|
Mount Morgan Railway Station
Mount Morgan railway station is a heritage-listed railway station at Railway Parade, Mount Morgan, Rockhampton Region, Queensland, Australia. It is on the Mount Morgan - Wowan railway line. The station was constructed in 1898 to service the former goldrush and gold mining township of Mount Morgan and its mine. The station was designed by Henrik Hansen, who also designed the Archer Park, Shorncliffe and South Brisbane railway stations. The station operated as a functional railway station from 1898 until 1987, after which it was restored as a Railway Heritage Museum. The museum includes artefacts from the rail and mining history of Mount Morgan, including a restored Hunslett steam engine, "Silver Bullet" rail motor and timber rail carriages. The station was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 21 October 1992. History The Mount Morgan gold mine had been developed in 1883 and by 1889 with a mining population of 5,836 people, Mount Morgan's fortunes had attained t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
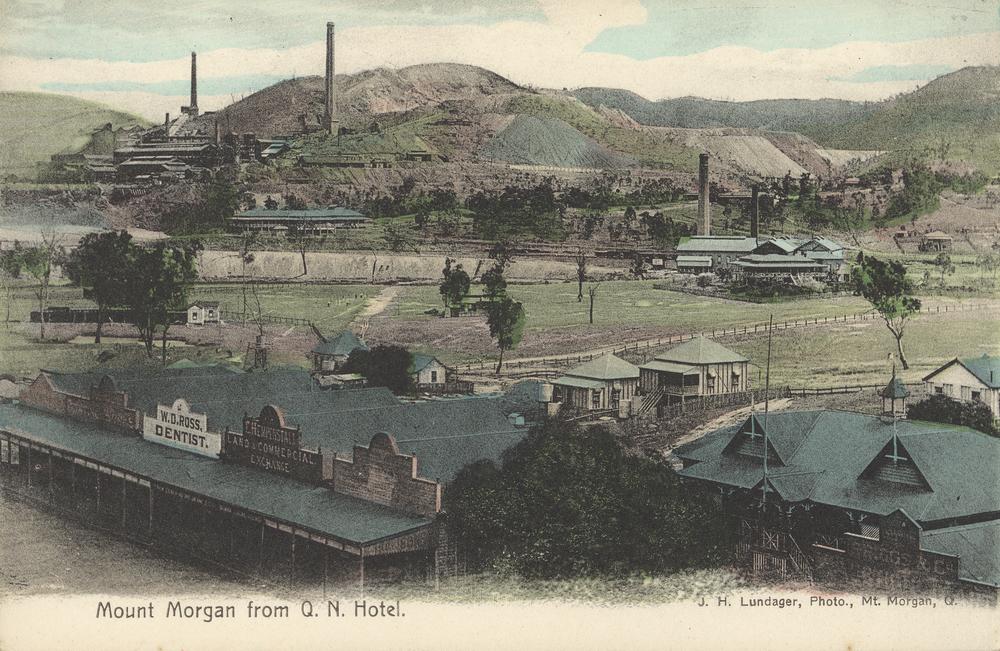
Mount Morgan, Queensland
Mount Morgan is a rural town and locality in the Rockhampton Region, Queensland, Australia. In the the locality of Mount Morgan had a population of 1,963 people. The town was the administrative centre of the Mount Morgan Shire until March 2008, when it was amalgamated with neighbouring local government areas to form the Rockhampton Region. Geography The town of Mount Morgan is situated on the Dee River, south of the city of Rockhampton, and is north of the state capital, Brisbane. The Burnett Highway passes through the town. There are a number of neighbourhoods within the locality: * Gordon Vale () * Kenbula (), located around the former Kenbula railway station * Talban (), located around the former Talban railway station The names ''Kenbula'' and ''Talban'' were both assigned by the Queensland Railway Department on 18 November 1911. Both are Aboriginal names, ''Kenbula'' meaning '' ironbark tree'' and ''Talban'' meaning ''stone curlew''. History Prior to European mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wowan, Queensland
Wowan is a rural town and locality in the Shire of Banana, Queensland, Australia. In the , the locality of Wowan had a population of 216 people. The town of Deeford is also within the locality. Geography The '' Dee River'' forms part of the eastern boundary. Both towns are located in the north-east of the locality with Deeford at near a crossing point of the Dee River. There are also a number of neighbourhoods within the location: * Buneru () * Cooneel () * Muruguran () The Leichhardt Highway runs through from north to south through the localityl, passing through the town of Wowan. History Wowan takes its name from the Wowan railway station, which in turn was named from the Aboriginal word for Australian brush-turkey. Deeford was originally known as Dundee, but was renamed Deeford on 6 November 1913 by the Queensland Surveyor-General. Dundee Provisional School opened on 1 June 1900. It closed in 1904 but reopened in 1905. On 1 January 1909 it became Dundee State Schoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dee River (Queensland)
The Dee River is a river located in Central Queensland, Australia. Course and features Part of the Fitzroy River system, the Dee River rises in the Razorback Range south of Bouldercombe Gorge Resources Reserve near Mount Gavial, south of . The river flows generally south by west through the mining settlement of , Waluml and , where the river is crossed by the Burnett Highway. The river is joined by seven minor tributaries including Limestone Creek, Horse Creek, Hamilton Creek, Nine Mile Creek, Boulder Creek, Oaky Creek and Pruce Creek. The Dee River forms its confluence with the Don River near Rannes. The largest dam on the river is Number 7 Dam, built for the Mount Morgan Mine, which has a history of acid mine discharge from gold and copper mining entering the Dee River. Mine pit In January 2013, the mine pit overflowed. Approximately of rain fell after ex-tropical Cyclone Oswald Tropical Cyclone Oswald in 2013 was a tropical cyclone that passed over parts of Quee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanwell, Queensland
Stanwell is a rural town and locality in the Rockhampton Region, Queensland, Australia. In the the locality of Stanwell had a population of 337 people. Geography Stanwell is located on the Capricorn Highway and the Central Western railway line. Neerkol Creek flows past the town. History Early settlers in the Stanwell area were involved in dairying, quarrying or working for the railways. Stanwell State School opened on 7 November 1873. A postal receiving office opened in about 1874; a post office opened on 1 October 1880. A Primitive Methodist Church opened in Stanwell on Saturday 13 August 1881 by the Reverend R. Hartley. Although the land was provided by the Methodists, other denominations contributed to the construction of the church as part of an arrangement whereby the other denominations could also use the church for their services. In 1893, a quarry leased by Bishop John Cani was used to provide sandstone for the construction of St Josephs Roman Catholic Cathedral in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emerald, Queensland
Emerald is a rural town and locality in the Central Highlands Region, Queensland, Australia. In the , Emerald had a population of 14,906 people. The town is the headquarters for the Central Highlands Regional Council. Geography Emerald lies on the Nogoa River, a tributary of the Fitzroy River. The town lies approximately from the Coral Sea coast and approximately 270 km west of the city of Rockhampton by road at the junction of the Capricorn and Gregory highways. Emerald sits approximately 10 km south of the Tropic of Capricorn. History The traditional owners include the Gayiri people who occupied the area for tens of thousands of years before European colonisation began in the nineteenth century. The Gayiri (Kairi, Khararya) language region takes in the landscape of the Central Highlands Region, including Emerald and the Nogoa River. The first European to explore the area was Ludwig Leichhardt between 1843 and 1845. The British Colony of Queensland was es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winton, Queensland
Winton is a town and Suburbs and localities (Australia), locality in the Shire of Winton in Central West Queensland, Australia. It is northwest of Longreach, Queensland, Longreach. The main industries of the area are sheep and cattle raising. The town was named in 1876 by postmaster Robert Allen, after his place of birth, Winton, Dorset. Winton was the first home of the airline Qantas. History Dispossession of Aboriginal land owners The traditional owners of the Winton area, the Koa people, consider Bladensburg National Park area (near Winton) to be a special part of their traditional country, and the park is also important to the Maiawali and Karuwali people. Yirandhali language, Jirandali (also known as Yirandali, Warungu, Yirandhali) is an Australian Aboriginal language of North West Queensland, North-West Queensland, particularly the Hughenden, Queensland, Hughenden area. The language region includes the local government area of the Shire of Flinders (Queensland), Shire of F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunnamulla
Cunnamulla () is a town and a locality in the Shire of Paroo, Queensland, Australia. It is south of Charleville, and approximately west of the state capital, Brisbane. In the , Cunnamulla had a population of 1,140 people. Geography Cunnamulla lies on the Warrego River in South West Queensland within the Murray-Darling drainage basin. It flows from the north (Coongoola) through the town, which is in the centre of the locality, and exits to the south ( Tuen). The Mitchell Highway passes through the locality from north (Coongoola) to south (Tuen), while the Balonne Highway enters the location from the east ( Linden). The two highways intersect in the town, which is located in the centre of the locality. The Bulloo Developmental Road starts in Cunnamulla and exits the locality to the west (Eulo). Cunnamulla is the administrative centre for the Paroo Shire, which also includes the townships of Wyandra, Yowah and Eulo, and covers an area of . Major industries of the area are wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
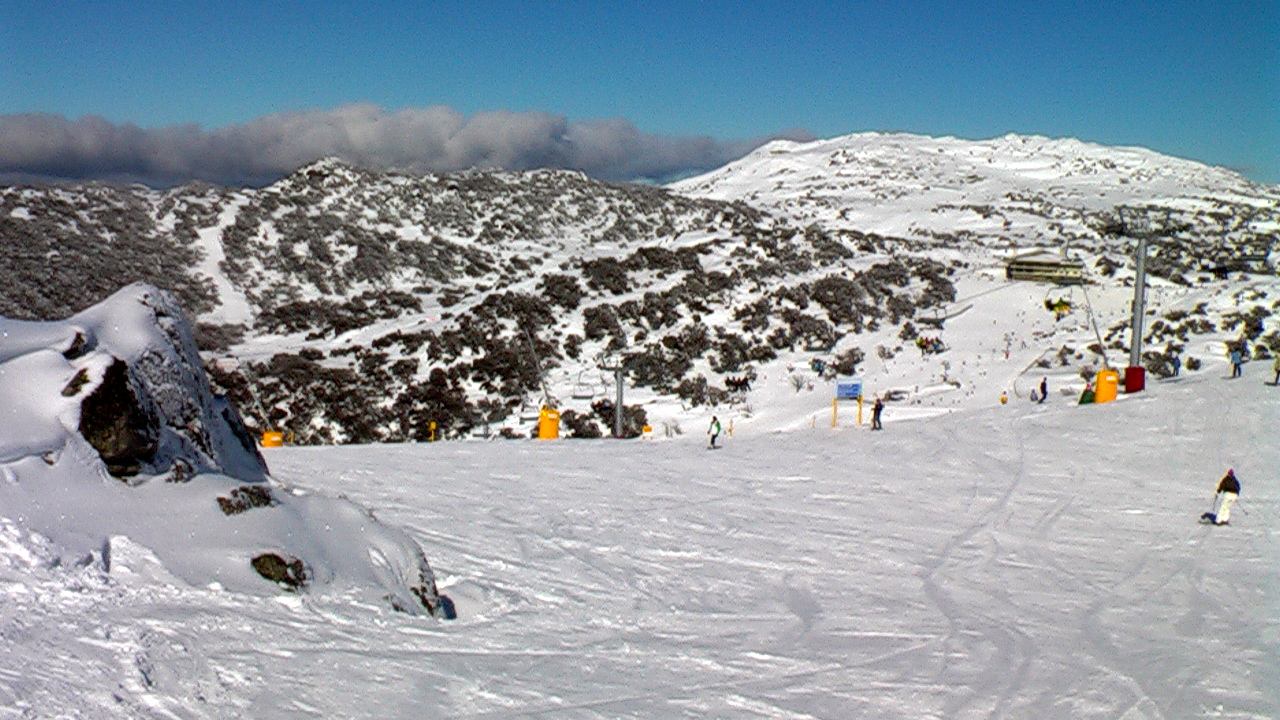
Blue Cow Mountain
Blue Cow is a ski resort that is part of Perisher located in the Snowy Mountains of New South Wales, Australia, within the Snowy Monaro Regional Council. The resort is situated within the Kosciuszko National Park and is administered by the NSW National Parks & Wildlife Service. During winter months, the only access to the village is via the Skitube underground railway. In summer, access is via off-road only. Blue Cow is one of the four resort bases within Perisher, Australia's largest ski resort. Also known as the Blue Cow Mountain, Mount Blue Cow or The Blue Cow, the mountain lies within the Main Range of Snowy Mountains, part of the Great Dividing Range. Blue Cow Mountain has an elevation of above sea level. Skiing The last establishment of a major skifield in New South Wales came with the development of Mount Blue Cow in the 1980s. In 1987 the Skitube Alpine Railway opened to deliver skiers from Bullocks Flat, on the Alpine Way, to Perisher Valley and to Blue Cow, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skitube Alpine Railway
The Skitube Alpine Railway is an Australian standard gauge electric rack railway in the Kosciuszko National Park in New South Wales. It provides access to the snowfields at Blue Cow Mountain and the Perisher Valley. History In the 1980s, development of the Thredbo and Perisher Valley skifields was increasing, but the mountain road providing access to them was limited. In 1980 the National Parks & Wildlife Service proposed the establishment of a day visitors resort at Blue Cow Mountain, which would increase the traffic demands. A number of transport modes were examined, including a funicular railway, chairlift, and an aerial gondola, but all were of limited capacity, affected by weather, and would scar the mountainsides. A rack and pinion railway was found to be the best option, running mostly underground. The Perisher Skitube Joint Venture was established, with Transfield and Kumagai Gumi each holding a 49% share. The main proponent of the scheme, Canberra engineer Ken Bils ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
