|
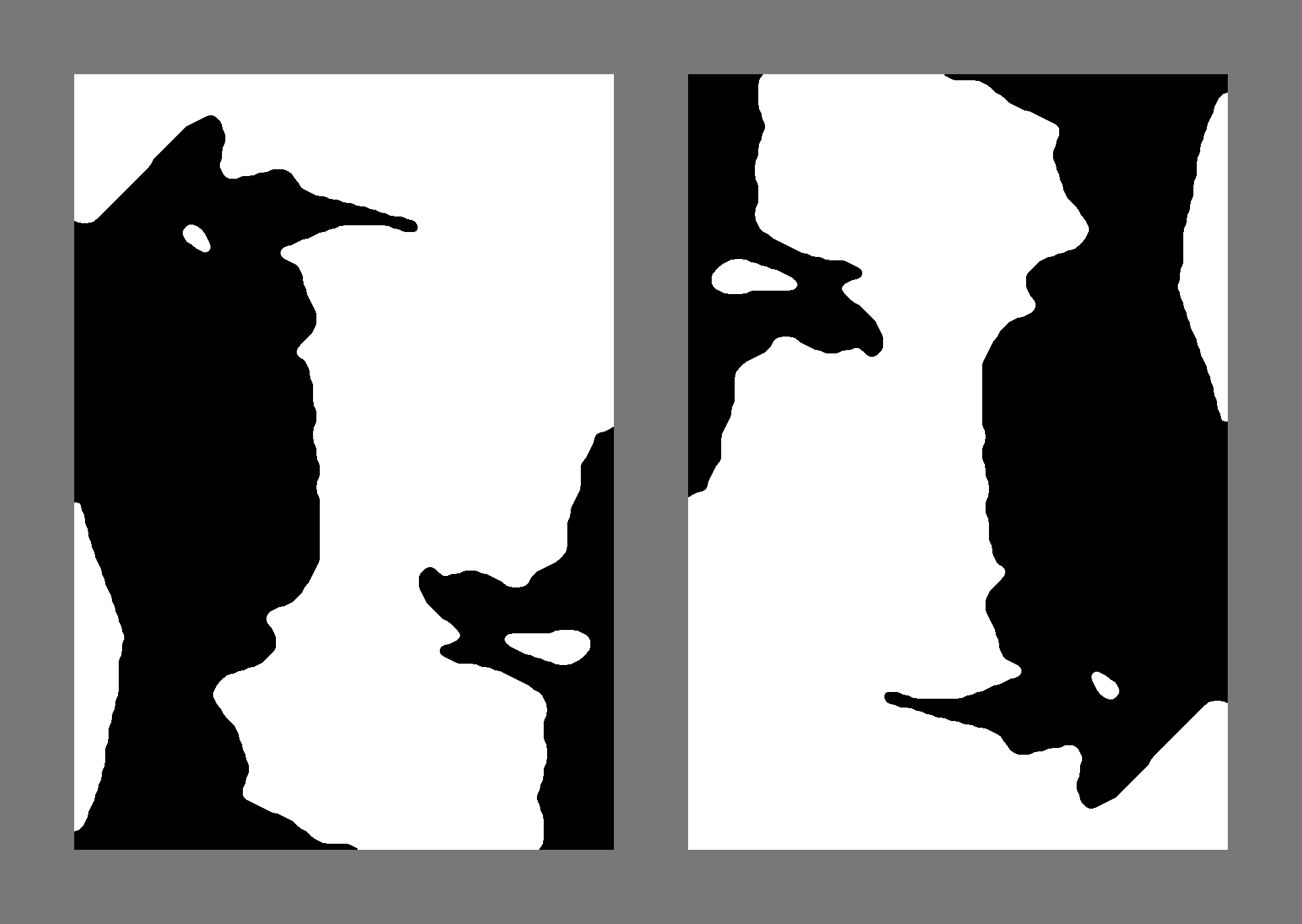
Mooney Face Test
The Mooney Face Test, developed by Craig M. Mooney, was first introduced in his 1957 article “''Age in the development of closure ability in children''.” Participants in the test are shown series of black and white distorted photographs, presented in such a way that would require them to perform closure. The law of closure is one of the seven Gestalt principles that describes a tendency of our perception to view an incomplete object as continuing and complete. The test assumes that perception is based on the collected information taken from the different regions of the image, which then constitute a holistic representation of a face. Today, there are many iterations of the Mooney Face Test, a number of which contain images that involve image color inversion and facial feature scrambling. Although the Mooney Face Test is widely used in the area of Gestalt facial recognition, it is recognized as the most reliable in Gestalt perception, more recent tests have shown flaws in the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mooney Faces
Mooney is a family name, which is probably predominantly derived from the Irish Ó Maonaigh, pronounced Om-weeneey. It can also be spelled Moony, Moonie, Mainey, Mauney, Meaney and Meeney depending on the dialectic pronunciation that was anglicised. Origins The origin of the Moony or Mooney families is lost in antiquity. The name is derived from ''maoin'', a Gaelic word meaning ''wealth'' or ''treasure of treasure'', hence when O'Maonaigh was anglicised to Mooney it meant ''the descendant of the wealthy one.'' According to Irish lore, the Mooney family comes from one of the largest and most noble Irish lines. They are said to be descendants of the ancient Irish King Heremon, who, along with his brother Herber, conquered Ireland. Heremon slew his brother shortly after their invasion, took the throne for himself, and fathered a line of kings of Ireland that include Malachi II, and King Niall of the Nine Hostages. Baptismal records, parish records, ancient land grants, the An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Closure
Gestalt-psychology, gestaltism, or configurationism is a school of psychology that emerged in the early twentieth century in Austria and Germany as a theory of perception that was a rejection of basic principles of Wilhelm Wundt's and Edward Titchener's elementalist and structuralist psychology.Mather, George (2006) Foundations of Perception, Psychology Pressch.1 p.32 As used in Gestalt psychology, the German word ''Gestalt'' ( , ; meaning "form") is interpreted as "pattern" or "configuration". Gestalt psychologists emphasize that organisms perceive entire patterns or configurations, not merely individual components. The view is sometimes summarized using the adage, "the whole is more than the sum of its parts." Gestalt psychology was founded on works by Max Wertheimer, Wolfgang Köhler, and Kurt Koffka. Origin and history Max Wertheimer (1880–1943), Kurt Koffka (1886–1941), and Wolfgang Köhler (1887-1967) founded Gestalt psychology in the early 20th century. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestalt Principles
Gestalt-psychology, gestaltism, or configurationism is a school of psychology that emerged in the early twentieth century in Austria and Germany as a theory of perception that was a rejection of basic principles of Wilhelm Wundt's and Edward Titchener's elementalist and structuralist psychology.Mather, George (2006) Foundations of Perception, Psychology Pressch.1 p.32 As used in Gestalt psychology, the German word ''Gestalt'' ( , ; meaning "form") is interpreted as "pattern" or "configuration". Gestalt psychologists emphasize that organisms perceive entire patterns or configurations, not merely individual components. The view is sometimes summarized using the adage, "the whole is more than the sum of its parts." Gestalt psychology was founded on works by Max Wertheimer, Wolfgang Köhler, and Kurt Koffka. Origin and history Max Wertheimer (1880–1943), Kurt Koffka (1886–1941), and Wolfgang Köhler (1887-1967) founded Gestalt psychology in the early 20th century. The domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestalt Psychology
Gestalt-psychology, gestaltism, or configurationism is a school of psychology that emerged in the early twentieth century in Austria and Germany as a theory of perception that was a rejection of basic principles of Wilhelm Wundt's and Edward Titchener's elementalist and structuralist psychology.Mather, George (2006) Foundations of Perception, Psychology Pressch.1 p.32 As used in Gestalt psychology, the German word ''Gestalt'' ( , ; meaning "form") is interpreted as "pattern" or "configuration". Gestalt psychologists emphasize that organisms perceive entire patterns or configurations, not merely individual components. The view is sometimes summarized using the adage, "the whole is more than the sum of its parts." Gestalt psychology was founded on works by Max Wertheimer, Wolfgang Köhler, and Kurt Koffka. Origin and history Max Wertheimer (1880–1943), Kurt Koffka (1886–1941), and Wolfgang Köhler (1887-1967) founded Gestalt psychology in the early 20th century. The domi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Theory
Information theory is the scientific study of the quantification (science), quantification, computer data storage, storage, and telecommunication, communication of information. The field was originally established by the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley, in the 1920s, and Claude Shannon in the 1940s. The field is at the intersection of probability theory, statistics, computer science, statistical mechanics, information engineering (field), information engineering, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is information entropy, entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a fair coin flip (with two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy) than specifying the outcome from a roll of a dice, die (with six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measures in information theory are mutual informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perceptual
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sense, sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous system, which in turn result from physical or chemical stimulation of the Sensory nervous system, sensory system.Goldstein (2009) pp. 5–7 Visual system, Vision involves Photon, light striking the retina of the eye; Sense of smell, smell is mediated by Olfactory system#Peripheral, odor molecules; and hearing involves Sound wave, pressure waves. Perception is not only the passive receipt of these Signal processing, signals, but it is also shaped by the recipient's Perceptual learning, learning, memory, Expectation (epistemic), expectation, and attention.Richard Gregory, Gregory, Richard. "Perception" in Gregory, Zangwill (1987) pp. 598–601. Sensory input is a process that transforms this low-level information to higher-level informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Detection Theory
Detection theory or signal detection theory is a means to measure the ability to differentiate between information-bearing patterns (called stimulus in living organisms, signal in machines) and random patterns that distract from the information (called noise, consisting of background stimuli and random activity of the detection machine and of the nervous system of the operator). In the field of electronics, signal recovery is the separation of such patterns from a disguising background. According to the theory, there are a number of determiners of how a detecting system will detect a signal, and where its threshold levels will be. The theory can explain how changing the threshold will affect the ability to discern, often exposing how adapted the system is to the task, purpose or goal at which it is aimed. When the detecting system is a human being, characteristics such as experience, expectations, physiological state (e.g., fatigue) and other factors can affect the threshold app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Polymorphism
A gene is said to be polymorphic if more than one allele occupies that gene's locus within a population. In addition to having more than one allele at a specific locus, each allele must also occur in the population at a rate of at least 1% to generally be considered polymorphic. Gene polymorphisms can occur in any region of the genome. The majority of polymorphisms are silent, meaning they do not alter the function or expression of a gene. Some polymorphisms are visible. For example, in dogs the E locus can have any of five different alleles, known as E, Em, Eg, Eh, and e. Varying combinations of these alleles contribute to the pigmentation and patterns seen in dog coats. A polymorphic variant of a gene can lead to the abnormal expression or to the production of an abnormal form of the protein; this abnormality may cause or be associated with disease. For example, a polymorphic variant of the gene encoding the enzyme CYP4A11, in which thymidine replaces cytosine at the gene's nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RAPGEF5
Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RAPGEF5'' gene. Members of the RAS subfamily (see HRAS; MIM 190020) of GTPases function in signal transduction as GTP/GDP-regulated switches that cycle between inactive GDP- and active GTP-bound states. Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), such as RAPGEF5, serve as RAS activators by promoting acquisition of GTP to maintain the active GTP-bound state and are the key link between cell surface receptors Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. They are specialized integral me ... and RAS activation (Rebhun et al., 2000). upplied by OMIMref name="entrez" /> References Further reading * * * * * * * {{gene-7-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Tests
Cognitive tests are assessments of the cognitive capabilities of humans and other animals. Tests administered to humans include various forms of IQ tests; those administered to animals include the mirror test (a test of visual self-awareness) and the T maze test (which tests learning ability). Such study is important to research concerning the philosophy of mind and psychology, as well as determination of human and animal intelligence. Modern cognitive tests originated through the work of James McKeen Cattell who coined the term "mental tests". They followed Francis Galton's development of physical and physiological tests. For example, Galton measured strength of grip and height and weight. He established an "Anthropometric Laboratory" in the 1880s where patrons paid to have physical and physiological attributes measured. Galton's measurements had an enormous influence on psychology. Cattell continued the measurement approach with simple measurements of perception. Cattell's t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |