|
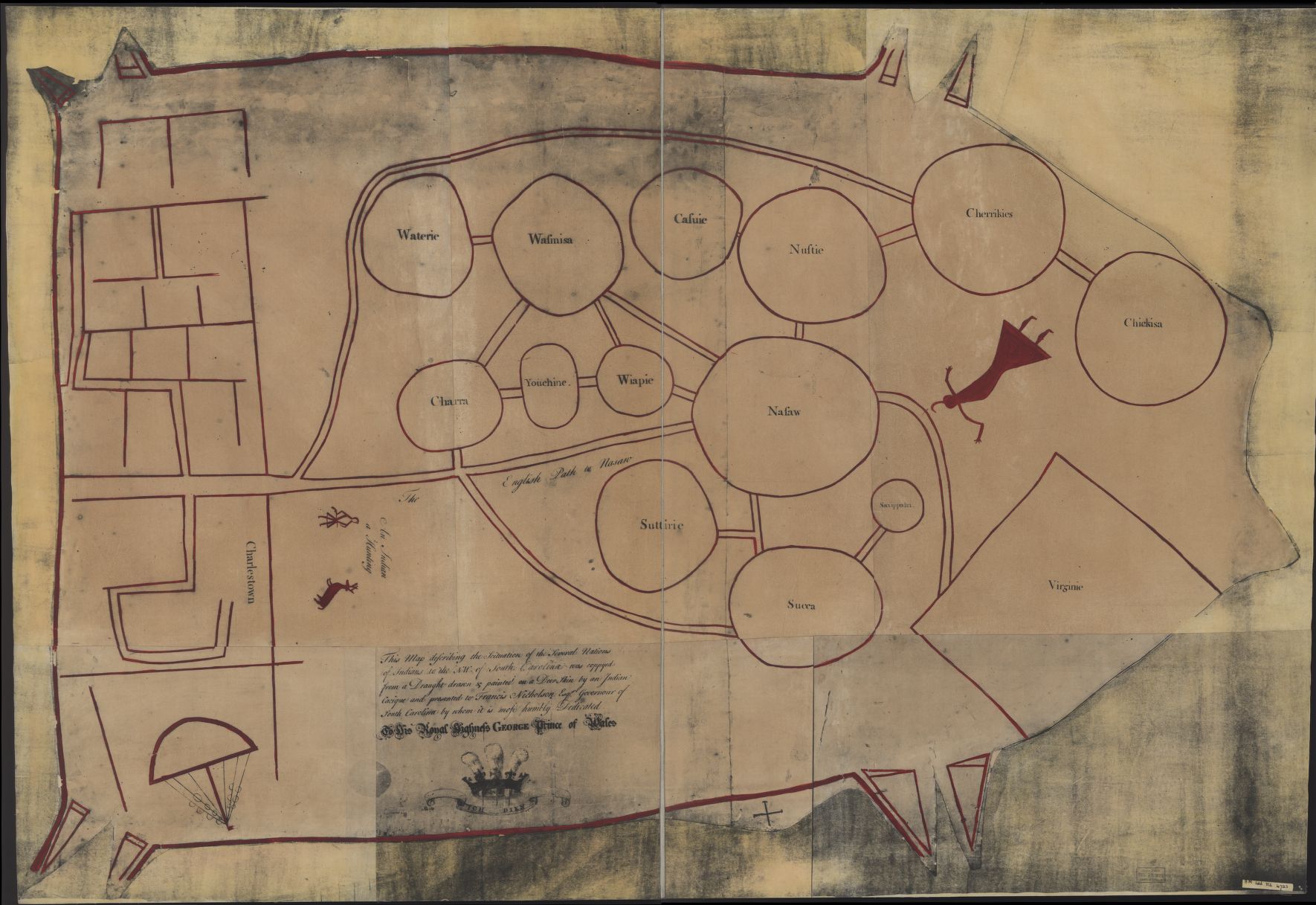
Mougoulacha
The Mougoulacha were a Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribe that lived near Lake Pontchartrain. Population In 1699 Iberville said that the Bayagoula and Mougoulacha together had about 180-250 warriors and an estimated 1,250 people. Language The Mougoulacha language was closely related to Choctaw language, Choctaw and Chickasaw, which are both Muskogean languages. Early History In the year 1699 Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville journeyed to the east of the Mississippi River Delta and encountered the Mougoulacha tribe. d'Iberville was amazed that the Mougoulacha chief was wearing a Bluecoat, blue serge coat. The chief said that the coat was given to him many years ago when Henri de Tonti explored the area. The Mougoulacha chief then showed d'Iberville a letter that was written in french. d'Ibberville determined that the letter was left by Tonti with the Quinipissa tribe fourteen years earlier. This led d'Iberville to believe that the Mougoulacha were actually the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quinipissa
The Quinipissa (sometimes spelled Kinipissa in French sources) were an indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous group living on the lower Mississippi River, in present-day Louisiana, as reported by René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle in 1682. They were joined together with the Mougoulacha. The combined group shared a village with the Bayagoula. In 1700 the Bayagoula massacred both the Quinipissa and Mougoulacha. In 1682, René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, La Salle encountered a group of Quinipissa living with the Koroa in a village on the western bank of the Mississippi River. Language The Quinipissa may have spoken the same language as the Mougoulacha and Bayagoula. The Bayogoula language, Bayagoula language is only attested with a single word. Albert Gatschet considered Quinipissa a Muskogean language ''Coast Choctaw'' ("Coast Chaʼhta") based on evidence that many peoples of this area spoke the lingua franca Mobilian Jargon and have names that appear to be ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayagoula
The Bayagoula were a Native American tribe from what is now called Mississippi and Louisiana in the southern United States. Due to transcription errors amongst cartographers who mistakenly rewrote the tribe's name as their name is erroneously assumed to translate as "bayou people"; further corruptions of the tribe's name into the two-word led most later 19th and 20th century cartographers to mistakenly assume the annotation referred not to a tribe but to a bayou near present day Donaldsonville, Louisiana named after some tribe known simply as the "Goula", or to the name of a settlement named after that nonexistent bayou. The Bayagoula were a part of the peoples who spoke Muskogean languages. The Houma people were recorded as attacking them around 1699–1700. They lived with another tribe, the Mougoulacha, in 1700. In the early 18th-century the Bayagoula killed many Mougoulacha, almost exterminating the entire tribe. This was triggered by a fight between the two tribes' chiefs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acolapissa
The Acolapissa were a small tribe of Native Americans of North America, who lived in the Southeast of what is the present-day United States. They lived along the banks of the Pearl River, between present-day Louisiana and Mississippi. They are believed to have spoken a Muskogean language, closely related to the Choctaw and Chickasaw spoken by other Southeast tribes of the Muskogean family. Early history The Acolapissa had at least six villages. Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville claimed that the Tangipahoa settlement was an additional Acolapissan settlement. In 1699, a band of 200 Chickasaw, led by two English slave traders, attacked several Acolapissa villages, intending to take captives as slaves to be sold in Charleston, South Carolina. Around 1702 the Acolapissa moved from Pearl River and settled on a bayou on the north side of Lake Pontchartrain. Shortly afterward, Louis Juchereau de St. Denis sent the Natchitoches tribe to live with the Acolapissa, who welcomed them and allowed them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United States are generally known by other terms). There are 574 federally recognized tribes living within the US, about half of which are associated with Indian reservations. As defined by the United States Census, "Native Americans" are Indigenous tribes that are originally from the contiguous United States, along with Alaska Natives. Indigenous peoples of the United States who are not listed as American Indian or Alaska Native include Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, and the Chamorro people. The US Census groups these peoples as " Native Hawaiian and other Pacific Islanders". European colonization of the Americas, which began in 1492, resulted in a precipitous decline in Native American population because of new diseases, wars, ethni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Pontchartrain
Lake Pontchartrain ( ) is an estuary located in southeastern Louisiana in the United States. It covers an area of with an average depth of . Some shipping channels are kept deeper through dredging. It is roughly oval in shape, about from west to east and from south to north. In descending order of area, the lake is located in parts of six Louisiana parishes: St. Tammany, Orleans, Jefferson, St. John the Baptist, St. Charles, and Tangipahoa. The water boundaries were defined in 1979 (see list of parishes in Louisiana). The lake is crossed by the Lake Pontchartrain Causeway, the longest continuous bridge over water in the world. A power line also crosses the lake. Its towers stand on caissons in Lake Pontchartrain, and its length can be used to visually demonstrate the curvature of the earth. Toponymy Lake Pontchartrain is named for , . He was the French Minister of the Marine, Chancellor, and Controller-General of Finances during the reign of France's "Sun King", L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choctaw Language
The Choctaw language (Choctaw: ), spoken by the Choctaw, an Indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands, is part of the Muskogean language family. Chickasaw is separate but closely related language to Choctaw. The Choctaw Nation of Oklahoma published the ''New Choctaw dictionary'' in 2016. Orthography The written Choctaw language is based upon the English version of the Roman alphabet and was developed in conjunction with the "civilization program" of the United States, a program to westernize and forcefully assimilate Indigenous Americans, particularly those adhering to what were to become the Five Civilized Tribes (of which the Choctaw are a part) into Anglo-American Culture and Sympathies during the early 19th century. Although there are other variations of the Choctaw alphabet, the three most commonly seen are the Byington (Traditional), Byington/Swanton (Linguistic), and Modern (Mississippi Choctaw). Many publications by linguists about the Choctaw language use a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chickasaw
The Chickasaw ( ) are an indigenous people of the Southeastern Woodlands. Their traditional territory was in the Southeastern United States of Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee as well in southwestern Kentucky. Their language is classified as a member of the Muskogean language family. In the present day, they are organized as the Federally recognized tribe, federally recognized Chickasaw Nation. Chickasaw people have a migration story in which they moved from a land west of the Mississippi River, where they settled mostly in present-day northeast Mississippi, northwest Alabama, and into Lawrence County, Tennessee. They had interaction with French, English, and Spanish colonists during the Colonial history of the United States, colonial period. The United States considered the Chickasaw one of the Five Civilized Tribes of the Southeast, as they adopted numerous practices of European Americans. Resisting European-American settlers encroaching on their territory, they were force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muskogean Languages
Muskogean (also Muskhogean, Muskogee) is a Native American language family spoken in different areas of the Southeastern United States. Though the debate concerning their interrelationships is ongoing, the Muskogean languages are generally divided into two branches, Eastern Muskogean and Western Muskogean. Typologically, Muskogean languages are agglutinative. One documented language, Apalachee, is extinct and the remaining languages are critically endangered. Genetic relationships Family division The Muskogean family consists of six languages that are still spoken: Alabama, Chickasaw, Choctaw, Creek-Seminole, Koasati, and Mikasuki, as well as the now-extinct Apalachee, Houma, and Hitchiti (the last is generally considered a dialect of Mikasuki). "Seminole" is listed as one of the Muskogean languages in Hardy's list, but it is generally considered a dialect of Creek rather than a separate language, as she comments. The major subdivisions of the family have long been controve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Le Moyne D'Iberville
Pierre Le Moyne d'Iberville (16 July 1661 – 9 July 1706) or Sieur d'Iberville was a French soldier, explorer, colonial administrator, and trader. He is noted for founding the colony of Louisiana in New France. He was born in Montreal to French colonist parents. Early life Pierre Le Moyne was born in July 1661 at Fort Ville-Marie (now Montreal), in the French colony of Canada, the third son of Charles le Moyne de Longueuil et de Châteauguay, a native of Dieppe or of Longueuil near Dieppe, Normandy in France and lord of Longueuil in Canada, and of (called Catherine Primot in some sources) from Rouen. He is also known as ''Sieur d'Iberville'' (''et d'Ardillières''). He had eleven brothers, most of whom became soldiers. One, Jacques Le Moyne de Sainte-Hélène, led French and Indian forces in the Schenectady massacre in present-day New York's Mohawk Valley. Charles le Moyne de Longueuil, Baron de Longueuil, was governor of Montreal. Another, Jean-Baptiste Le Moyne Bienville, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi River Delta
The Mississippi River Delta is the confluence of the Mississippi River with the Gulf of Mexico in Louisiana, southeastern United States. The river delta is a area of land that stretches from Vermilion Bay on the west, to the Chandeleur Islands in the east, on Louisiana's southeastern coast.Couvillion, B.R.; Barras, J.A.; Steyer, G.D.; Sleavin, William; Fischer, Michelle; Beck, Holly; Trahan, Nadine; Griffin, Brad; and Heckman, David, 2011, Land area change in coastal Louisiana from 1932 to 2010: U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Map 3164, scale 1:265,000, 12 p. pamphlet. It is part of the Gulf of Mexico and the Louisiana coastal plain, one of the largest areas of coastal wetlands in the United States.Louisiana's Coastal Area. "Ecosystem Restoration." LCA – Louisiana Coastal Area. The Mississippi River Delta is the 7th largest river delta on Earth (USGS) and is an important coastal region for the United States, containing more than of coastal wetlands and 37 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bluecoat
The bluecoat is a style of dress code, traditionally worn in Bluecoat schools (English private schools deriving from charity schools). The main element of the bluecoat is a long (dark blue or black) coat, belted at the waist, with white neck decoration. Underneath a white shirt and grey shorts are worn, with knee-length socks and smart shoes. History The uniform has its origin in the 16th-century dress of foundlings housed at Christ's Hospital, then in the City of London. Bluecoat schools based on the model of Christ's Hospital were set up in emulation in other urban centres. The last Bluecoat school to be founded was that in Wigan in 1773. The essayist Leigh Hunt (educated at Christ's Hospital from 1791 to 1799) described the bluecoat uniform: "Our dress was of the coarsest and quaintest kind, but was respected out of doors, and is so. It consisted of a blue drugget gown, or body, with ample coats to it; a yellow vest underneath in winter-time; small-clothes of Russia duck; w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri De Tonti
Henri de Tonti (''né'' Enrico Tonti; – September 1704), also spelled Henri de Tonty, was an Italian-born French military officer, explorer, and ''voyageur'' who assisted René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, with North American exploration and colonization from 1678 to 1686."A tour of Mobile's first 100 years", staff reporter, ''The Press-Register'', Mobile, AL, February 24, 2002 de Tonti was one of the first explorers to navigate and sail the upper Great Lakes. He also sailed the Illinois and the Mississippi, which they traveled to its mouth and claimed for Louis XIV of France. de Tonti established the first permanent European settlement in the lower Mississippi valley, known as '' Poste de Arkansea'', making him "The Father of Arkansas." Early life and military service Henri de Tonti was born in Gaeta, , to Lorenzo and Isabelle (née di Lietto) de Tonti. His father was the governor of Gaeta and a Neapolitan banker. He is credited with inventing the tontine, a form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |