|
Mount Peale
Mount Peale is the highest point in the La Sal Mountains of San Juan County, in the southeastern part of Utah, United States. It is also the highest point in Utah outside the Uinta Mountains. It is located about southeast of Moab. The summit is the highest point in the Manti-La Sal National Forest and the Mount Peale Research Natural Area. Mount Peale was named for Albert Peale, a mineralogist on the Hayden Survey of 1875. The La Sal Mountains sit on the arid Colorado Plateau, near such famous desert landmarks as Canyonlands National Park and Arches National Park. However, due to their height, the La Sals are heavily forested and usually snow-capped until early summer (there is one snowfield on the north side that usually lasts year round).Michael R. Kelsey, ''Guide to the World's Mountains'' (third edition), Kelsey Publishing, 1996, , pp. 682–683. Mount Peale can be seen on a clear day from the Wasatch Plateau of central Utah, near Orangeville, over away. Mount Peale ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Mellenthin
Mount Mellenthin is a 12,645-foot (3,854 meter) elevation summit located in San Juan County of Utah, United States. Mount Mellenthin is the second-highest peak of the La Sal Mountains. It is situated in a dry, rugged, sparsely settled region, and set on land administered by Manti-La Sal National Forest. Precipitation runoff from this mountain drains into tributaries of the Colorado River. The nearest town is Moab, to the northwest, and the nearest higher neighbor is Mount Peale, to the south. The mountain's name honors Rudolf E. Mellenthin (1884–1918), forest ranger of La Sal National Forest, who was shot to death near this peak on August 23, 1918, while attempting to apprehend two draft evaders. This geographical feature's name was officially adopted in 1932 by the U.S. Board on Geographic Names. Climate Spring and fall are the most favorable seasons to visit Mount Mellenthin. According to the Köppen climate classification system, it is located in a Cold semi-arid climat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Natural Area
Research Natural Area is a designation for certain protected areas in the United States. Research Natural Areas (RNAs) are part of a nationwide network of ecological areas set aside for both research and education. The network includes areas managed by many Federal agencies. The United States Forest Service and other agencies establish these areas to typify certain types of important forest, shrubland, grassland, aquatic, geological, alpine, or similar environments that have unique characteristics of scientific interest. The areas "contain important ecological and scientific values and are managed for minimum human disturbance". The first RNA was established on the Coronado National Forest in Arizona in 1927. The Bureau of Land Management is another agency that designates and manages Research Natural Areas. According to the Bureau of Land Management, the objectives of the RNA program are "(1) To preserve examples of all significant natural ecosystems for comparison with those inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Utah
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ultras Of The United States
The following sortable table comprises the 200 most topographically prominent mountain peaks of the United States of America. The summit of a mountain or hill may be measured in three principal ways: #The topographic elevation of a summit measures the height of the summit above a geodetic sea level.All elevations in the 48 states of the contiguous United States include an elevation adjustment from the National Geodetic Vertical Datum of 1929 (NGVD 29) to the North American Vertical Datum of 1988 (NAVD 88). For further information, please see this United States National Geodetic Surveybr>noteIf the elevation or prominence of a summit is calculated as a range of values, the arithmetic mean is shown. #The topographic prominence of a summit is a measure of how high the summit rises above its surroundings.The topographic prominence of a summit is the topographic elevation difference between the summit and its highest or key col to a higher summit. The summit may be near its ke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orangeville, Utah
Orangeville is a city in northwestern Emery County, Utah, United States, at the edge of the Manti-La Sal National Forest. The city is at the junction of State Routes 29 and 57, straddling the banks of Cottonwood Creek. The population was 1,470 at the 2010 census. Geography Orangeville is west of Castle Dale, the Emery County seat. According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of , all land. Demographics As of the census of 2000, there were 1,398 people, 430 households, and 350 families residing in the city. The population density was 1,073.5 people per square mile (415.2/km2). There were 471 housing units at an average density of 361.7 per square mile (139.9/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 98.43% White, 0.07% African American, 0.43% Native American, 0.14% Asian, 0.50% from other races, and 0.43% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.22% of the population. There were 430 households, out of which 51.4% had children u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wasatch Plateau
The Wasatch Plateau is a plateau located southeast of the southernmost part of the Wasatch Range in central Utah. It is a part of the Colorado Plateau. Geography The plateau has an elevation of and includes an area of . Its highest point in the South Tent Mountain, with an elevation of . The plateau is roughly bordered by the Spanish Fork Canyon on the north, the Price Canyon on the northeast, the Castle Valley on the east and southeast, Interstate 70 on the south, the Plateau Valley and the Sevier Plateau on the southwest, and the Sanpete Valley on the northwest. The majority of the plateau is within the boundaries of the Manti–La Sal National Forest and is managed by the United States Forest Service The United States Forest Service (USFS) is an agency of the U.S. Department of Agriculture that administers the nation's 154 national forests and 20 national grasslands. The Forest Service manages of land. Major divisions of the agency inc .... See also References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arches National Park
Arches National Park is a national park in eastern Utah, United States. The park is adjacent to the Colorado River, north of Moab, Utah. More than 2,000 natural sandstone arches are located in the park, including the well-known Delicate Arch, as well as a variety of unique geological resources and formations. The park contains the highest density of natural arches in the world. The park consists of of high desert located on the Colorado Plateau. The highest elevation in the park is at Elephant Butte, and the lowest elevation is at the visitor center. The park receives an average of less than of rain annually. Administered by the National Park Service, the area was originally named a national monument on April 12, 1929, and was redesignated as a national park on November 12, 1971. The park received more than 1.6 million visitors in 2018. Park purpose As stated in the foundation document in U.S. National Park Service website: Geology The national park lies above an unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canyonlands National Park
Canyonlands National Park is an American national park located in southeastern Utah near the town of Moab. The park preserves a colorful landscape eroded into numerous canyons, mesas, and buttes by the Colorado River, the Green River, and their respective tributaries. Legislation creating the park was signed into law by President Lyndon Johnson on September 12, 1964. The park is divided into four districts: the Island in the Sky, the Needles, the Maze, and the combined rivers—the Green and Colorado—which carved two large canyons into the Colorado Plateau. While these areas share a primitive desert atmosphere, each retains its own character. Author Edward Abbey, a frequent visitor, described the Canyonlands as "the most weird, wonderful, magical place on earth—there is nothing else like it anywhere." History In the early 1950s, Bates Wilson, then superintendent of Arches National Monument, began exploring the area to the south and west of Moab, Utah. After seeing what is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
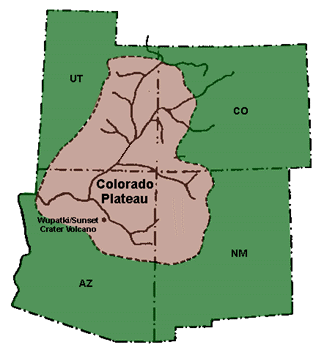
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hayden Survey
Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden (September 7, 1829 – December 22, 1887) was an American geologist noted for his pioneering surveying expeditions of the Rocky Mountains in the late 19th century. He was also a physician who served with the Union Army during the Civil War. Early life Ferdinand Hayden was born in Westfield, Massachusetts. As a young boy he was fascinated with all nature and wildlife, which led him into the field of medicine. He worked in Cleveland under Jared Potter Kirtland and thereafter in Albany, NY, where he worked under James Hall, of the ''Geological Survey of New York''. He graduated from Oberlin College in 1850 and from the Albany Medical College in 1853, where he attracted the notice of Professor James Hall, state geologist of New York, through whose influence he was induced to join in an exploration of Nebraska Territory, with Fielding B. Meek to study geology and collect fossils. Hall sent him on his first geological venture in the summer of 1853. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Charles Peale
Albert Charles Peale (1 April 1849 – 5 December 1914) was an American geologist, mineralogist and paleobotanist. Biography Born in Heckscherville, Pennsylvania, Albert C. Peale was the son of Charles Willson Peale (1821-1871) and Harriet Friel. Albert Peale's paternal grandfather was Rubens Peale and his paternal great-grandfather was the painter Charles Willson Peale. Albert Peale graduated from the Central High School, Philadelphia with A.B. in 1868 and A.M in 1873. He studied during 1870 at the auxiliary medical department of the University of Pennsylvania and graduated there with M.D. in 1871. Although he had a medical degree, he never practiced medicine. From 1871 to 1879, Peale served as a mineralogist and geologist for the United States Geological and Geographic Survey of the Territories. As such, he traveled on several of the Ferdinand Hayden expeditions that explored and mapped the western United States. In 1875, he married Emilie Wiswell, the daughter of the Rev. G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |