|
Most–Grottkau Debate
"Anarchism or Communism?", better known as the Most–Grottkau debate, was a nationally advertised, public debate between America's foremost revolutionary anarchist Johann Most and Paul Grottkau in Chicago on May 24, 1884. The session consisted of two statements and two rebuttals and was published by the Chicago International Working People's Association as a 48-page pamphlet. Debate Johann Most of the anarchist International Working People's Association and Paul Grottkau of the Socialist Labor Party The Socialist Labor Party (SLP)"The name of this organization shall be Socialist Labor Party". Art. I, Sec. 1 of thadopted at the Eleventh National Convention (New York, July 1904; amended at the National Conventions 1908, 1912, 1916, 1920, 1924 ... debated the relative merits of their movements. Grottkau spoke in favor of socialism without government, which if defined as the ruling class's executive committee, would be without purpose in a classless socialist society. He suppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Most
Johann Joseph "Hans" Most (February 5, 1846 – March 17, 1906) was a German-American Social Democratic and then anarchism, anarchist politician, newspaper editor, and orator. He is credited with popularizing the concept of "propaganda of the deed". His grandson was Boston Celtics radio play-by-play man Johnny Most. Biography Early years According to biographer Frederic Trautmann, Johann Joseph Most was born Legitimacy (family law), out of wedlock to a governess and a Clerk (position), clerk, in Augsburg, Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria.Frederic Trautmann, ''The Voice of Terror: A Biography of Johann Most.'' Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, 1980, , , p. 4. Most's mother died of cholera when he was very young. Most was subjected to physical abuse by his stepmother and a schoolteacher;Trautmann, ''The Voice of Terror,'' p. 5. his aversion to religion earned him more beatings at school. To the end of his life Most was "a militant atheist with the zeal of a religious fanaticism, religio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
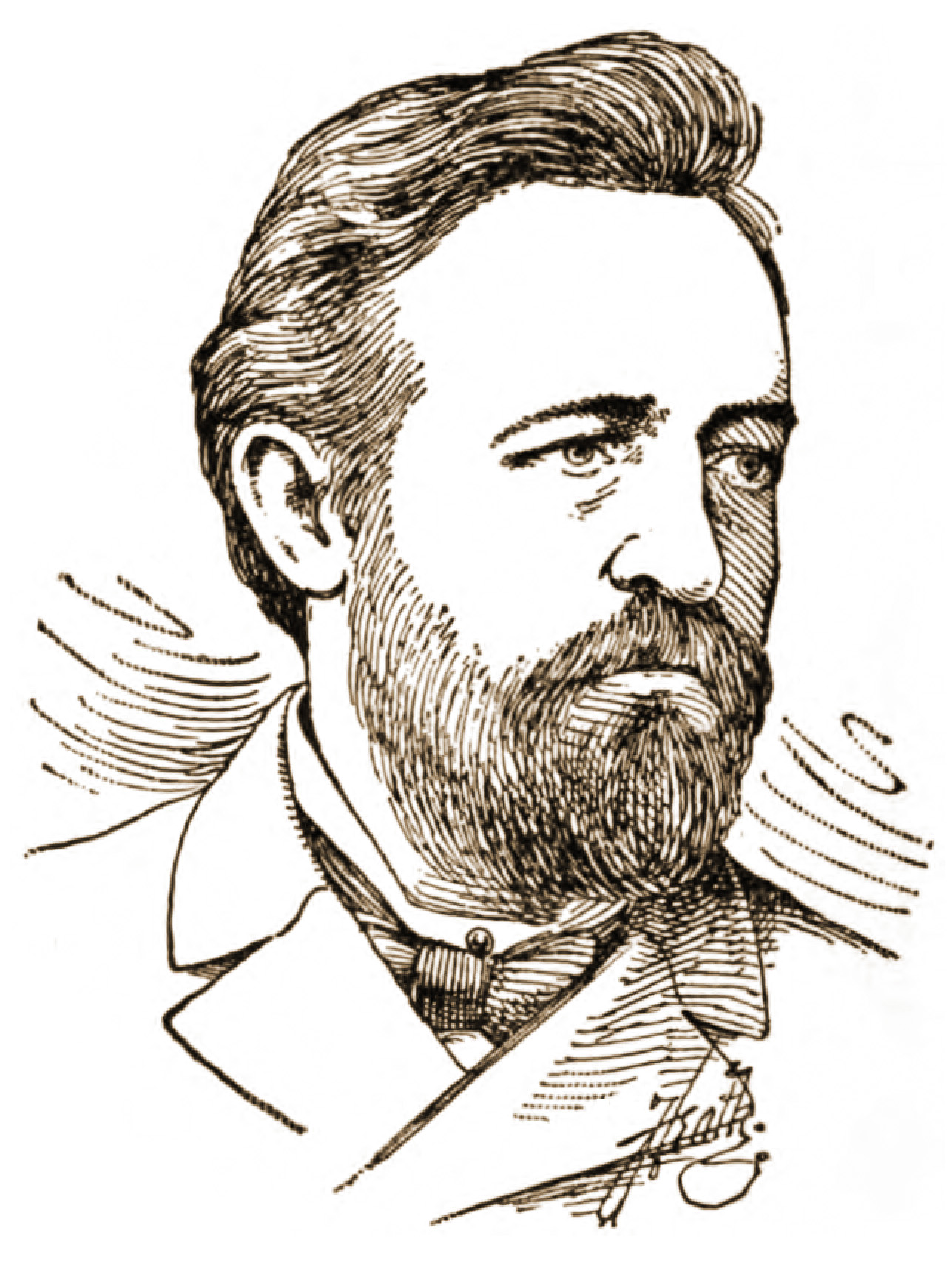
Paul Grottkau
Paul Grottkau (1846–1898) was a German-American socialist political activist and newspaper publisher. Grottkau is best remembered as an editor alongside Haymarket affair victim August Spies of the '' Chicagoer Arbeiter-Zeitung,'' one of the leading American radical newspapers of the decade of the 1880s. Later moving to Milwaukee, Grottkau became one of the leading luminaries of the socialist movement in Wisconsin. Biography Early years Paul Grottkau was born in Cottbus in 1846 and raised in Berlin, Prussia (now part of Germany), the son of a relatively prosperous noble family.Harmut Keil, "The German Immigrant Working Class of Chicago, 1875-90: Workers, Labor Leaders, and the Labor Movement," in Dirk Hoerder (ed.), ''American Labor and Immigration History, 1877-1920s: Recent European Research.'' Urbana: University of Illinois Press, 1983; pg. 165. Grottkau was trained as an architect. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Working People's Association
The International Working People's Association (IWPA), sometimes known as the "Black International," was an international anarchist political organization established in 1881 at a convention held in London, England. In America the group is best remembered as the political organization uniting Albert Parsons, August Spies, and other anarchist leaders prosecuted in the wake of the 1886 Haymarket bombing in Chicago. Organizational history Origins The slow pace of progress and limited results managed by the Socialist Labor Party of America (organized as the "Workingmen's Party" in 1876) during its first years proved frustrating and demoralizing for many Sections of the organization. Absent of significant electoral success, many Sections of the SLP began to debate the question of armed struggle and to organize paramilitary ''Lehr-und-Wehr Vereine'' (Education and Defense Societies).Alan Dawley"The International Working People's Association," The Lucy Parsons Project, http://flag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialist Labor Party
The Socialist Labor Party (SLP)"The name of this organization shall be Socialist Labor Party". Art. I, Sec. 1 of thadopted at the Eleventh National Convention (New York, July 1904; amended at the National Conventions 1908, 1912, 1916, 1920, 1924, 1928, 1932, 1936, 1940, 1944, 1948, 1952, 1956, 1960, 1964, 1968, 1972, 1976, 1977, 1978, 1979, 1980, 1981, 1982, 1983, 1984, 1987, 1989, 1991, 1993, 2001, 2005 and 2007) (cited February 18, 2016). is the first Socialism, socialist political party in the United States, established in 1876. Originally known as the Workingmen's Party of the United States, the party changed its name in 1877 to Socialistic Labor Party [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The German Anarchist Movement In New York City, 1880–1914
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Haymarket Tragedy
''The Haymarket Tragedy'' is a 1984 history book by Paul Avrich about the Haymarket affair and the resulting trial. Among other books about the Haymarket affair, ''The New York Times ''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...'' wrote in 2006, Avrich's book compared as "a tour de force of archival research, clear narrative and probing analysis," especially on the history of American anarchism. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * External links * * 1984 non-fiction books American history books History books about the United States English-language books Books by Paul Avrich History books about anarchism Princeton University Press books Works about the Haymarket affair {{US-his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anarchism In The United States
Anarchism in the United States began in the mid-19th century and started to grow in influence as it entered the American labor movements, growing an anarcho-communist current as well as gaining notoriety for violent propaganda of the deed and campaigning for diverse social reforms in the early 20th century. By around the start of the 20th century, the heyday of individualist anarchism had passed and anarcho-communism and other social anarchist currents emerged as the dominant anarchist tendency. Social anarchists, like Emma Goldman, can be credited with the introduction of LGBTQ social movements to the United States. In the post-World War II era, anarchism regained influence through new developments such as anarcho-pacifism, the American New Left and the counterculture of the 1960s. Contemporary anarchism in the United States influenced and became influenced and renewed by developments both inside and outside the worldwide anarchist movement such as platformism, insurrectiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Socialism In The United States
The history of the socialist movement in the United States spans a variety of tendencies, including anarchists, communists, democratic socialists, Marxists, Marxist–Leninists, Trotskyists and utopian socialists. It began with utopian communities in the early 19th century such as the Shakers, the activist visionary Josiah Warren and intentional communities inspired by Charles Fourier. Labor activists, usually British, German, or Jewish immigrants, founded the Socialist Labor Party of America in 1877. The Socialist Party of America was established in 1901. By that time, anarchism also rose to prominence around the country. Socialists of different tendencies were involved in early American labor organizations and struggles. These reached a high point in the Haymarket massacre in Chicago, which founded the International Workers' Day as the main labour holiday around the world, Labor Day and making the eight-hour day a worldwide objective by workers organizations and social ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
May 1884 Events
May is the fifth month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars and is the third of seven months to have a length of 31 days. May is a month of spring in the Northern Hemisphere, and autumn in the Southern Hemisphere. Therefore, May in the Southern Hemisphere is the seasonal equivalent of November in the Northern Hemisphere and vice versa. Late May typically marks the start of the summer vacation season in the United States (Memorial Day) and Canada (Victoria Day) that ends on Labor Day, the first Monday of September. May (in Latin, ''Maius'') was named for the Greek goddess Maia, who was identified with the Roman era goddess of fertility, Bona Dea, whose festival was held in May. Conversely, the Roman poet Ovid provides a second etymology, in which he says that the month of May is named for the ''maiores,'' Latin for "elders," and that the following month (June) is named for the ''iuniores,'' or "young people" (''Fasti VI.88''). Eta Aquariids meteor shower appea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)