|
Mount Otgontenger
Otgontenger ( mn, Отгонтэнгэр, , "youngest sky") is the highest peak in the Khangai Mountains in Mongolia. Its summit is currently calculated to reach an elevation of 4,008 meters above mean sea level (some earlier topographic maps record a maximum elevation of 4,021 m). The mountain is located in Zavkhan Province and is the only peak in the Khangai range that is capped with a permanent glacier. The south face of Mount Otgontenger is the most extensive granite wall in Mongolia. Since the introduction of Buddhism, traditional Mongolian beliefs have held that wrathful deities inhabit many of Mongolia's sacred mountains. Ochirvaani is particularly associated with Otgontenger. Accidents In August 1963, an Ilyushin 14 aircraft crashed into the side of the mountain while on route. In October 2017, 27 hikers climbed the mountain and only 10 of them came back. They requested the rescue team a day after the other 17 went missing. The rescue operation took about 4 d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra Prominent Peak
An ultra-prominent peak, or Ultra for short, is a mountain summit with a topographic prominence of or more; it is also called a P1500. The prominence of a peak is the minimum height of climb to the summit on any route from a higher peak, or from sea level if there is no higher peak. There are approximately 1,524 such peaks on Earth. Some well-known peaks, such as the Matterhorn and Eiger, are not Ultras because they are connected to higher mountains by high cols and therefore do not achieve enough topographic prominence. The term "Ultra" originated with earth scientist Steve Fry, from his studies of the prominence of peaks in Washington (state), Washington in the 1980s. His original term was "ultra major mountain", referring to peaks with at least of prominence. Distribution Currently, 1,518 Ultras have been identified above sea level: 639 in Asia, 356 in North America, 209 in South America, 120 in Europe (including 12 in the Caucasus), 84 in Africa, 69 in Oceania, and 41 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, making it the world's most sparsely populated sovereign nation. Mongolia is the world's largest landlocked country that does not border a closed sea, and much of its area is covered by grassy steppe, with mountains to the north and west and the Gobi Desert to the south. Ulaanbaatar, the capital and largest city, is home to roughly half of the country's population. The territory of modern-day Mongolia has been ruled by various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu, the Xianbei, the Rouran, the First Turkic Khaganate, and others. In 1206, Genghis Khan founded the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous land empire in history. His grandson Kublai Khan conquered China proper and established the Yuan dynasty. After the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
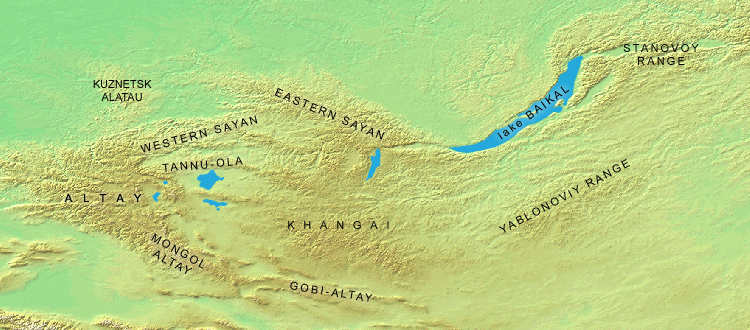
Khangai Mountains
The Khangai Mountains ( mn, Хангайн нуруу, Hangain nuruu, ); form a mountain range, range in central Mongolia, some west of Ulaanbaatar. Name Two provinces of Mongolia are named after the Khangai mountains: Arkhangai (North Khangai) and Ovorkhangai (South Khangai). The mild climate area where the two provinces meet (in eastern Khangai) is known as the cradle of Mongolian and nomadic civilization. The plains at the foot of the eastern Khangai host the Orkhon Valley, Orkhon Valley World Heritage Site. The Xiongnu capital Luut Khot (Lungcheng), the Xianbei state, Xianbei capital Ordo and the Rouran capital Moomt (Mume) are said to have been located there. Later empires also established their capitals there: e.g. the Uyghur Khaganate (745–840) built their capital Ordu-Baliq in the region. Features The tallest mountain is Otgontenger ( "Youngest sky"), which is about 4,000 metres tall. It is revered by the Mongols and state ceremonies are held there. Suvraga Khairkha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zavkhan Province
Zavkhan (; mn, Завхан, Zawhan, ) is one of the 21 aimags (provinces) of Mongolia, located in the west of the country, 1,104 km from Ulaanbaatar. Its capital is Uliastai. The aimag is named after the Zavkhan River, which forms the border between Zavkhan and Gobi-Altai aimag. Environment Locally, Zavkhan's environment is considered "Gobi-Khangai" (Говь хангай), since it connects the Gobi Desert in the south with the western Khangai Mountain Range and the broad lake basin of Khovd aimag. The highest peak in the province is Otgontenger (Отгонтэнгэр, lit. "youngest sky") both the highest (4,031 m) and only peak in the Khangai range capped with a permanent glacier. The mountain is located in the 95,510 hectare Otgon Tenger Strictly Protected Area, about 60 km east of Uliastai. An image of the mountain can be seen on the aimag's coat of arms. Otgontenger is associated with the Bodhisattva Ochirvaani (Очирваань). The western and south-wes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deities
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greater than those of ordinary humans, but who interacts with humans, positively or negatively, in ways that carry humans to new levels of consciousness, beyond the grounded preoccupations of ordinary life". Religions can be categorized by how many deities they worship. Monotheistic religions accept only one deity (predominantly referred to as "God"), whereas polytheistic religions accept multiple deities. Henotheistic religions accept one supreme deity without denying other deities, considering them as aspects of the same divine principle. Nontheistic religions deny any supreme eternal creator deity, but may accept a pantheon of deities which live, die and may be reborn like any other being. Although most monotheistic religions traditionall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Mountains
Sacred mountains are central to certain religions, and are usually the subjects of many legends. For many, the most symbolic aspect of a mountain is the peak because it is believed that it is closest to heaven or other religious realms. Many religions have traditions centered on sacred mountains, which either are or were considered holy (such as Mount Olympus in Greek mythology) or are related to famous events (like Mount Sinai in Judaism, Christianity and descendant religions or Mount Kailash in Hinduism). In some cases, the sacred mountain is purely mythical, like the Hara Berezaiti in Zoroastrianism. Mount Kailash is believed to be the abode of the deities Shiva and Parvati, and is considered sacred in four religions: Hinduism, Bon, Buddhism, and Jainism. Volcanoes, such as Mount Etna in Italy, were also considered sacred, Mount Etna being believed to have been the home of Vulcan, the Roman god of fire and the forge. Themes of sacrality in sacred mountains Edwin Bernbaum, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vajrapani
(Sanskrit; Pali: Vajirapāṇi, meaning, "Vajra in ishand") is one of the earliest-appearing bodhisattvas in Mahayana Buddhism. He is the protector and guide of Gautama Buddha and rose to symbolize the Buddha's power. Vajrapāni is also called Chana Dorji and Chador and extensively represented in Buddhist iconography as one of the earliest three protective deities or bodhisattvas surrounding the Buddha. Each of them symbolizes one of the Buddha's virtues: Manjushri manifests all the Buddhas' wisdom, Avalokiteśvara manifests all the Buddhas' immense compassion, and Vajrapāni protects Buddha and manifests all the Buddhas' power as well as the power of all five tathāgatas (Buddhahood of the rank of Buddha). Vajrapāni is one of the earliest Dharmapalas of Mahayana Buddhism and also appears as a deity in the Pali Canon of the Theravada school. He is worshiped in the Shaolin Monastery, in Tibetan Buddhism and in Pure Land Buddhism (where he is known as Mahasthamaprapta a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilyushin Il-14
The Ilyushin Il-14 (NATO reporting name: Crate) was a Soviet twin-engine commercial and military personnel and cargo transport aircraft that first flew in 1950, and entered service in 1954. The Il-14 was also manufactured in East Germany by VEB Flugzeugwerke as the VEB 14 and in Czechoslovakia as the Avia 14. The Ilyushin Il-14 was typically replaced by the Antonov An-24 and Yakovlev Yak-40. Design and development The Il-14 was developed as a replacement for the widespread Douglas DC-3 and its Soviet built version, the Lisunov Li-2. A development of the earlier Ilyushin Il-12, (that first flew in 1945), the Il-14 was intended for use in both military and civil applications. The Il-12 had major problems with poor engine-out behaviour. Also, it had less payload capability than was originally planned (although the Il-12 was intended to carry 32 passengers, in service it only carried 18, which was uneconomical). The development into the Il-14 was a vast improvement over the Il-12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mountains In Mongolia ...
Mongolia has three major mountain ranges. The highest is the Altai Mountains, which stretch across the western and the southwestern regions of the country on a northwest-to-southeast axis. The Khangai Mountains, mountains also trending northwest to southeast, occupy much of central and north-central Mongolia. These are older, lower, and more eroded mountains, with many forests and alpine pastures. The Khentii Mountains near the Russian border to the northeast of Ulaanbaatar, are lower still. Thirteen mountains are capped with a glacier in Mongolia. The following is a list of mountains in Mongolia: See also * Geography of Mongolia * List of Mongolia-related topics {{Authority control * Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ultras Of Central Asia
This is a list of the Ultra prominent peaks (with topographic prominence greater than 1,500 metres) in Central Asia. The list is divided topographically rather than politically. There are 75 in total; 21 in the Pamirs, 1 in the Karakum, 5 in the Alays, 24 in the Tian Shan and 24 in the Altai and Mongolia. Karakum Desert Pamir Mountains Pamir-Alay Tian Shan Altai region and Mongolia Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ... Sources List - Central Asian RepublicsMap - Central AsiaMap - High Asia {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Ultras Of Central Asia Central Asian Ultras Geography of Central Asia Landforms of Central Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Mongolia
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four-thousanders Of Asia
A four-thousander is a mountain summit that is at least 4,000 metres above sea level. Because the highest peaks in Europe fall into this category, the summits of four-thousanders are popular in Europe with climbers and mountaineers as climbing goals. Although climbing these peaks does not require an expedition to be mounted (unlike the highest peaks in other continents), knowledge and experience of high altitude climbing is a pre-requisite for attempting these peaks. Europe → See: '' List of Alpine four-thousanders'' Four-thousanders are the highest mountains and summits in Europe and are all found in the Alps. There is no agreement over where the boundary is between Europe and Asia which is why there is a dispute over which continent the over 5,000 metres high Caucasus range is in. In the Alps the highest four-thousander is Mont Blanc at 4,810 metres, the lowest, at exactly 4,000 metres is the eastern summit of Les Droites. The exact number of Alpine four-th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |