|
Motherwell TMD
Motherwell TMD is a traction maintenance depot in Motherwell, Scotland. The depot code is ML. History In 1987 the depot had an allocation of Classes 08, 20 and 37 locomotives, and the depot had an Anvil and Hammer logo. Classes 26, 27 and 47 were also usually stabled at the depot. Following the privatisation of British Rail, the depot was operated by EWS. It closed in 2007, with its operations relocated to nearby Mossend. Following the closure of the depot, the office space was taken over by site owners Network Rail as a new maintenance depot for the Motherwell area. It was later reopened by Direct Rail Services who currently use it to stable Class 68 locomotives and Mark 2 carriages operated on Fife Circle services for ScotRail ScotRail Trains Limited, trading as ScotRail ( gd, Rèile na h-Alba), is a Scottish train operating company that is publicly owned by Scottish Rail Holdings on behalf of the Scottish Government. It has been operating the ScotRail franchi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 24
The British Railways Class 24 diesel locomotives, also known as the Sulzer Type 2, were built from 1958 to 1961. One hundred and fifty-one were built at Derby, Crewe and Darlington, the first twenty of them as part of the British Railways 1955 Modernisation Plan. This class was used as the basis for the development of the Class 25 locomotives. The final survivor, no. 24081, was withdrawn from Crewe depot in 1980. Technical details Engine The main power for the class 24 was the Sulzer 6LDA28 diesel engine - denoting 6 cylinders; Locomotive use; Direct fuel injection; (turbo-charged); bore cylinders. This was effectively an off-the-shelf purchase with small changes to bearings, injectors and some other minor items. The same engine was used in the CIE 101 Class locomotives in Ireland. Transmission The diesel engine powered another off-the-shelf product, the British Thomson-Houston (BTH) RTB15656 main generator which, in the class 24, was rated at , 750/525 V and 980/140 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 26
The British Rail Class 26 diesel locomotives, also known as the BRCW Type 2, were built by the Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company (BRCW) at Smethwick in 1958-59. Forty seven examples were built, and the last were withdrawn from service in 1994. Like their higher-powered sisters, the BRCW Classes 27 and 33, they had all-steel bodies and cab ends with fibreglass cab roofs. They were numbered D5300-D5346. Origins The BR Modernisation Plan contained a large requirement for small diesel locomotives in the - range and under BR's 'Pilot Scheme', small batches of locomotives were ordered from numerous different manufacturers for evaluation. BRCW obtained an order for 20 mixed traffic diesel-electric locomotives powered by Sulzer 6LDA28 engines. The Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company was a rolling stock manufacturer, although they were building diesel multiple units for BR. The first standalone locomotives made by the company were produced in 1956-57 BRCW: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
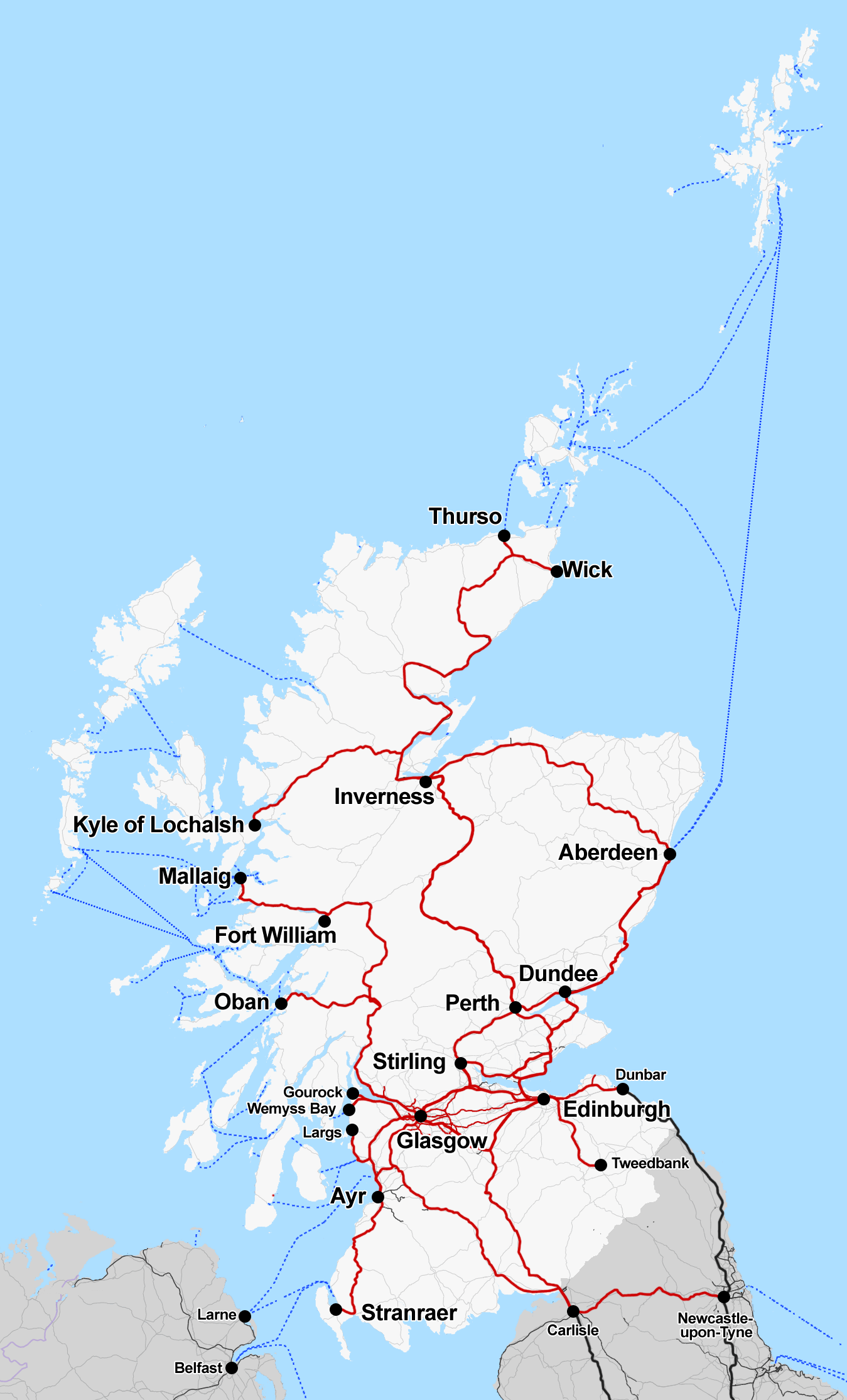
Railway Depots In Scotland
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prepared flat surface, rail vehicles (rolling stock) are directionally guided by the tracks on which they run. Tracks usually consist of steel rails, installed on sleepers (ties) set in ballast, on which the rolling stock, usually fitted with metal wheels, moves. Other variations are also possible, such as "slab track", in which the rails are fastened to a concrete foundation resting on a prepared subsurface. Rolling stock in a rail transport system generally encounters lower frictional resistance than rubber-tyred road vehicles, so passenger and freight cars (carriages and wagons) can be coupled into longer trains. The operation is carried out by a railway company, providing transport between train stations or freight customer faciliti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ScotRail
ScotRail Trains Limited, trading as ScotRail ( gd, Rèile na h-Alba), is a Scottish train operating company that is publicly owned by Scottish Rail Holdings on behalf of the Scottish Government. It has been operating the ScotRail franchise as an operator of last resort since 1 April 2022. History The ScotRail network had since 2015 been operated by the private-sector franchisee Abellio ScotRail. In December 2019, Transport Scotland announced Abellio had not met the performance criteria necessary to have its seven-year franchise extended for a further three years, and the franchise would conclude on 31 March 2022. In March 2021, Transport Scotland announced that the franchise would not be re-tendered for another private-sector operator to run, but would be operated by an operator of last resort owned by the Scottish Government.ScotRail to be Nationalised ''Rail Express'' issue 300 May 2021 page 6 The move was welcomed by the ASLEF, RMT and TSSA unions. The Minister for Tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fife Circle
The Fife Circle Line is the local rail service north from Edinburgh. It links towns of south Fife and the coastal towns along the Firth of Forth before heading to Edinburgh. Operationally, the service is not strictly a circle route, but, rather, a point to point service that reverses at the Edinburgh end, and has a large bi-directional balloon loop at the Fife end. Service The service includes the Edinburgh-Dunfermline stretch of the East Coast Main Line, which includes the world-famous Forth Bridge. On the Fife side, while this main line hugs the coast, the circle is formed by a line from Inverkeithing that loops back round to Kirkcaldy by an inland route via Cowdenbeath through the old Fife coalfield. Narrowly speaking, just this line could be called the Fife Circle. The current service is actually a combination of two previously separate local routes - Edinburgh to and Edinburgh to & . During the 1970s and 80s British Rail only ran a regular daytime service on the Dunferm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Mark 2
The Mark 2 family of railway carriages are British Rail's second design of carriages. They were built by British Rail workshops (from 1969 British Rail Engineering Limited (BREL)) between 1964 and 1975. They were of steel construction. Introduction File:BR Mk2 prototype.jpg, Prototype Mk2 13252 at the Mid-Norfolk Railway in April 2009 File:Mk 2A TSO 5278 'Melisande' at Cheltenham Spa.JPG, Mark 2A Tourist Standard Open (TSO) 5278 "Melisande" at Cheltenham Spa on 18 September 2004 on a charter service to Swindon File:5174 NLR 260108 d.adkins.jpg, Mark 2 coaches 5174, 5132 and 9102 at the Northampton & Lamport Railway on 26 January 2008 File:Mk 2F TSO 6035 at Carlisle.JPG, Arriva Trains Northern Mark 2F TSO 6035 at on 27 August 2004 File:British Rail Mk 2b, Cheriton, 1994.jpg, Mark 2C TSO 5541 at Cheriton in BR blue/grey livery in 1994 The Mark 2 has a semi-integral construction, giving it more strength than a Mark 1 in the event of an accident. A key driver of the changed c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
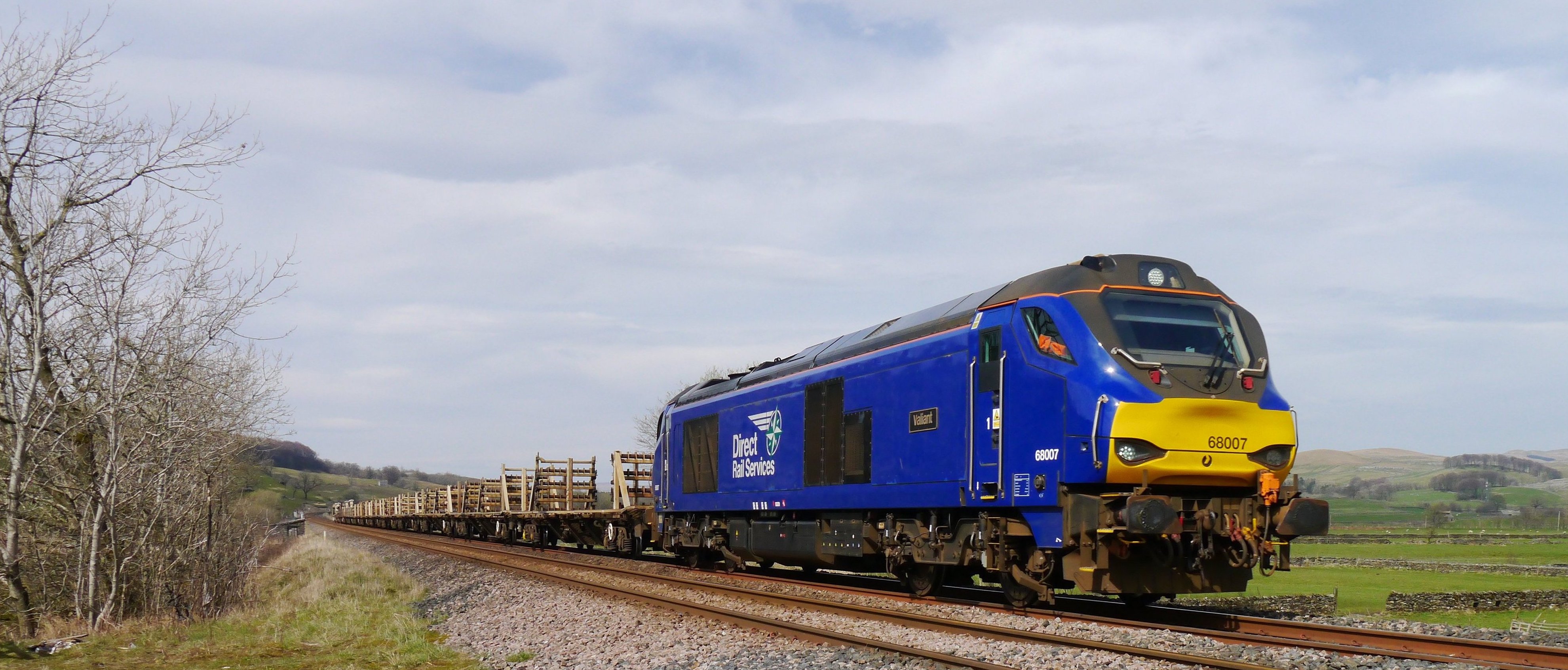
British Rail Class 68
The Class 68 is a type of mainline mixed traffic diesel-electric locomotive manufactured by Stadler Rail (and previously by Vossloh España) for Direct Rail Services (DRS) in the United Kingdom. The design is derived from the Stadler Eurolight, and Stadler's product name for this variant is the ''UKLight''. On 5 January 2012, DRS announced the placement of an order for fifteen Class 68 locomotives, the first of which arriving in the UK during January 2014. DRS testing determined the type to have satisfied its specification and to be suitable for operations. The first batch of Class 68s was quickly followed by a second batch, also intended for DRS and the first to be built by Stadler; the delivery of these units was completed during April 2016. A third batch of Class 68s was also ordered, deliveries of which were completed during July 2017. The Class 68 has since been followed by two closely-associated locomotives, the Class 88 and Class 93. Since its introduction in 2014, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mossend
Mossend is a small town in North Lanarkshire, Scotland, located on the A775 road to the immediate east of its 'sister town' Bellshill, west of the villages of Holytown and New Stevenston, north of the larger town of Motherwell and south of the Eurocentral industrial park and the M8 motorway. Along with Holytown, it forms a council ward which had a population of 13,480 in 2019, Mossend's estimated population being around half of that total. The town is the site of two railway freight terminals: Mossend International Railfreight Park and Mossend EuroTerminal. The yard is primarily used by DB Cargo UK. Mossend formed around the steel industry, with Clydesdale Steel Works once dominating the east end of the town. It is also home to the Mossend Football Club, a local community football club for children from the age of 6 to 21 years old. Early map references Mossend first appears on an early Timothy Pont map at the end of the 16th century as Mossid (Moss-Side), but the name most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DB Schenker Rail (UK)
DB Cargo UK (formerly DB Schenker Rail UK and English, Welsh & Scottish Railway (EWS)), is a British rail freight company headquartered in Doncaster, England. The company was established in early 1995 as ''North & South Railways'', successfully acquiring and merging five of the six freight companies that were sold during the privatisation of British Rail,The sixth rail freight company created during privatisation, Freightliner, was privatised through a management buyout. On 25 April 1996, the EWS brand was revealed and implemented over successive months. By the end of March 1997, it controlled 90% of the UK rail freight market, operated a fleet of 900 locomotives and 19,000 wagons, and had 7,000 employees. During the late 1990s, EWS invested heavily into rolling stock renewal, procuring a large number of British Rail Class 66 diesel locomotives, headcount was also reduced. It also acquired National Power's open-access freight operator in April 1998. During January 2001, the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privatisation Of British Rail
The privatisation of British Rail was the process by which ownership and operation of the railways of Great Britain passed from government control into private hands. Begun in 1994, it had been completed by 1997. The deregulation of the industry was initiated by EU Directive 91/440 in 1991, which aimed to create a more efficient rail network by creating greater competition. British Railways (BR) had been in state ownership since 1948, under the control of the British Railways Board (BRB). Under the Conservative government of Margaret Thatcher elected in 1979, various state-owned businesses were sold off, including various functions related to the railways – Sealink ferries and British Transport Hotels by 1984, Travellers Fare catering by 1988 and British Rail Engineering Limited (train building) by 1989. It was under Thatcher's successor John Major that the railways themselves were privatised, using the Railways Act 1993. The operations of the BRB were broken up and sold o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
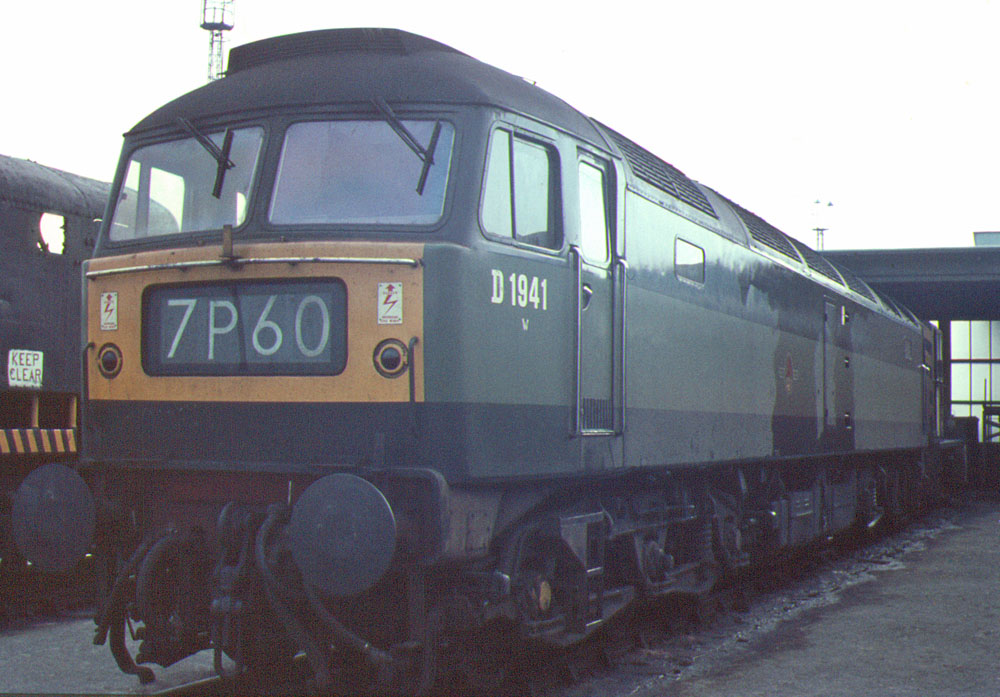
British Rail Class 47
The British Rail Class 47 or Brush Type 4 is a class of diesel-electric locomotive that was developed in the 1960s by Brush Traction. A total of 512 Class 47s were built at Brush's Falcon Works in Loughborough and at British Railways' Crewe Works between 1962 and 1968, which made them the most numerous class of British mainline diesel locomotive. They were fitted with the Sulzer 12LDA28C twin-bank twelve-cylinder unit producing though this was later derated to to improve reliabilityand have been used on both passenger and freight trains on Britain's railways for over 55 years. Despite the introduction of more modern types of traction, a significant number are still in use, both on the mainline and on heritage railways. As of December 2021, 78 locomotives still exist as Class 47s, including 31 which have been preserved. 33 further locomotives were converted to Class 57s between 1998 and 2004. Origins The Class 47 history begins in the early 1960s with the stated aim of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Class 27
British Rail's Class 27 comprised 69 diesel locomotives built by the Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company (BRCW) during 1961 and 1962. They were a development of the earlier Class 26; both were originally classified as the BRCW Type 2. The Class 27s were numbered D5347-D5415. Working life Original allocations were D5347–D5369 to Glasgow Eastfield, D5370–D5378 to Thornaby and D5379–D5415 to London Cricklewood for Tilbury Boat trains and Cross-London freight services. In the period September to December 1963, some of the Cricklewood allocation were transferred to Leicester and in December 1965 the Thornaby allocation was also nominally transferred to Leicester to join them. Traffic changes combined with reallocation of Class 25s led to the gradual transfer of the Leicester and Cricklewood locomotives to Scotland during 1969 thus concentrating the whole class within Scotland and being part of the replacement fleet that allowed the withdrawal of the poorly perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

_-_geograph.org.uk_-_626601.jpg)




.jpg)