurasia resulted in the formation of the Sunda and Banda island arcs. The transitional zone between the arcs is located south of Flores Island and is characterized by the change in the tectonic regime along the boundary. Terminology Some academic literature refers to the arcs by location – so that main arc can be referred to as the 'southern', the 'western' Situated at the centre of three converging and colliding major tectonic plates, Indo-Australia, Eurasia, Pacific, the Banda arc includes young oceanic crust enclosed by a volcanic inner arc, outer arc islands and a trough parallel to the Australian contine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumarole
A fumarole (or fumerole) is a vent in the surface of the Earth or other rocky planet from which hot volcanic gases and vapors are emitted, without any accompanying liquids or solids. Fumaroles are characteristic of the late stages of volcanic activity, but fumarole activity can also precede a volcanic eruption and has been used for eruption prediction. Most fumaroles die down within a few days or weeks of the end of an eruption, but a few are persistent, lasting for decades or longer. An area containing fumaroles is known as a fumarole field. The predominant vapor emitted by fumaroles is steam, formed by the circulation of groundwater through heated rock. This is typically accompanied by volcanic gases given off by magma cooling deep below the surface. These volcanic gases include sulfur compounds, such as various sulfur oxides and hydrogen sulfide, and sometimes hydrogen chloride, hydrogen fluoride, and other gases. A fumarole that emits significant sulfur compounds is some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow, crystalline solid at room temperature. Sulfur is the tenth most abundant element by mass in the universe and the fifth most on Earth. Though sometimes found in pure, native form, sulfur on Earth usually occurs as sulfide and sulfate minerals. Being abundant in native form, sulfur was known in ancient times, being mentioned for its uses in ancient India, ancient Greece, China, and ancient Egypt. Historically and in literature sulfur is also called brimstone, which means "burning stone". Today, almost all elemental sulfur is produced as a byproduct of removing sulfur-containing contaminants from natural gas and petroleum.. Downloahere The greatest commercial use of the element is the production o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin Summit
A double summit, double peak, twin summit, or twin peak refers to a mountain or hill that has two summits, separated by a col or saddle. One well-known double summit is Austria’s highest mountain, the Großglockner, where the main summit of the Großglockner is separated from that of the Kleinglockner by the Glocknerscharte col in the area of a geological fault. Other double summits have resulted from geological folding. For example, on Mont Withrow in British Columbia, resistant sandstones form the limbs of the double summit, whilst the softer rock in the core of the fold was eroded.{{cite web , url=http://gsc.nrcan.gc.ca/natmap/cf/intro_e.php , title=Mt. Withrow syncline , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20060404185911/http://gsc.nrcan.gc.ca/natmap/cf/intro_e.php , archive-date=2006-04-04 , access-date=2009-05-12 Triple peaks occur more rarely; one example is the Rosengartenspitze in the Dolomites. The Illimani in Bolivia is an example of a rare quadruple summit. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Crater
A volcanic crater is an approximately circular depression in the ground caused by Volcano, volcanic activity. It is typically a bowl-shaped feature containing one or more vents. During Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions, molten magma and volcanic gases rise from an underground magma chamber, through a conduit, until they reach the crater's vent, from where the gases escape into the atmosphere and the magma is erupted as lava. A volcanic crater can be of large dimensions, and sometimes of great depth. During certain types of explosive eruptions, a volcano's magma chamber may empty enough for an area above it to subside, forming a type of larger depression known as a caldera. Geomorphology In most volcanoes, the crater is situated at the top of a mountain formed from the erupted volcanic deposits such as lava flows and tephra. Volcanoes that terminate in such a summit crater are usually of a conical form. Other volcanic craters may be found on the flanks of volcanoe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Indonesia
The geography of Indonesia is dominated by volcanoes that are formed due to subduction zones between the Eurasian plate and the Indo-Australian plate. Some of the volcanoes are notable for their eruptions, for instance, Krakatoa for its global effects in 1883, the Lake Toba Caldera for its supervolcanic eruption estimated to have occurred 74,000 years before present which was responsible for six years of volcanic winter, and Mount Tambora for the most violent eruption in recorded history in 1815. Volcanoes in Indonesia are part of the Pacific Ring of Fire. The 150 entries in the list below are grouped into six geographical regions, four of which belong to the volcanoes of the Sunda Arc trench system. The remaining two groups are volcanoes of Halmahera, including its surrounding volcanic islands, and volcanoes of Sulawesi and the Sangihe Islands. The latter group is in one volcanic arc together with the Philippine volcanoes. The most active volcano is Mount Merapi on Java. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes Of The Lesser Sunda Islands
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)