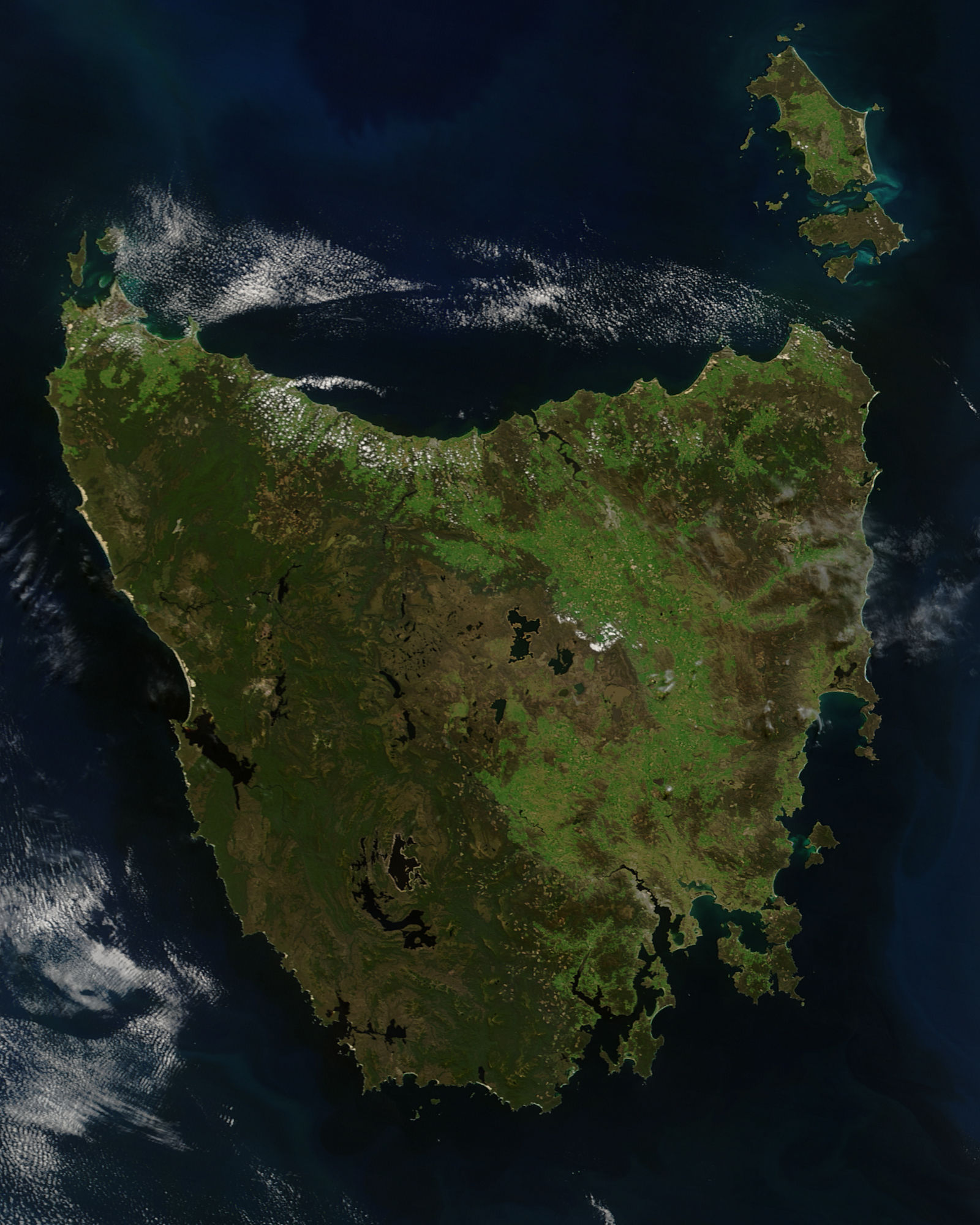
Tasmania
) , nickname = , image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg , map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates: , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Australia , established_title = Before federation , established_date = Colony of Tasmania , established_title2 = Federation , established_date2 = 1 January 1901 , named_for = Abel Tasman , demonym = , capital = Hobart , largest_city = capital , coordinates = , admin_center = 29 local government areas , admin_center_type = Administration , leader_title1 = Monarch , leader_name1 = Charles III , leader_title2 = Governor , leader_name2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Coast Wilderness Railway
The West Coast Wilderness Railway is a reconstruction of the Mount Lyell Mining and Railway Company Mount Lyell railway in Western Tasmania between Queenstown and Regatta Point, Strahan. The railway is significant because of its Abt rack system to conquer the mountainous terrain through rainforest, with original locomotives still operating on the railway today. Now operating as a tourist experience with a focus on sharing the history of Tasmania's West Coast, the original railway began operations in 1897 as the only link between Queenstown and the port of Strahan. History Original operation The Mount Lyell Mining Co (reformed on 29 March 1893 as the Mount Lyell Mining and Railway Company) began operations in November 1892. The railway officially opened in 1897, and again on 1 November 1899 when the line was extended from Teepookana to Regatta Point and Strahan. The railway was the only way to get copper from the mine at Queenstown to markets. Until 1932, when a Hobart road l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zürich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2020 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federalism, Federal assembly-independent Directorial system, directorial republic with elements of a direct democracy , leader_title1 = Federal Council (Switzerland), Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Walter Thurnherr , legislature = Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |