|
Mount Gardiner (Antarctica)
The Rawson Mountains lie within the Queen Maud Mountains to the southeast of the Ross Ice Shelf. They stand between the head of the Amundsen and Scott Glaciers. Peaks within the range include Mount Wyatt (2930 m) and Mount Weaver (2780 m). Features Geographical features include: * Amundsen Glacier * Mount Weaver * Mount Wyatt The Rawson Mountains lie within the Queen Maud Mountains to the southeast of the Ross Ice Shelf. They stand between the head of the Amundsen and Scott Glaciers. Peaks within the range include Mount Wyatt (2930 m) and Mount Weaver (2780 m). Feat ... * Scott Glacier Mountain ranges of the Ross Dependency Amundsen Coast {{RossDependency-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queen Maud Mountains
The Queen Maud Mountains are a major group of mountains, ranges and subordinate features of the Transantarctic Mountains, lying between the Beardmore and Reedy Glaciers and including the area from the head of the Ross Ice Shelf to the Antarctic Plateau in Antarctica. Captain Roald Amundsen and his South Pole party ascended Axel Heiberg Glacier near the central part of this group in November 1911, naming these mountains for the Norwegian queen Maud of Wales. Despite the name, they are not located within Queen Maud Land. Elevations bordering the Beardmore Glacier, at the western extremity of these mountains, were observed by the British expeditions led by Ernest Shackleton (1907–09) and Robert Falcon Scott (1910-13), but the mountains as a whole were mapped by several American expeditions led by Richard Evelyn Byrd (1930s and 1940s), and United States Antarctic Program (USARP) and New Zealand Antarctic Research Program (NZARP) expeditions from the 1950s through the 1970s. Featu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
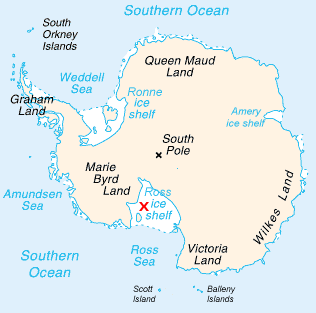
Ross Ice Shelf
The Ross Ice Shelf is the largest ice shelf of Antarctica (, an area of roughly and about across: about the size of France). It is several hundred metres thick. The nearly vertical ice front to the open sea is more than long, and between high above the water surface. Ninety percent of the floating ice, however, is below the water surface. Most of Ross Ice Shelf is in the Ross Dependency claimed by New Zealand. It floats in, and covers, a large southern portion of the Ross Sea and the entire Roosevelt Island located in the east of the Ross Sea. The ice shelf is named after Sir James Clark Ross, who discovered it on 28 January 1841. It was originally called "The Barrier", with various adjectives including "Great Ice Barrier", as it prevented sailing further south. Ross mapped the ice front eastward to 160° W. In 1947, the U.S. Board on Geographic Names applied the name "Ross Shelf Ice" to this feature and published it in the original U.S. Antarctic Gazetteer. In Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amundsen Glacier
Amundsen Glacier () is a major Antarctic glacier, about 7 to 11 km (4 to 6 nmi) wide and 150 km (80 nmi) long, originating on the polar plateau where it drains the area to the south and west of Nilsen Plateau, and descending through the Queen Maud Mountains to enter the Ross Ice Shelf just west of the MacDonald Nunataks. The tributary Blackwall Glacier flows northwest along the northeast side of Hansen Spur to join Amundsen Glacier. It was discovered by Rear Admiral Byrd on the South Pole flight in November 1929. The name was proposed for Roald Amundsen by Laurence Gould, leader of the Byrd AE geological party which sledged past the mouth of the glacier in December 1929. See also * List of glaciers in the Antarctic * Glaciology Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or more generally ice and natural phenomena that involve ice. Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scott Glacier (Transantarctic Mountains)
The Scott Glacier is a major glacier, long, that drains the East Antarctic Ice Sheet through the Queen Maud Mountains to the Ross Ice Shelf. The Scott Glacier is one of a series of major glaciers flowing across the Transantarctic Mountains, with the Amundsen Glacier to the west and the Leverett and Reedy glaciers to the east. Geography The Scott Glacier originates on the Antarctic Plateau in the vicinity of D'Angelo Bluff and Mount Howe, and descends between the Nilsen Plateau and the mountains of the Watson Escarpment to enter Ross Ice Shelf just west of the Tapley Mountains. The Tapley Mountains, Watson Escarpment, Mount Blackburn, and the La Gorce Mountains bound the Scott Glacier on its eastern margin, while the Karo Hills, Hays Mountains, Faulkner Escarpment, and Rawson Mountains define the western edge of the Scott's drainage. History Scott Glacier was discovered in December 1929 by the Byrd Antarctic Expedition geological party under Laurence Gould. The Scot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Wyatt
The Rawson Mountains lie within the Queen Maud Mountains to the southeast of the Ross Ice Shelf. They stand between the head of the Amundsen and Scott Glaciers. Peaks within the range include Mount Wyatt (2930 m) and Mount Weaver (2780 m). Features Geographical features include: * Amundsen Glacier Amundsen Glacier () is a major Antarctic glacier, about 7 to 11 km (4 to 6 nmi) wide and 150 km (80 nmi) long, originating on the polar plateau where it drains the area to the south and west of Nilsen Plateau, and descendin ... * Mount Weaver * Mount Wyatt * Scott Glacier Mountain ranges of the Ross Dependency Amundsen Coast {{RossDependency-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Weaver
The Rawson Mountains lie within the Queen Maud Mountains to the southeast of the Ross Ice Shelf. They stand between the head of the Amundsen and Scott Glaciers. Peaks within the range include Mount Wyatt (2930 m) and Mount Weaver (2780 m). Features Geographical features include: * Amundsen Glacier * Mount Weaver * Mount Wyatt The Rawson Mountains lie within the Queen Maud Mountains to the southeast of the Ross Ice Shelf. They stand between the head of the Amundsen and Scott Glaciers. Peaks within the range include Mount Wyatt (2930 m) and Mount Weaver (2780 m). Feat ... * Scott Glacier Mountain ranges of the Ross Dependency Amundsen Coast {{RossDependency-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Ranges Of The Ross Dependency
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (1,000 feet) above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |