|
Morton Deyo
Vice Admiral Morton Lyndholm Deyo (1 July 1887 – 10 November 1973) was an officer in the United States Navy, who was a naval gunfire support task force commander of World War II. Born on 1 July 1887 in Poughkeepsie, New York, he graduated from the United States Naval Academy in 1911, and served over a career of 38 years. His highest Navy rank in active service was Rear Admiral, attaining Vice Admiral at retirement. He was awarded three medals of personal honor, the Distinguished Service Medal (Navy), and the Legion of Merit with Gold Star. Deyo served in both the Atlantic and Pacific Fleets. In the Atlantic, he commanded the destroyers which provided the first American escort assistance to allied convoys to England just prior to the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor. He later commanded naval gunfire support at Utah Beach in the Normandy invasion, Task Force 129 at the Bombardment of Cherbourg, as well as during the invasion of Southern France. When transferred to the Pacif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poughkeepsie, New York
Poughkeepsie ( ), officially the City of Poughkeepsie, separate from the Town of Poughkeepsie around it) is a city in the U.S. state of New York. It is the county seat of Dutchess County, with a 2020 census population of 31,577. Poughkeepsie is in the Hudson River Valley region, midway between the core of the New York metropolitan area and the state capital of Albany. It is a principal city of the Poughkeepsie–Newburgh–Middletown metropolitan area which belongs to the New York combined statistical area. It is served by the nearby Hudson Valley Regional Airport and Stewart International Airport in Orange County, New York. Poughkeepsie has been called "The Queen City of the Hudson". It was settled in the 17th century by the Dutch and became New York State's second capital shortly after the American Revolution. It was chartered as a city in 1854. Major bridges in the city include the Walkway over the Hudson, a former railroad bridge called the Poughkeepsie Bridge which r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed in 1885 by Fernando Villaamil for the Spanish NavySmith, Charles Edgar: ''A short history of naval and marine engineering.'' Babcock & Wilcox, ltd. at the University Press, 1937, page 263 as a defense against torpedo boats, and by the time of the Russo-Japanese War in 1904, these "torpedo boat destroyers" (TBDs) were "large, swift, and powerfully armed torpedo boats designed to destroy other torpedo boats". Although the term "destroyer" had been used interchangeably with "TBD" and "torpedo boat destroyer" by navies since 1892, the term "torpedo boat destroyer" had been generally shortened to simply "destroyer" by nearly all navies by the First World War. Before World War II, destroyers were light vessels with little endurance for unattended o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Gleaves
Albert Gleaves (January 1, 1858 – January 6, 1937) was a decorated admiral in the United States Navy, also notable as a naval historian. Biography Born in Nashville, Tennessee, Gleaves graduated from the United States Naval Academy in 1877. After serving on board and , he was appointed an Ensign in 1881. Assigned to many ships and stations, he commanded during the Spanish–American War and later the battleship . Promoted to rear admiral in 1915, in World War I he commanded the Cruiser and Transport Force. For his outstanding contribution he was awarded the Army and Navy Distinguished Service Medals. In 1919 he was promoted to Admiral and commanded the Asiatic Fleet. While serving at the Naval Ordnance Proving Ground, Admiral Gleaves made outstanding contributions in the field of gunnery and torpedoes. While carrying out some tests on torpedo steering devices he changed these weapons from instruments of luck into instruments of precision. The gear which he tested in ''Cush ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Robison
Admiral Samuel Shelburne Robison CB, USN (May 10, 1867 – November 20, 1952) was a United States Navy officer whose service extended from the 1890s through the early 1930s. He held several major commands during World War I, and from 1928 to 1931 served as Superintendent of the United States Naval Academy. In 1933, Admiral Robison also founded a Naval Preparatory Academy in Pine Beach, New Jersey called Admiral Farragut Academy. Early life and career Robison was born on May 10, 1867, in Juniata County, Pennsylvania. He entered the United States Naval Academy on September 4, 1884. After finishing his academic studies at Annapolis he served the two years at sea as a passed naval cadet in on the Asiatic Station and was commissioned ensign July 1, 1890. In 1891 he was transferred to , still on the Asiatic Station; and, from 1893, he served in USS ''Thetis'' until ordered to the Mare Island Navy Yard in 1895. In 1896 he returned to the Asiatic Station in ''Boston''. In August 1899 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after its defeat in the First World War. Austria-Hungary was ruled by the House of Habsburg and constituted the last phase in the constitutional evolution of the Habsburg monarchy. It was a multinational state and one of Europe's major powers at the time. Austria-Hungary was geographically the second-largest country in Europe after the Russian Empire, at and the third-most populous (after Russia and the German Empire). The Empire built up the fourth-largest machine building industry in the world, after the United States, Germany and the United Kingdom. Austria-Hungary also became the world's third-largest manufacturer and exporter of electric home appliances, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Walter Eberle
Edward Walter Eberle (August 17, 1864 – July 6, 1929) was an admiral in the United States Navy, who served as Superintendent of the United States Naval Academy and the third Chief of Naval Operations. Early years Edward Walter Eberle was born in Denton, Texas, to Swiss-born immigrant and Confederate Officer ohannJoseph Eberle (1828–1877), who originally was from Walenstadt in Sarganserland, and his wife Maria Anna, née Stemmler (1835–1886). He was raised at Fort Smith, Arkansas. He entered the United States Naval Academy on September 28, 1881 and graduated on June 5, 1885. Naval career Following the two years of sea service—spent in screw sloops-of-war and and the steamer , as then required before commissioning—Eberle was promoted to ensign on July 1, 1887. Brief duty in Washington, D.C., in the late summer and early autumn preceded his reporting to on November 22, 1887 to begin three years of duty in that U.S. Fish Commission steamer. During his time on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John M
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sasebo, Nagasaki
is a Core cities of Japan, core city located in Nagasaki Prefecture, Japan. It is also the second largest city in Nagasaki Prefecture, after its capital, Nagasaki. On 1 June 2019, the city had an estimated population of 247,739 and a population density of 581 persons per km2 (1,505 persons per square mile). The total area is . The city includes a part of Saikai National Park. Located in the southern part of the city is the Dutch-styled theme park ''Huis Ten Bosch (theme park), Huis Ten Bosch''. The island of Ukujima is also administered as part of Sasebo city. History The area of present-day Sasebo was a small fishing village under the control of nearby Hirado Domain until shortly after the start of the Meiji period. Imperial Japanese Navy Admiral Tōgō Heihachirō, when surveying the coasts of northwestern Kyūshū for the site of a navy base, selected his location based on its protected, deep-water harbor, geographic proximity to China and Korea, and the presence of nearby Coal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
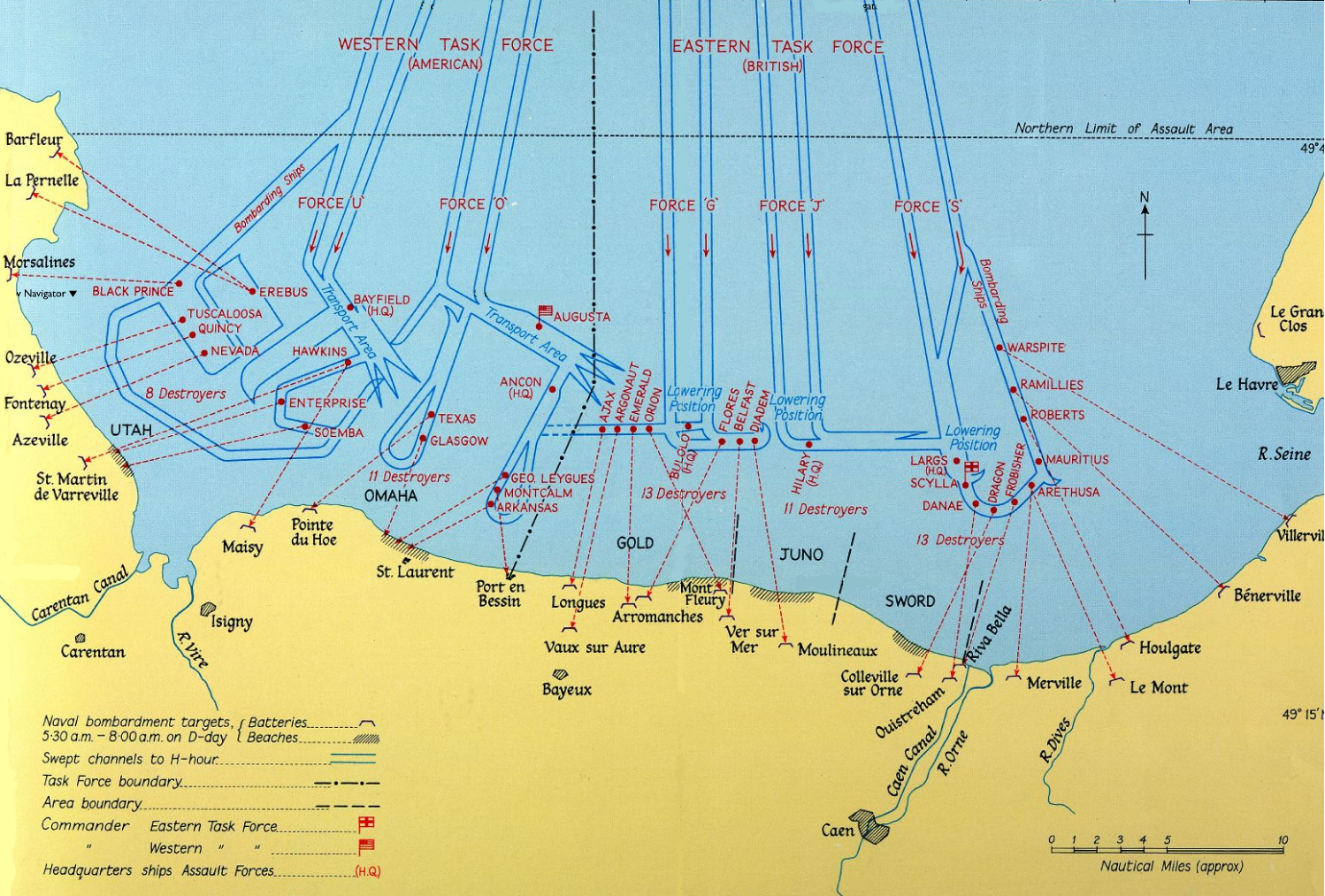
Bombardment Of Cherbourg
The bombardment of Cherbourg took place on June 25, 1944, during World War II, when ships from the United States Navy and the British Royal Navy attacked German fortifications in and near the city, firing in support of U.S. Army units that were engaged in the Battle of Cherbourg. In doing so, the Allied naval forces engaged in a series of duels with coastal batteries and provided close support to infantry as they fought to gain control of the city. The bombardment was initially scheduled to last just two hours but it was later extended by an hour to support army units attempting to break into Cherbourg's city streets. After the bombardment, German resistance lasted until June 29, when the port was eventually captured by the Allies. Afterwards, the task of clearing the port for use lasted several weeks. When the Allies managed to secure a bridgehead after the Normandy landings, the Germans adopted a strategy to bottle up the Allied forces in Normandy and deny them the nearest maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invasion Of Normandy
Operation Overlord was the codename for the Battle of Normandy, the Allied operation that launched the successful invasion of German-occupied Western Europe during World War II. The operation was launched on 6 June 1944 (D-Day) with the Normandy landings. A 1,200-plane airborne assault preceded an amphibious assault involving more than 5,000 vessels. Nearly 160,000 troops crossed the English Channel on 6 June, and more than two million Allied troops were in France by the end of August. The decision to undertake a cross-channel invasion in 1944 was taken at the Trident Conference in Washington in May 1943. General Dwight D. Eisenhower was appointed commander of Supreme Headquarters Allied Expeditionary Force, and General Bernard Montgomery was named commander of the 21st Army Group, which comprised all the land forces involved in the invasion. The coast of Normandy of northwestern France was chosen as the site of the invasion, with the Americans assigned to land at sectors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utah Beach
Utah, commonly known as Utah Beach, was the code name for one of the five sectors of the Allied invasion of German-occupied France in the Normandy landings on June 6, 1944 (D-Day), during World War II. The westernmost of the five code-named landing beaches in Normandy, Utah is on the Cotentin Peninsula, west of the mouths of the Douve and Vire rivers. Amphibious landings at Utah were undertaken by United States Army troops, with sea transport, mine sweeping, and a naval bombardment force provided by the United States Navy and Coast Guard as well as elements from the British, Dutch and other Allied navies. The objective at Utah was to secure a beachhead on the Cotentin Peninsula, the location of important port facilities at Cherbourg. The amphibious assault, primarily by the US 4th Infantry Division and 70th Tank Battalion, was supported by airborne landings of the 82nd and 101st Airborne Division. The intention was to rapidly seal off the Cotentin Peninsula, prevent the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |