|
Monotone (software)
Monotone is an open source software tool for distributed revision control. Monotone tracks revisions to files, groups sets of revisions into changesets, and tracks history across renames. The focus of the project is on integrity over performance. Monotone is designed for distributed operation, and makes heavy use of cryptographic primitives to track file revisions (via the SHA-1 secure hash) and to authenticate user actions (via RSA cryptographic signatures). History Milestones Monotone version 0.26 introduced major changes to the internal database structures, including a new structure known by Monotone developers as a ''roster''. Monotone databases created with version 0.26 can not exchange revisions with older Monotone databases. Older databases must first be upgraded to the new format. The new netsync protocol is incompatible with earlier versions of Monotone. As Git inspiration In April 2005, Monotone became the subject of increased interest in the FOSS comm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linus Torvalds
Linus Benedict Torvalds ( , ; born 28 December 1969) is a Finnish software engineer who is the creator and, historically, the lead developer of the Linux kernel, used by Linux distributions and other operating systems such as Android. He also created the distributed version control system Git. He was honored, along with Shinya Yamanaka, with the 2012 Millennium Technology Prize by the Technology Academy Finland "in recognition of his creation of a new open source operating system for computers leading to the widely used Linux kernel." He is also the recipient of the 2014 IEEE Computer Society Computer Pioneer Award and the 2018 IEEE Masaru Ibuka Consumer Electronics Award. Life and career Early years Torvalds was born in Helsinki, Finland, the son of journalists Anna and Nils Torvalds, the grandson of statistician Leo Törnqvist and of poet Ole Torvalds, and the great-grandson of journalist and soldier Toivo Karanko. His parents were campus radicals at the Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rsync
rsync is a utility for efficiently transferring and synchronizing files between a computer and a storage drive and across networked computers by comparing the modification times and sizes of files. It is commonly found on Unix-like operating systems and is under the GPL-3.0-or-later license. Rsync is written in C as a single threaded application. The rsync algorithm is a type of delta encoding, and is used for minimizing network usage. Zlib may be used for additional data compression, and SSH or stunnel can be used for security. Rsync is typically used for synchronizing files and directories between two different systems. For example, if the command rsync local-file user@remote-host:remote-file is run, rsync will use SSH to connect as user to remote-host. Once connected, it will invoke the remote host's rsync and then the two programs will determine what parts of the local file need to be transferred so that the remote file matches the local one. One application of r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SQLite
SQLite (, ) is a database engine written in the C programming language. It is not a standalone app; rather, it is a library that software developers embed in their apps. As such, it belongs to the family of embedded databases. It is the most widely deployed database engine, as it is used by several of the top web browsers, operating systems, mobile phones, and other embedded systems. Many programming languages have bindings to the SQLite library. It generally follows PostgreSQL syntax, but does not enforce type checking by default. This means that one can, for example, insert a string into a column defined as an integer. History D. Richard Hipp designed SQLite in the spring of 2000 while working for General Dynamics on contract with the United States Navy. Hipp was designing software used for a damage-control system aboard guided-missile destroyers, which originally used HP-UX with an IBM Informix database back-end. SQLite began as a Tcl extension. In August 2000, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
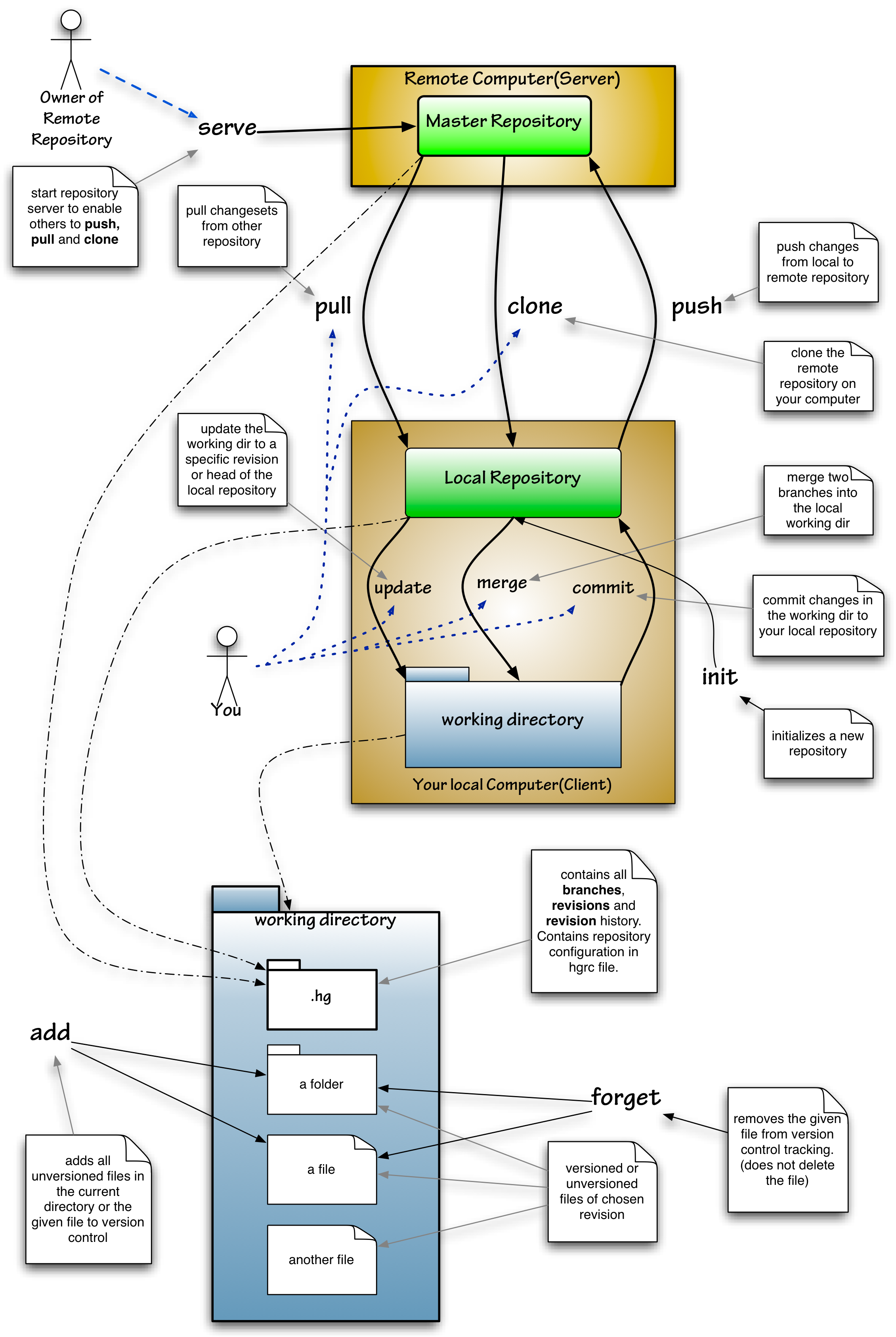
Mercurial (software)
Mercurial is a distributed revision control tool for software developers. It is supported on Microsoft Windows and Unix-like systems, such as FreeBSD, macOS, and Linux. Mercurial's major design goals include high performance and scalability, decentralization, fully distributed collaborative development, robust handling of both plain text and binary files, and advanced branching and merging capabilities, while remaining conceptually simple. It includes an integrated web-interface. Mercurial has also taken steps to ease the transition for users of other version control systems, particularly Subversion. Mercurial is primarily a command-line driven program, but graphical user interface extensions are available, e.g. TortoiseHg, and several IDEs offer support for version control with Mercurial. All of Mercurial's operations are invoked as arguments to its driver program hg (a reference to Hg – the chemical symbol of the element mercury). Olivia Mackall originated Mercurial and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subversion (software)
Apache Subversion (often abbreviated SVN, after its command name ''svn'') is a software versioning and revision control system distributed as open source under the Apache License. Software developers use Subversion to maintain current and historical versions of files such as source code, web pages, and documentation. Its goal is to be a mostly compatible successor to the widely used Concurrent Versions System (CVS). The open source community has used Subversion widely: for example, in projects such as Apache Software Foundation, Free Pascal, FreeBSD, SourceForge, and from 2006 to 2019, GCC. CodePlex was previously a common host for Subversion repositories. Subversion was created by CollabNet Inc. in 2000, and is now a top-level Apache project being built and used by a global community of contributors. History CollabNet founded the Subversion project in 2000 as an effort to write an open-source version-control system which operated much like CVS but which fixed the bugs a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Arch
GNU arch software is a distributed revision control system that is part of the GNU Project and licensed under the GNU General Public License. It is used to keep track of the changes made to a source tree and to help programmers combine and otherwise manipulate changes made by multiple people or at different times. As of 2009, GNU arch's official status is deprecation, and only security fixes are applied. Bazaar (or 'bzr') has since also been made an official GNU project and can thus be considered the replacement for GNU arch. It is not a fork of arch. Features Being a distributed, decentralized versioning system, each revision stored using arch is uniquely globally identifiable; such identifier can be used in a distributed setting to easily merge or "cherry-pick" changes from completely disparate sources. Being decentralized means that there is no need for a central server for which developers have to be authorized in order to contribute. As with other systems, a full read-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downstream (computer Science)
In a telecommunications network or computer network, downstream refers to data sent from a network service provider to a customer. One process sending data primarily in the downstream direction is downloading. However, the overall download speed depends on the downstream speed of the user, the upstream speed of the Server (computing), server, and the network between them. In the client–server model, downstream can refer to the direction from the server to the client (computing), client. References Data transmission Orientation (geometry) {{Network-stub nl:Downstream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Maintenance
Software maintenance in software engineering is the modification of a software product after delivery to correct faults, to improve performance or other attributes. A common perception of maintenance is that it merely involves fixing defects. However, one study indicated that over 80% of maintenance effort is used for non-corrective actions. This perception is perpetuated by users submitting problem reports that in reality are functionality enhancements to the system. More recent studies put the bug-fixing proportion closer to 21%. History Software maintenance and evolution of systems was first addressed by Meir M. Lehman in 1969. Over a period of twenty years, his research led to the formulation of Lehman's Laws (Lehman 1997). Key findings of his research conclude that maintenance is really evolutionary development and that maintenance decisions are aided by understanding what happens to systems (and software) over time. Lehman demonstrated that systems continue to evolve over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upstream (software Development)
In software development, when software has been forked or uses a chain of libraries/ dependencies, upstream refers to an issue that occurs in software farther up the chain. It is the direction that is toward the original authors or maintainers of software. It is usually used in the context of a version, a bug, or a patch. Upstream development allows other distributions to benefit from it when they pick up the future release or merge recent (or all) upstream patches. Likewise, the original authors (maintaining upstream) can benefit from contributions that originate from custom distributions, if their users send patches upstream. The term also pertains to bugs; responsibility for a bug is said to lie upstream when it is not caused through the distribution's porting, non-upstream modification or integration efforts. Examples * A patch ''sent upstream'' is offered to the original authors or maintainers of the software. If accepted, the authors or maintainers will include the pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GMANE
Gmane (pronounced "mane") is an e-mail to news gateway. It allows users to access electronic mailing lists as if they were Usenet newsgroups, and also through a variety of web interfaces. Since Gmane is a bidirectional gateway, it can also be used to post on the mailing lists. Gmane is an archive; it never expires messages (unless explicitly requested by users). Gmane also supports importing list postings made prior to a list's inclusion on the service. The project was initiated in 2001 by Lars Magne Ingebrigtsen, one of the authors of Gnus, a newsreader for Emacs. It began operating publicly on 11 February 2002 after a one-month test period. , Gmane's homepage stated that it included 129,592,482 messages in its archives, from a total of 20,070 mailing lists. In July 2016, Ingebrigtsen announced that he was considering shutting Gmane down, and the web interface was taken offline. In August 2016 Gmane was acquired by Yomura Holdings. Only the message spool was transferred, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Git (software)
Git () is a distributed version control system: tracking changes in any set of files, usually used for coordinating work among programmers collaboratively developing source code during software development. Its goals include speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows (thousands of parallel branches running on different systems). "So I'm writing some scripts to try to track things a whole lot faster." Git was originally authored by Linus Torvalds in 2005 for development of the Linux kernel, with other kernel developers contributing to its initial development. Since 2005, Junio Hamano has been the core maintainer. As with most other distributed version control systems, and unlike most client–server systems, every Git directory on every computer is a full-fledged repository with complete history and full version-tracking abilities, independent of network access or a central server. Git is free and open-source software distributed under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |