|
Mortar Schooner
This glossary defines the various types of ships and accessory watercraft that have been used in service of the United States. Such service is mainly defined as military vessels used in the United States Navy and United States Coast Guard, as well as the defunct, incorporated, or renamed institutions such as the United States Revenue Cutter Service. Service of the United States can also be defined in this context as special government missions in the form of expeditions, such as the Wilkes Expedition or the North Pacific Exploring and Surveying Expedition. The scope of the glossary encompasses both the "Old Navy" of the United States (sail or later steam vessels, with ship type named for the rigging or propulsion method x. steamer, cutter, schooner, from its beginnings as the "Continental Navy", through the "New Navy" (revolutionary steam or fueled vessels, with naming derived from a hull classification scheme) and up to modern day. The watercraft included in the glossary are d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watercraft
Any vehicle used in or on water as well as underwater, including boats, ships, hovercraft and submarines, is a watercraft, also known as a water vessel or waterborne vessel. A watercraft usually has a propulsive capability (whether by sail, oar, paddle, or engine) and hence is distinct from a stationary device, such as a pontoon, that merely floats. Types Most watercraft may be described as either a ship or a boat. However, numerous items, including surfboards, underwater robots, seaplanes and torpedoes, may be considered neither ships nor boats. Although ships are typically larger than boats, the distinction between those two categories is not one of size per se. *Ships are typically large ocean-going vessels; whereas boats are smaller, and typically travel most often on inland or coastal waters. *A rule of thumb says "a boat can fit on a ship, but a ship can't fit on a boat", and a ship ''usually'' has sufficient size to carry its own boats, such as lifeboats, dingh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
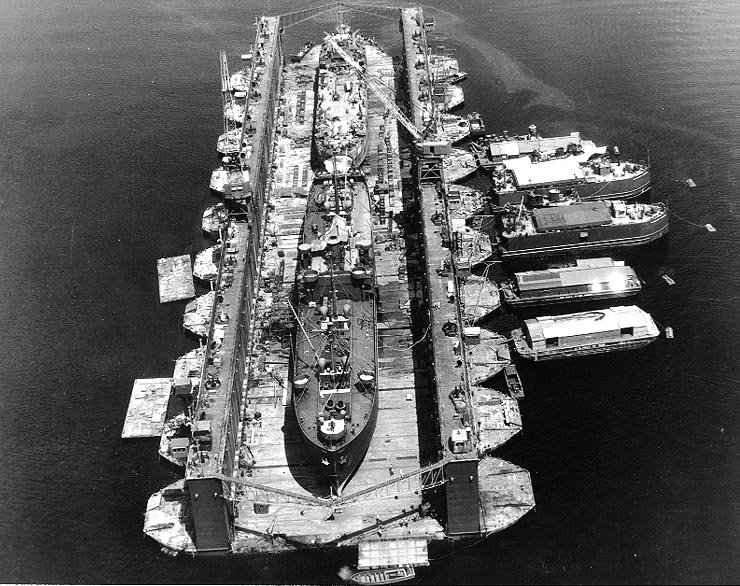
Auxiliary Floating Drydock
An auxiliary floating drydock is a type of US Navy floating dry dock. Floating dry docks are able to submerge underwater and to be placed under a ship in need of repair below the water line. Water is then pumped out of the floating dry dock, raising the ship out of the water. The ship becomes blocked on the deck of the floating dry dock for repair. Most floating dry docks have no engine and are towed by tugboats to their destinations. Floating dry docks come in different sizes to accommodate varying ship sizes, while large floating dry docks come in sections and can be combined to increase their size and lift power. Ballast pontoon tanks are flooded with water to submerge or pumped dry to raise the ship. World War II At the start of World War II, the US Navy had only three steel auxiliary floating dry docks: To reduce travel time for repair work, over 150 auxiliary floating dry docks of different sizes were built during World War II between 1942 and 1945. These newly built f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate States Of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confederacy comprised U.S. states that declared secession and warred against the United States during the American Civil War: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, Texas, Virginia, Arkansas, Tennessee, and North Carolina. Kentucky and Missouri also declared secession and had full representation in the Confederate Congress, though their territory was largely controlled by Union forces. The Confederacy was formed on February 8, 1861, by seven slave states: South Carolina, Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana, and Texas. All seven were in the Deep South region of the United States, whose economy was heavily dependent upon agriculture—particularly cotton—and a plantation system that relied upon enslaved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blockade Runner
A blockade runner is a merchant vessel used for evading a naval blockade of a port or strait. It is usually light and fast, using stealth and speed rather than confronting the blockaders in order to break the blockade. Blockade runners usually transport cargo, for example bringing food or arms to a blockaded city. They have also carried mail in an attempt to communicate with the outside world. Blockade runners are often the fastest ships available, and come lightly armed and armored. Their operations are quite risky since blockading fleets would not hesitate to fire on them. However, the potential profits (economically or militarily) from a successful blockade run are tremendous, so blockade-runners typically had excellent crews. Although having ''modus operandi'' similar to that of smugglers, blockade-runners are often operated by state's navies as part of the regular fleet, and states having operated them include the Confederate States of America during the American Civil W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
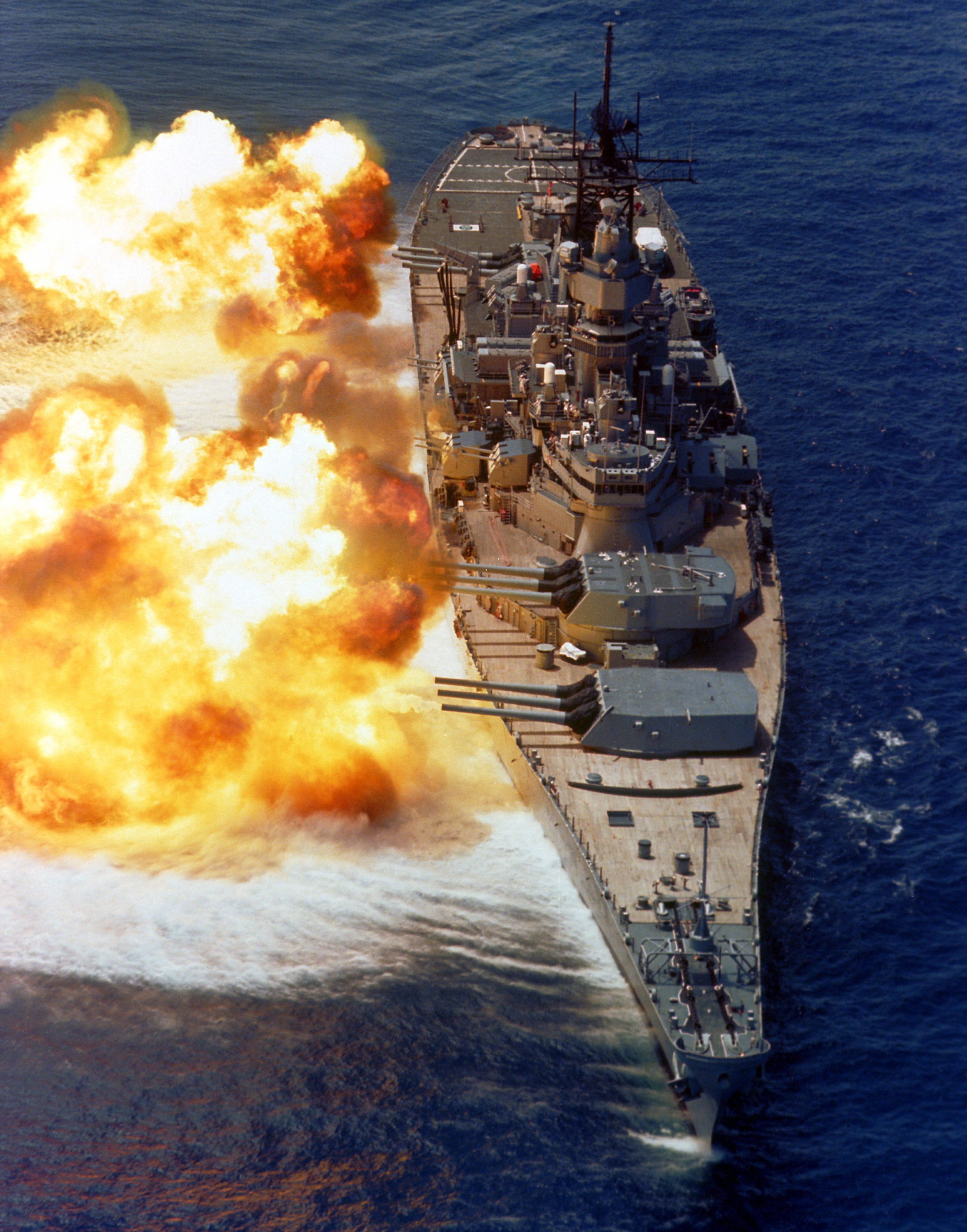
Battleship
A battleship is a large armored warship with a main battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1880s to describe a type of ironclad warship,Stoll, J. ''Steaming in the Dark?'', Journal of Conflict Resolution Vol. 36 No. 2, June 1992. now referred to by historians as pre-dreadnought battleships. In 1906, the commissioning of into the United Kingdom's Royal Navy heralded a revolution in the field of battleship design. Subsequent battleship designs, influenced by HMS ''Dreadnought'', were referred to as "dreadnoughts", though the term eventually became obsolete as dreadnoughts became the only type of battleship in common use. Battleships were a symbol of naval dominance and national might, and for decades the battleship was a major factor in both diplomacy and military strategy.Sondhaus, L. ''Naval Warfare 1815–1914'', . A global arms race in battleship cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
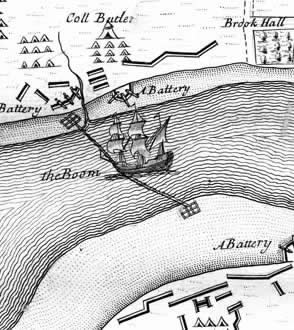
Boom (navigational Barrier)
A boom or a chain (also boom defence, harbour chain, river chain, chain boom, boom chain or variants) is an obstacle strung across a navigable stretch of water to control or block navigation. In modern times they usually have civil uses, such as to prevent access to a dangerous river channel. But, especially historically, they have been used militarily, with the goal of denying access to an enemy's ships: a modern example is the anti-submarine net. Booms have also been used to force passing vessels to pay a toll. Description A boom generally floats on the surface, while a chain can be on the surface or below the water. A chain could be made to float with rafts, logs, ships or other wood, making the chain a boom as well. Historical uses Especially in medieval times, the end of a chain could be attached to a chain tower or boom tower. This allowed safe raising or lowering of the chain, as they were often heavily fortified. By raising or lowering a chain or boom, access could be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barrier Boat
The United States Navy's 19BB (Barrier Boat) was built by Chuck's Boat and Drive of Longview, Washington in 2002 to deploy and maintain port security booms surrounding Navy ships and installations in port. The first boat of the 13-boat order was delivered in January 2003. Originally designed to raft and pull floating logs for the commercial logging industry, the Barrier Boats are affectionately known as the ''Boomin Beaver'' by the sailors who operate them. Chuck's Boats founder Chuck Slape had decades of experience building rugged boats serving the Pacific Northwest coast booming grounds. The powerful little 12 to 16-ft boats were known as "log broncs" due to the boat's action from the popular azimuth drive which would cause the boat to rear up like a rodeo horse when the props were spun around 180 degrees. The 19BB features a 260 hp Cummins 6BTA 5.9l pod mounted engine paired with a ZF 4:1 reduction marine transmission powering a conventional propeller with a 36-in. noz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barracks Ship
A barracks ship or barracks barge or berthing barge, or in civilian use accommodation vessel or accommodation ship, is a ship or a non-self-propelled barge containing a superstructure of a type suitable for use as a temporary barracks for sailors or other military personnel. A barracks ship, a military form of a dormitory ship, may also be used as a receiving unit for sailors who need temporary residence prior to being assigned to their ship. The United States Navy used to call them Yard Repair Berthing and Messing with designations YRBM and YRBM(L) and now classes them as either Auxiliary Personnel Barracks (APB) or Auxiliary Personnel Lighter (aka barge) (APL). Early use Barrack ships were common during the era of sailing ships when shore facilities were scarce or non-existent. Barrack ships were usually hulks. At times, barrack ships were also used as prison ships for convicts, prisoners of war or civilian internees. Use in World War II ''Barracks ships'' in the comb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
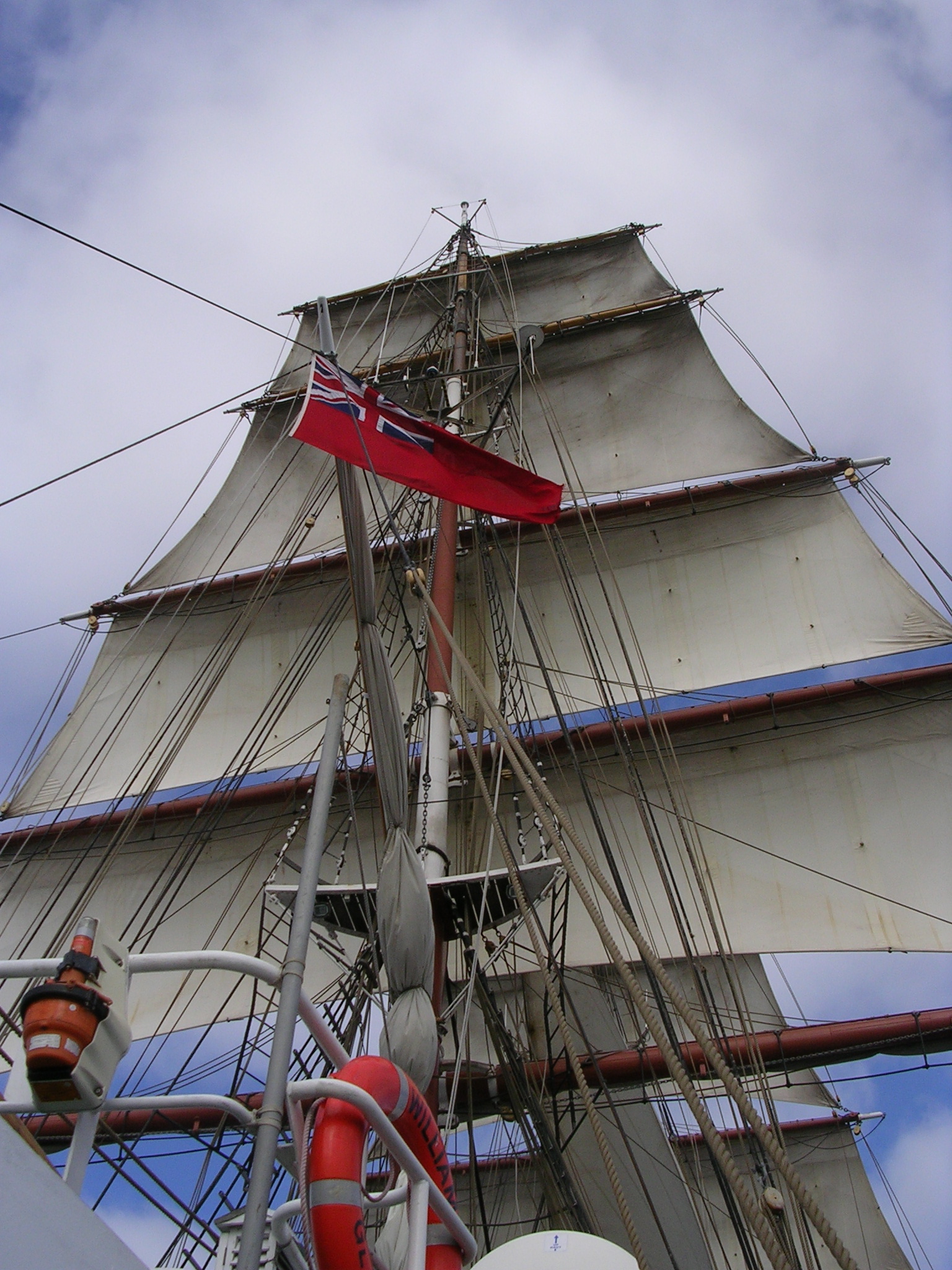
Fore-and-aft Rig
A fore-and-aft rig is a sailing vessel rigged mainly with sails set along the line of the keel, rather than perpendicular to it as on a square rigged vessel. Description Fore-and-aft rigged sails include staysails, Bermuda rigged sails, gaff rigged sails, gaff sails, gunter rig, lateen sails, lug sails, tanja sails, the spanker sail on a square rig and crab claw sails. Fore-and-aft rigs include: * Rigs with one mast: the proa, the catboat, the sloop, the cutter * Rigs with two masts: the ketch, the yawl * Rigs with two or more masts: the schooner Barques and barquentines are partially square rigged and partially fore-and-aft rigged. A rig which combines both on a foremast is known as a hermaphroditic rig. History Austronesia The fore-and-aft rig is believed to have been first developed independently by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC with the invention of the crab claw sail. It is suggested that it evolved from a more primitive "V"-shaped "square" s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barquentine
A barquentine or schooner barque (alternatively "barkentine" or "schooner bark") is a sailing vessel with three or more masts; with a square rigged foremast and fore-and-aft rigged main, mizzen and any other masts. Modern barquentine sailing rig While a full-rigged ship is square-rigged on all three masts, and the barque is square-rigged except for the mizzen-mast, the barquentine extends the principle by making only the foremast square-rigged. The advantages of a smaller crew, good performance before the wind and the ability to sail relatively close to the wind while carrying plenty of cargo made it a popular rig at the end of the nineteenth century. Today, barquentines are popular with modern tall ship and sail training operators as their suite of mainly fore-and-aft sails improve non-downwind performance, while their foremast of square sails offers long distance downwind speed and dramatic appearance in port. Etymology The term "barquentine" is seventeenth century in ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Rig
Square rig is a generic type of sail and rigging arrangement in which the primary driving sails are carried on horizontal spars which are perpendicular, or square, to the keel of the vessel and to the masts. These spars are called ''yards'' and their tips, outside the lifts, are called the ''yardarms.'' A ship mainly rigged so is called a square-rigger. The square rig is aerodynamically the most efficient running rig (i.e., sailing downwind), and stayed popular on ocean-going sailing ships until the end of the Age of Sail. The last commercial sailing ships, windjammers, were usually square-rigged four-masted barques. History The oldest archaeological evidence of use of a square-rig on a vessel is an image on a clay disk from Mesopotamia from 5000 BC. Single sail square rigs were used by the ancient Egyptians, the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Romans, and the Celts. Later the Scandinavians, the Germanic peoples, and the Slavs adopted the single square-rigged sail, with it be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fore-and-aft Rig
A fore-and-aft rig is a sailing vessel rigged mainly with sails set along the line of the keel, rather than perpendicular to it as on a square rigged vessel. Description Fore-and-aft rigged sails include staysails, Bermuda rigged sails, gaff rigged sails, gaff sails, gunter rig, lateen sails, lug sails, tanja sails, the spanker sail on a square rig and crab claw sails. Fore-and-aft rigs include: * Rigs with one mast: the proa, the catboat, the sloop, the cutter * Rigs with two masts: the ketch, the yawl * Rigs with two or more masts: the schooner Barques and barquentines are partially square rigged and partially fore-and-aft rigged. A rig which combines both on a foremast is known as a hermaphroditic rig. History Austronesia The fore-and-aft rig is believed to have been first developed independently by the Austronesian peoples some time around 1500 BC with the invention of the crab claw sail. It is suggested that it evolved from a more primitive "V"-shaped "square" s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)