|
Mount Matsuo
is a {{Convert, 687, m, ft, adj=mid, -high, 0 mountain in Sasayama, Hyōgo, Sasayama, Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan. Another name is Mount Kosen-ji, literally, "Mountain of Kosen-ji." Religion and History Mount Matsuo is one of the major objects of worships for the people in this area. On this mountain, a Buddhist temple named ‘Kosen-ji’ was established in 645 by Hodo Sennin. This temple was re-established by Saichō, Denkyo Taishi in the 9th century. The temple was burned by Akechi Mitsuhide in the 16th century, but re-established again by Toyotomi Hideyoshi. In the Edo period, it is said that there were 28 monk houses in the mountain. Kosen-ji was also destroyed as a result of the Shinbutsu bunri, literally, Shinto-Buddhism-separation. Sakai Castle once stood on the top of this mountain; however, it was destroyed after the decline of the Sakai clan. Access * Furuichi Station (Hyōgo), Furuichi Station of Fukuchiyama Line * Sasayamaguchi Station of Fukuchiyama Line Referen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Language
is spoken natively by about 128 million people, primarily by Japanese people and primarily in Japan, the only country where it is the national language. Japanese belongs to the Japonic or Japanese- Ryukyuan language family. There have been many attempts to group the Japonic languages with other families such as the Ainu, Austroasiatic, Koreanic, and the now-discredited Altaic, but none of these proposals has gained widespread acceptance. Little is known of the language's prehistory, or when it first appeared in Japan. Chinese documents from the 3rd century AD recorded a few Japanese words, but substantial Old Japanese texts did not appear until the 8th century. From the Heian period (794–1185), there was a massive influx of Sino-Japanese vocabulary into the language, affecting the phonology of Early Middle Japanese. Late Middle Japanese (1185–1600) saw extensive grammatical changes and the first appearance of European loanwords. The basis of the standard dialect moved f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toyotomi Hideyoshi
, otherwise known as and , was a Japanese samurai and ''daimyō'' (feudal lord) of the late Sengoku period regarded as the second "Great Unifier" of Japan.Richard Holmes, The World Atlas of Warfare: Military Innovations that Changed the Course of History, Viking Press 1988. p. 68. Hideyoshi rose from a peasant background as a Affinity (medieval), retainer of the prominent lord Oda Nobunaga to become one of the most powerful men in Japan. Hideyoshi succeeded Nobunaga after the Honnō-ji Incident in 1582 and continued Nobunaga's campaign to unite Japan that led to the closing of the Sengoku period. Hideyoshi became the ''de facto'' leader of Japan and acquired the prestigious positions of Daijō-daijin, Chancellor of the Realm and Sesshō and Kampaku, Imperial Regent by the mid-1580s. Hideyoshi launched the Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–1598), Japanese invasions of Korea in 1592 to initial success, but eventual military stalemate damaged his prestige before his death in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukuchiyama Line
The is a railway line operated by West Japan Railway Company (JR West) connecting Osaka and Fukuchiyama, Kyoto, Fukuchiyama, Japan. Within JR West's "Urban Network" covering the Osaka–Kobe–Kyoto metropolitan region, the line from Osaka to Sasayamaguchi is also called the JR Takarazuka Line (). The line traverses the cities of Kawanishi, Hyogo, Kawanishi and Takarazuka, Hyogo, Takarazuka in the northwestern corner of the Osaka metropolitan area. Although Amagasaki Station (JR West), Amagasaki is the line's official southeastern terminus, all trains continue east to Osaka Station, Osaka and beyond on the JR Kōbe Line, or to the Gakkentoshi Line via the JR Tōzai Line. Basic data *Operators, distances: 106.5 km / 66.2 mi. **West Japan Railway Company (Rail transport in Japan#Category-1, Category-1, Services and tracks) *Track: **Double-track line: ***From Amagasaki to Sasayamaguchi **Single-track line: ***From Sasayamaguchi to Fukuchiyama *Railway signalling: Autom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Furuichi Station (Hyōgo)
is a passenger railway station located in the city of Tamba-Sasayama, Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan, operated by West Japan Railway Company (JR West). Lines Furuichi Station is served by the Fukuchiyama Line (JR Takarazuka Line), and is located 53.5 kilometers from the terminus of the line at and 62.1 kilometers from . Station layout The station consists of two opposed ground-level side platforms connected to the station building by a footbridge. The station is unattended. Platforms Adjacent stations History Furuichi Station opened on 25 March 1899. With the privatization of the Japan National Railways (JNR) on 1 April 1987, the station came under the aegis of the West Japan Railway Company. Station numbering was introduced in March 2018 with Furuichi being assigned station number JR-G67. Passenger statistics In fiscal 2016, the station was used by an average of 197 passengers daily Surrounding area * Sasayama Municipal Furuichi Elementary School * Mount Shirakami an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakai Clan
The was a Japanese samurai clan that claimed descent from the Nitta branch of the Minamoto clan, who were in turn descendants of Emperor Seiwa. Serata (Nitta) Arichika, a samurai of the 14th century, was the common ancestor of both the Sakai clan and the Matsudaira clan, which the Sakai later served. In the Sengoku period, under Tokugawa Ieyasu (who was the head of what was formerly the main Matsudaira family line), the Sakai became chief retainers. In the Edo period, because of their longstanding service to the Tokugawa clan, the Sakai were classified as a '' fudai'' family, in contrast with the '' tozama'' ("outsider clans"). Clan branches and histories The ''fudai'' Sakai clan originated in 14th century Mikawa Province. They claim descent from Minamoto no Arichika. Arichika had two sons; one of them, Yasuchika, took the name of Matsudaira, while the other son, Chikauji, took the name of Sakai. Chikauji is the ancestor of the Sakai clan. Sakai Hirochika, Chikauji's son, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
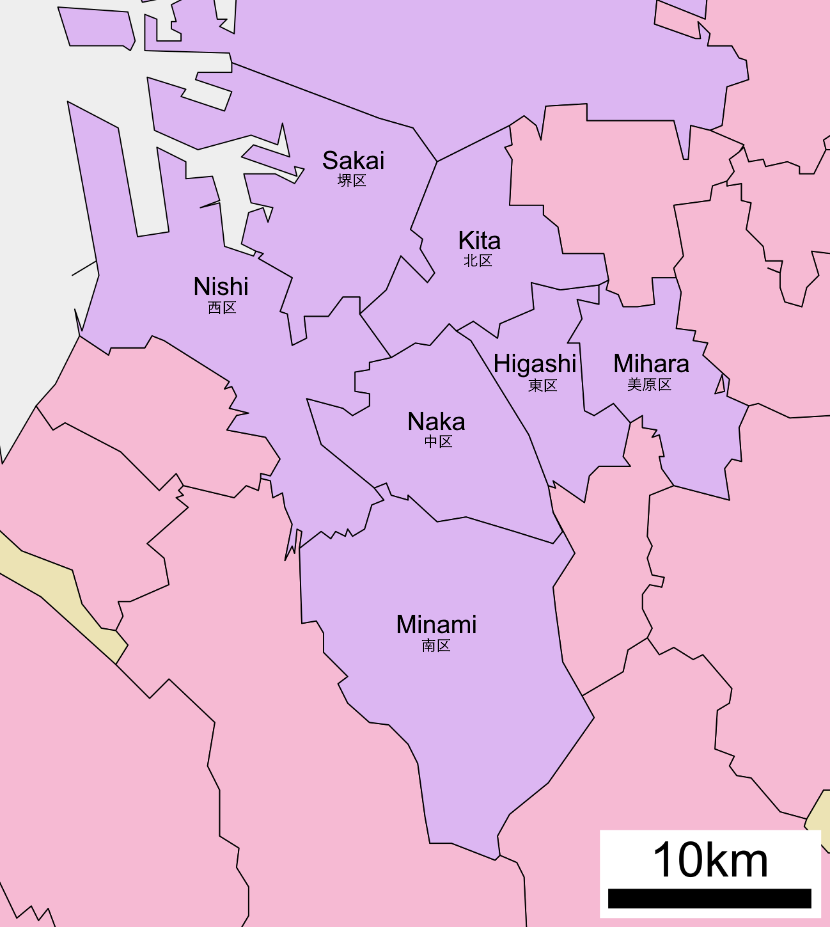
Sakai Castle
is a city located in Osaka Prefecture, Japan. It has been one of the largest and most important seaports of Japan since the medieval era. Sakai is known for its keyhole-shaped burial mounds, or kofun, which date from the fifth century and include Daisen Kofun, the largest grave in the world by area. Once known for swords, Sakai is now famous for the quality of its cutlery. , the city had an estimated population of 819,965, making it the fourteenth most populous city in Japan (excluding Tokyo). Geography Sakai is located in southern Osaka Prefecture, on the edge of Osaka Bay and directly south of the city of Osaka. Neighboring municipalities Osaka Prefecture *Osaka *Matsubara *Habikino *Ōsakasayama *Kawachinagano * Izumi * Takaishi Climate Sakai has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Sakai is . The average annual rainfall is with June as the wettest month. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shinbutsu Bunri
The Japanese term indicates the separation of Shinto from Buddhism, introduced after the Meiji Restoration which separated Shinto ''kami'' from buddhas, and also Buddhist temples from Shinto shrines, which were originally amalgamated. It is a yojijukugo phrase. Background before 1868 Until the end of the Edo period, in 1868, Shinto and Buddhism were intimately connected in what was called ''shinbutsu-shūgō'' (神仏習合), to the point that the same buildings were often used as both Shinto shrines and Buddhist temples, and Shinto gods were interpreted as manifestations of Buddhas. However, the tendency to oppose Buddhism as a foreign import and to uphold Shinto as the native religion can be seen already during the early modern era, partly as a nationalistic reaction.. In a broad sense, the term ''shinbutsu bunri'' indicates the effects of the anti-Buddhist movement that, from the middle of the Edo period onwards, accompanied the spread of Confucianism, the growth of studi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional '' daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by economic growth, strict social order, isolationist foreign policies, a stable population, perpetual peace, and popular enjoyment of arts and culture. The period derives its name from Edo (now Tokyo), where on March 24, 1603, the shogunate was officially established by Tokugawa Ieyasu. The period came to an end with the Meiji Restoration and the Boshin War, which restored imperial rule to Japan. Consolidation of the shogunate The Edo period or Tokugawa period is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's regional '' daimyo''. A revolution took place from the time of the Kamakura shogunate, which existed with the Tennō's court, to the Tok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akechi Mitsuhide
, first called Jūbei from his clan and later from his title, was a Japanese ''samurai'' general of the Sengoku period best known as the assassin of Oda Nobunaga. Mitsuhide was a bodyguard of Ashikaga Yoshiaki and later a successful general under ''daimyō'' Nobunaga during his war of political unification in Japan. Mitsuhide rebelled against Nobunaga for unknown reasons in the Honnō-ji Incident in 1582, forcing the unprotected Nobunaga to commit ''seppuku'' in Kyoto. Mitsuhide attempted to establish himself as ''shōgun'', but was pursued by Nobunaga's successor Toyotomi Hideyoshi and defeated at the Battle of Yamazaki. The 13-days short reign of Mitsuhide is listed as the inspiration for the yojijukugo set phrase . He is still popular in present culture. A ceremonial activity was held on April 15, 2018, in Kyoto. Early life Akechi Mitsuhide was believed to be born on 10 March 1528 in Tara Castle, Mino Province (present-day Kani, Gifu Prefecture) Mitsuhide was a descendan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasayama, Hyōgo
, formerly known as , is a city in the central eastern part of Hyōgo Prefecture, Japan. , the city had an estimated population of 40,050 in 17523 households and a population density of 110 persons per km2. The total area of the city is Geography Tamba-Sasayama is located in an inland basin surrounded by mountains on all sides in the eastern part of the prefecture. It is located in the mountains between the Seto Inland Sea and the Sea of Japan. The city has a slightly rectangular area east–west and north–south. Neighboring municipalities Hyōgo Prefecture * Tamba * Nishiwaki * Sanda * Katō * Inagawa Osaka Prefecture *Nose Kyoto Prefecture * Nantan *Fukuchiyama * Kyōtamba Climate Tamba-Sasayama has a Humid subtropical climate (Köppen ''Cfa'') characterized by warm summers and cool winters with light to no snowfall. The average annual temperature in Tamba-Sasayama is 13.3 °C. The average annual rainfall is 1582 mm with September as the wettest month. The tempe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saichō
was a Japanese Buddhist monk credited with founding the Tendai school of Buddhism based on the Chinese Tiantai school he was exposed to during his trip to Tang China beginning in 804. He founded the temple and headquarters of Tendai at Enryaku-ji on Mount Hiei near Kyoto. He is also said to have been the first to bring tea to Japan. After his death, he was awarded the posthumous title of Dengyō Daishi (伝教大師). Life Early life Saichō was born in the year 767 in the city of Ōmi, in present Shiga Prefecture, with the given name of Hirono. According to family tradition, Saichō's ancestors were descendants of emperors of Eastern Han China; however, no positive evidence exists for this claim. The region where Saichō was born did have a large Chinese immigrant population, so Saichō likely did have Chinese ancestry. During Saichō's time, the Buddhist temples in Japan were officially organized into a national network known as the provincial temple system, and at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodo Sennin
Odo (or Hodo) I (also ''Huodo'' or ''Huoto'') (c. 930 – 13 March 993) was margrave in the Saxon Eastern March of the Holy Roman Empire from 965 until his death. Odo was, if the onomastics are correct, a son (or maybe a nephew) of Christian (d. 950), a Saxon count in the Nordthüringgau and Schwabengau of Eastphalia. Count Christian, probably a scion of the Billung dynasty, had married Hidda (d. 970), a sister of Gero, margrave of the vast ''marca Geronis'' in the lands settled by Polabian Slavs. From 945 he also ruled over the adjacent gau of Serimunt beyond the Saale river. In 965, Margrave Gero died and his great ''marca Geronis'' was divided into five smaller marches. Count Thietmar, a known son of Hidda, and Odo inherited large parts of his march: Odo received the so-called ''marca Orientalis'' or Eastern March, stretching from the Gau Serimunt in the west up to the remotest outposts on the Bóbr river in the east, while Thietmar appeared as margrave of southern Meissen af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |