|
Mordvinic Languages
The Mordvinic languages, also known as the Mordvin, Mordovian or Mordvinian languages (russian: мордовские языки, ''mordovskiye yazyki''), are a subgroup of the Uralic languages, comprising the closely related Erzya language and Moksha language, both spoken in Mordovia. Previously considered a single "Mordvin language", it is now treated as a small language grouping. Due to differences in phonology, lexicon, and grammar, Erzya and Moksha are not mutually intelligible. The two Mordvinic languages also have separate literary forms. The Erzya literary language was created in 1922 and the Mokshan in 1923. Phonological differences between the two languages include: * Moksha retains a distinction between the vowels while in Erzya, both have merged as . * In unstressed syllables, Erzya features vowel harmony like many other Uralic languages, using in front-vocalic words and in back-vocalic words. Moksha has a simple schwa In linguistics, specifically phone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eighth of Earth's inhabitable landmass. Russia extends across eleven time zones and shares land boundaries with fourteen countries, more than any other country but China. It is the world's ninth-most populous country and Europe's most populous country, with a population of 146 million people. The country's capital and largest city is Moscow, the largest city entirely within Europe. Saint Petersburg is Russia's cultural centre and second-largest city. Other major urban areas include Novosibirsk, Yekaterinburg, Nizhny Novgorod, and Kazan. The East Slavs emerged as a recognisable group in Europe between the 3rd and 8th centuries CE. Kievan Rus' arose as a state in the 9th century, and in 988, it adopted Orthodox Christianity from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vowel Harmony
In phonology, vowel harmony is an assimilatory process in which the vowels of a given domain – typically a phonological word – have to be members of the same natural class (thus "in harmony"). Vowel harmony is typically long distance, meaning that the affected vowels do not need to be immediately adjacent, and there can be intervening segments between the affected vowels. Generally one vowel will trigger a shift in other vowels, either progressively or regressively, within the domain, such that the affected vowels match the relevant feature of the trigger vowel. Common phonological features that define the natural classes of vowels involved in vowel harmony include vowel backness, vowel height, nasalization, roundedness, and advanced and retracted tongue root. Vowel harmony is found in many agglutinative languages. The given domain of vowel harmony taking effect often spans across morpheme boundaries, and suffixes and prefixes will usually follow vowel harmony rules ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordvinic Languages
The Mordvinic languages, also known as the Mordvin, Mordovian or Mordvinian languages (russian: мордовские языки, ''mordovskiye yazyki''), are a subgroup of the Uralic languages, comprising the closely related Erzya language and Moksha language, both spoken in Mordovia. Previously considered a single "Mordvin language", it is now treated as a small language grouping. Due to differences in phonology, lexicon, and grammar, Erzya and Moksha are not mutually intelligible. The two Mordvinic languages also have separate literary forms. The Erzya literary language was created in 1922 and the Mokshan in 1923. Phonological differences between the two languages include: * Moksha retains a distinction between the vowels while in Erzya, both have merged as . * In unstressed syllables, Erzya features vowel harmony like many other Uralic languages, using in front-vocalic words and in back-vocalic words. Moksha has a simple schwa In linguistics, specifically phone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
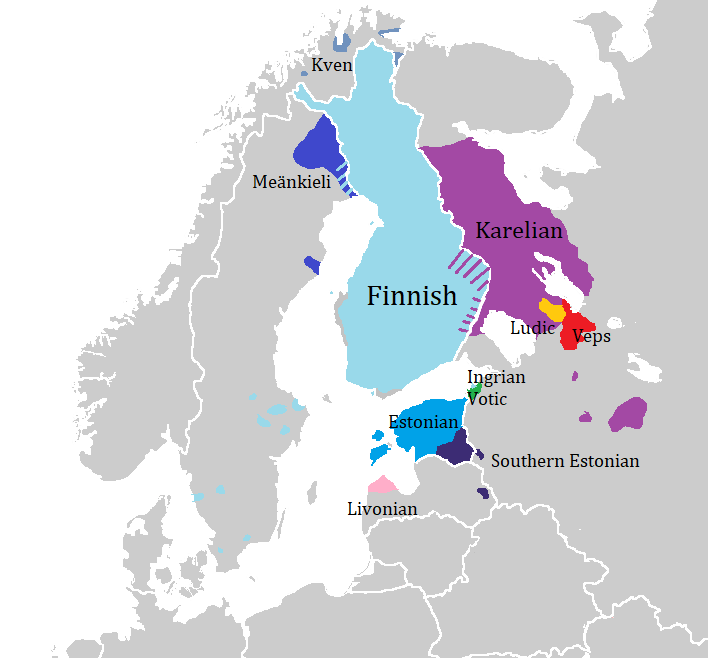
Finnic Languages
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.Finnic Peoples at Encyclopædia Britannica The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingrian and |
Mari Language
The Mari language (Mari: , ''marij jylme''; russian: марийский язык, ''mariyskiy yazyk''), formerly known as the Cheremiss language, spoken by approximately 400,000 people, belongs to the Uralic language family. It is spoken primarily in the Mari Republic (Mari: , ''Marij El'', i.e., 'Mari land') of the Russian Federation as well as in the area along the Vyatka river basin and eastwards to the Urals. Mari speakers, known as the Mari, are found also in the Tatarstan, Bashkortostan, Udmurtia, and Perm regions. Mari is the titular and official language of its republic, alongside Russian. The Mari language today has three standard forms: Hill Mari, Northwestern Mari, and Meadow Mari. The latter is predominant and spans the continuum Meadow Mari to Eastern Mari from the Republic into the Ural dialects of Bashkortostan, Sverdlovsk Oblast and Udmurtia), whereas the former, Hill Mari, shares a stronger affiliation with the Northwestern dialect (spoken in the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meshcherian Language
Meshchera is an extinct Uralic language. It was spoken around the left bank of the Middle Oka. Meshchera was either a Mordvinic or a Permic language. Pauli Rahkonen has suggested on the basis of toponymic evidence that it was a Permic or closely related language. Rahkonen's speculation has been criticized by Vladimir Napolskikh. Some Meshchera speaking people possibly assimilated into Mishar Tatars. However this theory is disputed. The first Russian written source which mentions them is the '' Tolkovaya Paleya'', from the 13th century. They are also mentioned in several later Russian chronicles from the period before the 16th century, and even later, in one of the letters by Andrey Kurbsky written in the second half of the 16th century, where he claimed the language spoken in the Meshchera region to be Mordvinic. Reconstruction Some words have been reconstructed from Meshchera based on toponymic data, for example: Meshchera hydronymic stems un-, ič-, vil- and ul, which can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semivowel
In phonetics and phonology, a semivowel, glide or semiconsonant is a sound that is phonetically similar to a vowel sound but functions as the syllable boundary, rather than as the nucleus of a syllable. Examples of semivowels in English are the consonants ''y'' and ''w'', in ''yes'' and ''west'', respectively. Written in IPA, ''y'' and ''w'' are near to the vowels ''ee'' and ''oo'' in ''seen'' and ''moon,'' written in IPA. The term ''glide'' may alternatively refer to any type of transitional sound, not necessarily a semivowel. Classification Semivowels form a subclass of approximants. Although "semivowel" and "approximant" are sometimes treated as synonymous, most authors use the term "semivowel" for a more restricted set; there is no universally agreed-upon definition, and the exact details may vary from author to author. For example, do not consider the labiodental approximant to be a semivowel, while proposes that it should be considered one. In the International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquid Consonant
In phonetics, liquids are a class of consonants consisting of voiced lateral approximants like together with rhotics like . Etymology The grammarian Dionysius Thrax used the Ancient Greek word (, ) to describe the sonorant consonants () of classical Greek. Most commentators assume that this referred to their "slippery" effect on meter in classical Greek verse when they occur as the second member of a consonant cluster. This word was calqued into Latin as , whence it has been retained in the Western European phonetic tradition. Phonological properties Liquids as a class often behave in a similar way in the phonotactics of a language: for example, they often have the greatest freedom in occurring in consonant clusters. Metathesis Cross-linguistically, liquids are the consonants most prone to metathesis. Spanish In Spanish, /r/ is liable for metathesis. More specifically, /r/ and /l/ frequently switch places: * Lat. ''crocodīlus'' > Span. ''cocodrilo'' “crocodile” * L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwa
In linguistics, specifically phonetics and phonology, schwa (, rarely or ; sometimes spelled shwa) is a vowel sound denoted by the International Phonetic Alphabet, IPA symbol , placed in the central position of the vowel chart. In English and some other languages, it represents the mid central vowel sound (rounded or unrounded), produced when the lips, tongue, and jaw are completely relaxed, such as the vowel sound of the in the English word ''about''. In English, some long-established phonetic transcription systems assert that the mid central vowel as an stress and vowel reduction in English, unstressed vowel and transcribed with schwa (ə) is always a different vowel sound from the open-mid back unrounded vowel as a stress and vowel reduction in English, stressed vowel and transcribed with turned v (ʌ), although they may recognize allophone, allophony between the pair. As Geoff Lindsey explains, within these systems, it is said that "schwa is never stressed"; but other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literary Language
A literary language is the form (register) of a language used in written literature, which can be either a nonstandard dialect or a standardized variety of the language. Literary language sometimes is noticeably different from the spoken language (''lects''), but the difference between literary language and non-literary language is greater in some languages; thus a great divergence between a written form and a spoken vernacular, the language exhibits diglossia, a community's use of two forms of speech. The understanding of the term differs from one linguistic tradition to another and is dependent on the terminological conventions adopted. Notably, in Eastern European and Slavic linguistics, the term "literary language" has also been used as a synonym of " standard language". Literary English For much of its history, there has been a distinction in the English language between an elevated literary language and a colloquial idiom.Matti Rissanen, ''History of Englishes: New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mordvins
The Mordvins (also Unified Mordvin people, Mordvinians, Mordovians; russian: мордва, Mordva, Mordvins (no equivalents in Moksha and Erzya)) is an obsolete but official term used in the Russian Federation to refer both to Erzyas and Mokshas since 1928 until the 2010s. Origin of the term According to recent Oxford studies: Erzya-Moksha Autonomy The Erzya-Moksha Autonomy was approved in 1928 as Mordvin Okrug according to personal position of Josef Stalin, who attended the meeting. Deputy president of Supreme Court of Mordovia Vasily Martyshkin quotes Stalin and Timofey Vasilyev. Since Mokshas and Erzyas lived sparcely in many governorates Stalin believed it was impossible to establish many autonomous districts. And that was Mikifor Surdin, ethnic Moksha who proposed to establish not Erzya-Moksha autonomy, but a Mordvin okrug. Stalin liked his variant. That is what he has been being cursed till now in spite of the fact he was executed during the Great Purge. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |