|
Momme
Momme may refer to: * Momme Andresen (1857–1951), German industrial research chemist * Momme Peterson (1771–1835), Danish-Norwegian businessperson and politician * A Japanese historic unit of weight: Japanese units of measurement#Momme; or units based on it: ** A unit of pearl weight: Pearl#Momme weight ** A unit of textile (silk) measurement, see Units of textile measurement#Momme ** Unit of several Japanese historic currencies originating from the value of silver weighed in ''momme'' *** A proposed denomination of Japanese coinage from the Meiji period The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization ... See also * San Mommè, an Italian village and hamlet (''frazione'') of the municipality of Pistoia, in the province of Pistoia, Tuscany * {{disambig, given name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Momme Andresen
Momme Andresen (; 17 October 1857 - 12 January 1951) was a Danish-German industrial research chemist. His main area of work was to formulate better developers and fixers for black-and-white photographs. Biography Andresen attended a Volksschule (a local state school) in Niebüll, Schleswig-Holstein, near his birthplace. He studied chemistry at the Technische Hochschule Dresden under Rudolf Schmitt. After doctoral studies at the University of Jena, he returned to Dresden to work as Schmitt's assistant. His first independent scientific work was to determine the structure of the dyestuff safranin, for the German chemical company Cassella. Around that time, he also discovered "Andresen's acid". He worked for some years in Buffalo, New York. In 1887, he took employment at Aktien-Gesellschaft für Anilinfabrikation (modern AGFA) in Berlin as a dyestuff chemist. He was already a keen amateur photographer. He had used, and was dissatisfied with, developers based on hydroquinone (whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Momme Peterson
Momme Peterson (28 March 1771 – 4 March 1835) was a Danish-Norwegian businessperson and politician. He is best known for founding the company M. Peterson & Søn. Biography Peterson was born at Lindholm in the Slesvig. He was the son of Peter Christian Andresen (1715–73) and Sissel Hanses (1726–73). After distillery training at Flensburg in Schleswig, Peterson came to Moss in 1793 to begin as a distillery master for wholesaler Johann Gude. He settled in the city of Moss and acquired burghership in 1801. In the same year he founded his own company, a general store with various groceries and manufactured goods. After several of the older, established trading houses went bankrupt during the 1820s, Peterson remained one of the large companies in the city. He later opened a tobacco spinning mill and also expanded to trade with timber. The name ''M. Peterson & Søn'' was taken in 1828. Momme Peterson was elected to the Norwegian Parliament The Storting ( no, Stortinget ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
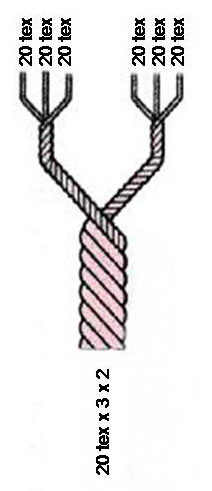
Units Of Textile Measurement
Textile fibers, threads, yarns and fabrics are measured in a multiplicity of units. * A fiber, a single filament of natural material, such as cotton, linen or wool, or artificial material such as nylon, polyester, metal or mineral fiber, or man-made cellulosic fibre like viscose, Modal, Lyocell or other rayon fiber is measured in terms of linear mass density, the weight of a given length of fiber. Various units are used to refer to the measurement of a fiber, such as: the denier and tex (linear mass density of fibers), super S (fineness of wool fiber), worsted count, woolen count, linen count (wet spun) (or Number English (Ne)), cotton count (or Number English (Ne)), Number metric (Nm) and yield (the reciprocal of denier and tex). * A yarn, a spun agglomeration of fibers used for knitting, weaving or sewing, is measured in terms of cotton count and yarn density. * Thread, usually consisting of multiple yarns plied together producing a long, thin strand used in sewing or weavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Units Of Measurement
Traditional Japanese units of measurement or the shakkanhō (, "''shaku–kan'' system") is the traditional system of measurement used by the people of the Japanese archipelago. It is largely based on the Chinese system, which spread to Japan and the rest of the Sinosphere in antiquity. It has remained mostly unaltered since the adoption of the measures of the Tang dynasty in 701. Following the 1868 Meiji Restoration, Imperial Japan adopted the metric system and defined the traditional units in metric terms on the basis of a prototype metre and kilogram. The present values of most Korean and Taiwanese units of measurement derive from these values as well. For a time in the early 20th century, the traditional, metric, and English systems were all legal in Japan. Although commerce has since been legally restricted to using the metric system, the old system is still used in some instances. The old measures are common in carpentry and agriculture, with tools such as chisels, spatels ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
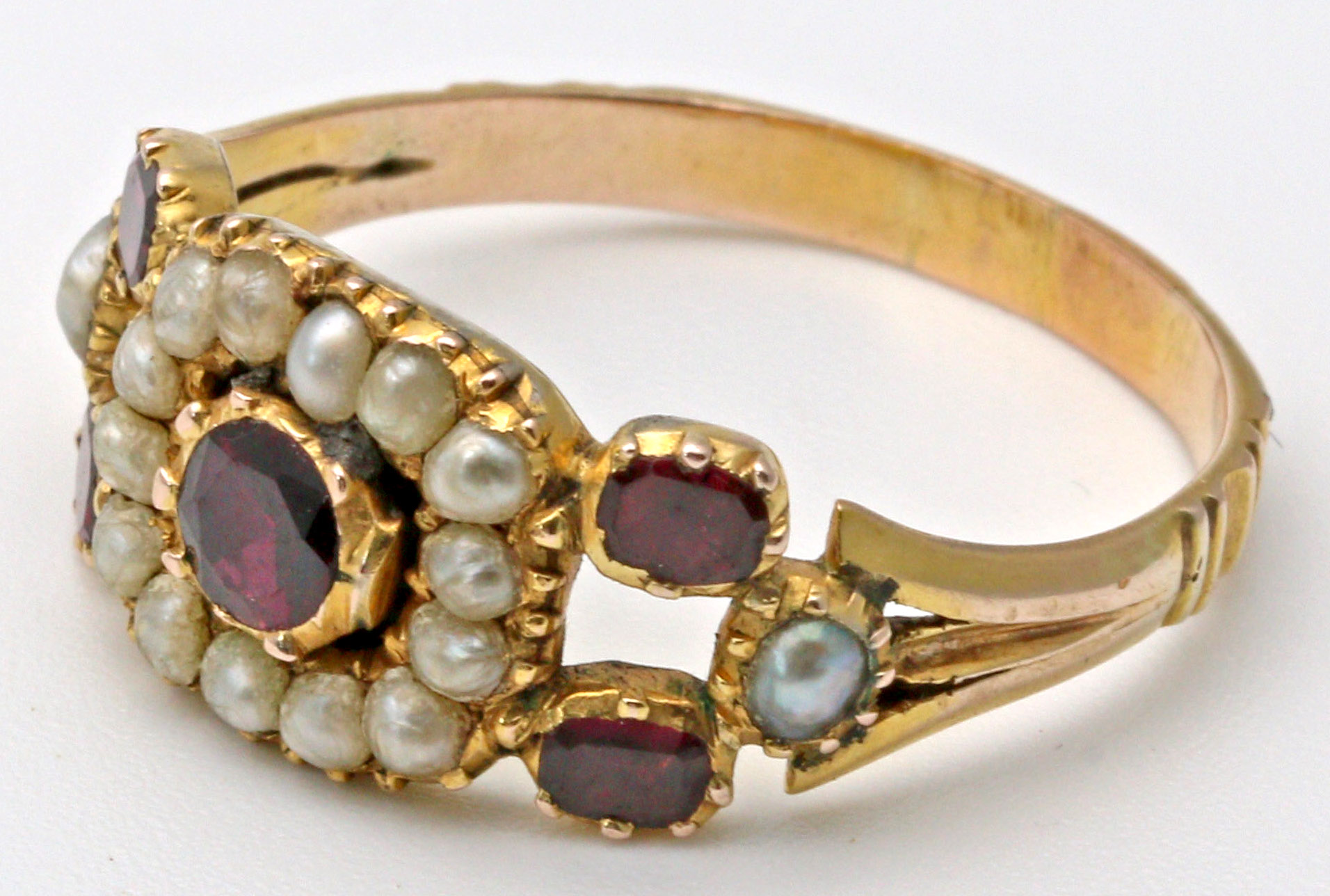
Pearl
A pearl is a hard, glistening object produced within the soft tissue (specifically the mantle) of a living shelled mollusk or another animal, such as fossil conulariids. Just like the shell of a mollusk, a pearl is composed of calcium carbonate (mainly aragonite or a mixture of aragonite and calcite) in minute crystalline form, which has deposited in concentric layers. The ideal pearl is perfectly round and smooth, but many other shapes, known as baroque pearls, can occur. The finest quality of natural pearls have been highly valued as gemstones and objects of beauty for many centuries. Because of this, ''pearl'' has become a metaphor for something rare, fine, admirable and valuable. The most valuable pearls occur spontaneously in the wild, but are extremely rare. These wild pearls are referred to as ''natural'' pearls. ''Cultured'' or ''farmed'' pearls from pearl oysters and freshwater mussels make up the majority of those currently sold. Imitation pearls are also widely s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
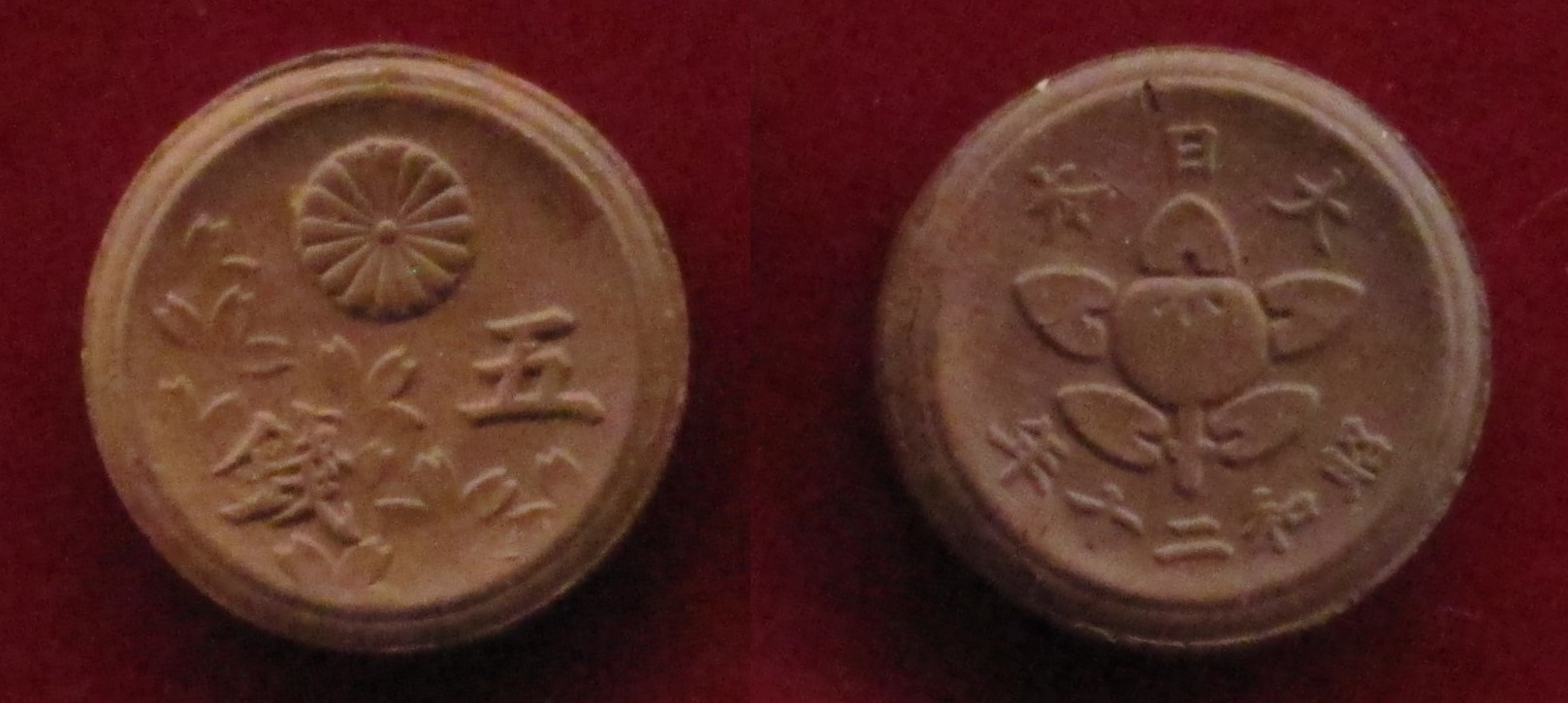
List Of Japanese Coinage Patterns
The following is a list of Japanese pattern coins from the yen based currency system started under the Meiji Restoration. The first patterns of the yen based system were made from 1869 to 1870 as presentation pieces to the Emperor. The new currency system was eventually adopted by the Meiji government in an Act signed on June 27, 1871. Pattern coins are almost never released into circulation as they are made for evaluation purposes only. Once a pattern is approved by government officials, it then goes to the minting process. Most of the patterns listed below are very rare, and sell for considerable amounts at auctions. The market value and rarity of any given coin is dependent on supply and demand. Selected terminology The following terms appear on the list below: Legend(s) - In numismatic terminology "legends" refer to inscriptions on any given coin. Common inscriptions for these coins include; , the reigning Emperor's name, the value of the coin, and the year of the Empero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiji Period
The is an era of Japanese history that extended from October 23, 1868 to July 30, 1912. The Meiji era was the first half of the Empire of Japan, when the Japanese people moved from being an isolated feudal society at risk of colonization by Western powers to the new paradigm of a modern, industrialized nation state and emergent great power, influenced by Western scientific, technological, philosophical, political, legal, and aesthetic ideas. As a result of such wholesale adoption of radically different ideas, the changes to Japan were profound, and affected its social structure, internal politics, economy, military, and foreign relations. The period corresponded to the reign of Emperor Meiji. It was preceded by the Keiō era and was succeeded by the Taishō era, upon the accession of Emperor Taishō. The rapid modernization during the Meiji era was not without its opponents, as the rapid changes to society caused many disaffected traditionalists from the former samurai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(48281353057).jpg)


