|
Mount Lemmon Observatory
Mount Lemmon Observatory (MLO), also known as the Mount Lemmon Infrared Observatory, is an astronomical observatory located on Mount Lemmon in the Santa Catalina Mountains approximately northeast of Tucson, Arizona (US). The site in the Coronado National Forest is used with special permission from the U.S. Forest Service by the University of Arizona's Steward Observatory, and contains a number of independently managed telescopes. History The MLO site was first developed in 1954 as Mount Lemmon Air Force Station, a radar installation of the Air Defense Command. Upon transfer to the Steward Observatory 1970, the site was converted to an infrared observatory. Until 2003, a radar tower operated from Fort Huachuca was used to track launches from the White Sands Missile Range in New Mexico and Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Telescopes Below are the 8 telescopes currently operating at the observatory. * The Steward Observatory Telescope is a Cassegrain reflector used for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(140) Mountlemmonobservatory
Fourteen or 14 may refer to: * 14 (number), the natural number following 13 and preceding 15 * one of the years 14 BC, AD 14, 1914, 2014 Music * 14th (band), a British electronic music duo * 14 (David Garrett album), ''14'' (David Garrett album), 2013 *''14'', an unreleased album by Charli XCX * 14 (song), "14" (song), 2007, from ''Courage'' by Paula Cole Other uses * Fourteen (film), ''Fourteen'' (film), a 2019 American film directed by Dan Sallitt * Fourteen (play), ''Fourteen'' (play), a 1919 play by Alice Gerstenberg * Fourteen (manga), ''Fourteen'' (manga), a 1990 manga series by Kazuo Umezu * 14 (novel), ''14'' (novel), a 2013 science fiction novel by Peter Clines * ''The 14'', a 1973 British drama film directed by David Hemmings * Fourteen, West Virginia, United States, an unincorporated community * Lot Fourteen, redevelopment site in Adelaide, South Australia, previously occupied by the Royal Adelaide Hospital * "The Fourteen", a nickname for NASA Astronaut Group 3 * Fourt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
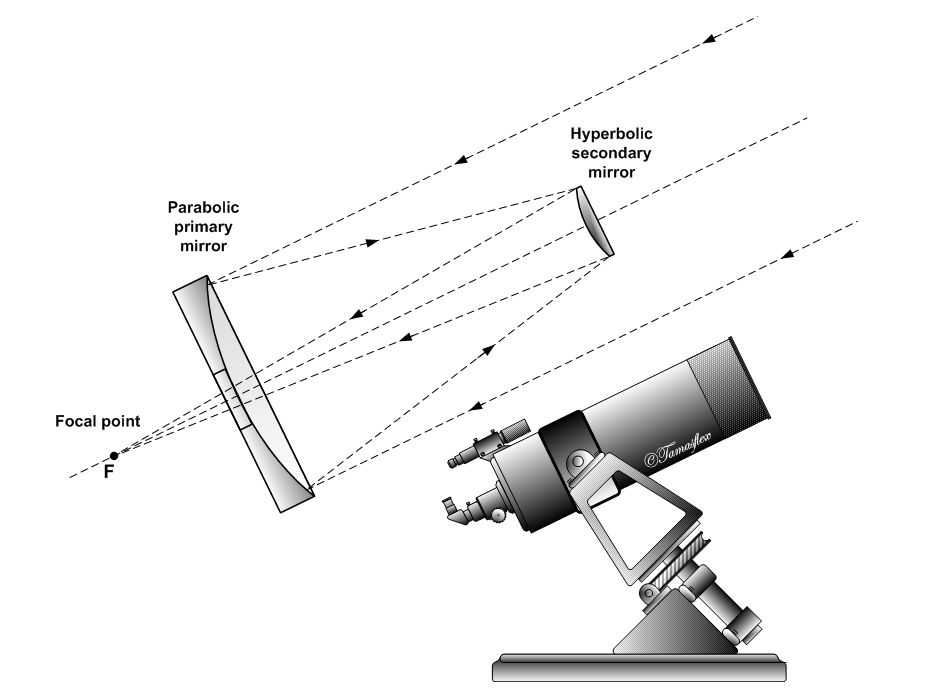
Cassegrain Reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the primary mirror (or both). The classic Cassegrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, San Diego
The University of California, San Diego (UC San Diego or colloquially, UCSD) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in San Diego, California. Established in 1960 near the pre-existing Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UC San Diego is the southernmost of the ten campuses of the University of California, and offers over 200 undergraduate and graduate degree programs, enrolling 33,096 undergraduate and 9,872 graduate students. The university occupies near the coast of the Pacific Ocean, with the main campus resting on approximately . UC San Diego is ranked among the best universities in the world by major college and university rankings. UC San Diego consists of twelve undergraduate, graduate and professional schools as well as seven undergraduate residential colleges. It received over 140,000 applications for undergraduate admissions in Fall 2021, making it the second most applied-to university in the United States. UC San Diego H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Astronomical Observatory (Mexico)
The National Astronomical Observatory (Spanish: ''Observatorio Astronómico Nacional''—OAN) is an astronomical observatory in Baja California, Mexico. History Mexico City The observatory was first established on the balcony of Chapultepec Castle in Mexico City in 1878. The observatory has been operated by the National Autonomous University of Mexico (UNAM) since 1929. It was later moved to Palacio del Ex-Arzobispado in Tacubaya, then on the outskirts of the city on the west side of the Federal District. The location is remembered by the name Metro Observatorio, the terminal station of the Line 1 of the Mexico City Metro located nearby. Puebla In the middle of the 20th century, OAN had to move from the increasingly crowded and polluted Valley of Mexico, to Tonantzintla in Puebla state, Central Mexico. Baja California In 1967 excessive air pollution and night light pollution caused another move, from Puebla to atop the Sierra San Pedro Mártir mountain range of Baja Cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Astronomy
Infrared astronomy is a sub-discipline of astronomy which specializes in the observation and analysis of astronomical objects using infrared (IR) radiation. The wavelength of infrared light ranges from 0.75 to 300 micrometers, and falls in between visible radiation, which ranges from 380 to 750 nanometers, and submillimeter waves. Infrared astronomy began in the 1830s, a few decades after the discovery of infrared light by William Herschel in 1800. Early progress was limited, and it was not until the early 20th century that conclusive detections of astronomical objects other than the Sun and Moon were made in infrared light. After a number of discoveries were made in the 1950s and 1960s in radio astronomy, astronomers realized the information available outside the visible wavelength range, and modern infrared astronomy was established. Infrared and optical astronomy are often practiced using the same telescopes, as the same mirrors or lenses are usually effective over a wavelengt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dall-Kirkham Telescope
A reflecting telescope (also called a reflector) is a telescope that uses a single or a combination of curved mirrors that reflect light and form an image. The reflecting telescope was invented in the 17th century by Isaac Newton as an alternative to the refracting telescope which, at that time, was a design that suffered from severe chromatic aberration. Although reflecting telescopes produce other types of optical aberrations, it is a design that allows for very large diameter objectives. Almost all of the major telescopes used in astronomy research are reflectors. Many variant forms are in use and some employ extra optical elements to improve image quality or place the image in a mechanically advantageous position. Since reflecting telescopes use mirrors, the design is sometimes referred to as a catoptric telescope. From the time of Newton to the 1800s, the mirror itself was made of metal usually speculum metal. This type included Newton's first designs and even the largest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torino Scale
The Torino scale is a method for categorizing the impact hazard associated with near-Earth objects (NEOs) such as asteroids and comets. It is intended as a communication tool for astronomers and the public to assess the seriousness of collision predictions, by combining probability statistics and known kinetic damage potentials into a single threat value. The Palermo Technical Impact Hazard Scale is a similar, but more complex scale. Near-Earth objects with a Torino scale of 1 pop up every couple of months or so and may last a few weeks until they have a longer observation arc. Overview The Torino Scale uses an integer scale from 0 to 10. A 0 indicates an object has a negligibly small chance of collision with the Earth, compared with the usual "background noise" of collision events, or is too small to penetrate Earth's atmosphere intact. A 10 indicates that a collision is certain, and the impacting object is large enough to precipitate a global disaster. An object is assigned a 0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2011 AG5
, provisional designation , is a sub-kilometer asteroid, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Apollo group. It has a diameter of about . It was removed from the Sentry Risk Table on 21 December 2012 and as such it now has a rating of 0 on the Torino Scale. It was recovered in December 2022 extending the observation arc from 4.8 years to 14 years. As of 2023, the distance between the orbits of Earth and is Description was discovered on 8 January 2011 by the Mount Lemmon Survey at an apparent magnitude of 19.6 using a reflecting telescope. Pan-STARRS precovery images from 8 November 2010 extended the observation arc to 317 days. Observations by the Gemini telescope at Mauna Kea recovered the asteroid on October 20, 21 and 27, 2012, and extended the observation arc to 719 days. The October 2012 observations reduced the orbit uncertainties by more than a factor of 60, meaning that the Earth's position in February 2040 no longer falls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy Camp
Astronomy Camp is a science summer camp hosted by the University of Arizona's Alumni Association, and run by astronomer Don McCarthy. Many of the early camps took place at the Mount Lemmon Station Observatory atop Mount Lemmon, near Tucson, Arizona. On Mount Lemmon, the campers have access to a 12″, 20″, 40″ and 60″ telescope, and on the nearby Mount Bigelow site, a 61″ telescope. In recent years, the camp has also taken place at the Kitt Peak National Observatory, where the students have access to a wide variety of telescopes, including the 90″ Bok Telescope, the ARO 12m Radio Telescope The ARO 12m Radio Telescope (ARO12m or KP12m) is a 12-meter dish located on Kitt Peak, approximately from Tucson in Arizona at an elevation of . History The original dish was built in 1967 under the umbrella of the National Radio Astronomy O ..., and a variety of smaller instruments. At both locations, the telescopes and other equipment are used for hands-on learning and re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cer-Vit
Cer-vit is a family of glass-ceramic materials that were invented by Owens Illinois in the mid-1960s. Its principle ingredients are the oxides of lithium, aluminum and silicon. It is melted to form a glass which is then heat treated to nucleate and crystallize it into a material that is more than 90% microscopic crystals. Its formulation and heat treatment can be modified to produce a variety of material properties. One form is a material that is transparent and has a near zero thermal expansion. Its transparency is because the microscopic crystals are smaller than the wave length of light and are transparent, and its low thermal expansion is because they have a spodumene structure. This material (Cer-Vit C 101) was used to form large mirror blanks (158 inches in diameter) that were used in telescopes in several places, including South America, France and Australia. Owens Illinois ceased production of C101 in 1978. In addition, Cer-Vit materials were used to make stove tops, cook wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Mirror
A primary mirror (or primary) is the principal light-gathering surface (the objective) of a reflecting telescope. Description The primary mirror of a reflecting telescope is a spherical or parabolic shaped disks of polished reflective metal (speculum metal up to the mid 19th century), or in later telescopes, glass or other material coated with a reflective layer. One of the first known reflecting telescopes, Newton's reflector of 1668, used a 3.3 cm polished metal primary mirror. The next major change was to use silver on glass rather than metal, in the 19th century such was with the Crossley reflector. This was changed to vacuum deposited aluminum on glass, used on the 200-inch Hale telescope. Solid primary mirrors have to sustain their own weight and not deform under gravity, which limits the maximum size for a single piece primary mirror. Segmented mirror configurations are used to get around the size limitation on single primary mirrors. For example, the Giant Mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Bigelow (Arizona)
Mount Bigelow is a mountain in the Santa Catalina Mountains of Arizona, U.S. It is home to the astronomical observing facility Catalina Station which operates the 61" Kuiper Telescope owned by the Steward Observatory of the University of Arizona The University of Arizona (Arizona, U of A, UArizona, or UA) is a public land-grant research university in Tucson, Arizona. Founded in 1885 by the 13th Arizona Territorial Legislature, it was the first university in the Arizona Territory. T .... It is one of the telescopes used by students at Astronomy Camp. References External links * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Bigelow Landforms of Pima County, Arizona Mountains of Pima County, Arizona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |