|
Molecular Orbital Theory
In chemistry, molecular orbital theory (MO theory or MOT) is a method for describing the electronic structure of molecules using quantum mechanics. It was proposed early in the 20th century. In molecular orbital theory, electrons in a molecule are not assigned to individual chemical bonds between atoms, but are treated as moving under the influence of the atomic nuclei in the whole molecule. Quantum mechanics describes the spatial and energetic properties of electrons as molecular orbitals that surround two or more atoms in a molecule and contain valence electrons between atoms. Molecular orbital theory revolutionized the study of chemical bonding by approximating the states of bonded electrons—the molecular orbitals—as linear combinations of atomic orbitals (LCAO). These approximations are made by applying the density functional theory (DFT) or Hartree–Fock (HF) models to the Schrödinger equation. Molecular orbital theory and valence bond theory are the founda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the elements that make up matter to the compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions: their composition, structure, properties, behavior and the changes they undergo during a reaction with other substances. Chemistry also addresses the nature of chemical bonds in chemical compounds. In the scope of its subject, chemistry occupies an intermediate position between physics and biology. It is sometimes called the central science because it provides a foundation for understanding both basic and applied scientific disciplines at a fundamental level. For example, chemistry explains aspects of plant growth ( botany), the formation of igneous rocks ( geology), how atmospheric ozone is formed and how environmental pollutants are degraded ( ecology), the properties of the soil on the moon ( cosmochemistry), how medications work (pharmacology), and how to collect DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variational Principle
In science and especially in mathematical studies, a variational principle is one that enables a problem to be solved using calculus of variations, which concerns finding functions that optimize the values of quantities that depend on those functions. For example, the problem of determining the shape of a hanging chain suspended at both ends—a catenary—can be solved using variational calculus, and in this case, the variational principle is the following: The solution is a function that minimizes the gravitational potential energy of the chain. Overview Any physical law which can be expressed as a variational principle describes a self-adjoint operator. These expressions are also called Hermitian. Such an expression describes an invariant under a Hermitian transformation. History Felix Klein's Erlangen program attempted to identify such invariants under a group of transformations. In what is referred to in physics as Noether's theorem, the Poincaré group of transformations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, diamagnetic materials are repelled by magnetic fields and form induced magnetic fields in the direction opposite to that of the applied magnetic field. Paramagnetic materials include most chemical elements and some compounds; they have a relative magnetic permeability slightly greater than 1 (i.e., a small positive magnetic susceptibility) and hence are attracted to magnetic fields. The magnetic moment induced by the applied field is linear in the field strength and rather weak. It typically requires a sensitive analytical balance to detect the effect and modern measurements on paramagnetic materials are often conducted with a SQUID magnetometer. Paramagnetism is due to the presence of unpaired electrons in the material, so most atoms w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dioxygen Molecule
There are several known allotropes of oxygen. The most familiar is molecular oxygen (O2), present at significant levels in Earth's atmosphere and also known as dioxygen or triplet oxygen. Another is the highly reactive ozone (O3). Others are: *Atomic oxygen (O1), a free radical. *Singlet oxygen (O2*), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. * Tetraoxygen (O4), another metastable form. * Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is and another one metallic. Atomic oxygen Atomic oxygen, denoted O(3P) or O(3P), is very reactive, as the single atoms of oxygen tend to quickly bond with nearby molecules. On Earth's surface, it exists naturally for a very short time. In outer space, the presence of ample ultraviolet radiation results in a low Earth orbit atmosphere in which 96% of the oxygen occurs in atomic form. Ryan D. McCulla, Saint Louis University (2010). /acswebcontent.acs.org/prfar/2010/reports/P11141.html "Atomic Oxygen O(3P): P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triplet State
In quantum mechanics, a triplet is a quantum state of a system with a spin of quantum number =1, such that there are three allowed values of the spin component, = −1, 0, and +1. Spin, in the context of quantum mechanics, is not a mechanical rotation but a more abstract concept that characterizes a particle's intrinsic angular momentum. It is particularly important for systems at atomic length scales, such as individual atoms, protons, or electrons. Almost all molecules encountered in daily life exist in a singlet state, but molecular oxygen is an exception. At room temperature, O2 exists in a triplet state, which can only undergo a chemical reaction by making the forbidden transition into a singlet state. This makes it kinetically nonreactive despite being thermodynamically one of the strongest oxidants. Photochemical or thermal activation can bring it into the singlet state, which makes it kinetically as well as thermodynamically a very strong oxidant. __TOC__ Two spin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erich Hückel
Erich Armand Arthur Joseph Hückel (August 9, 1896, Berlin – February 16, 1980, Marburg) was a German physicist and physical chemist. He is known for two major contributions: *The Debye–Hückel theory of electrolytic solutions *The Hückel method of approximate molecular orbital (MO) calculations on π electron systems. Hückel was born in the Charlottenburg suburb of Berlin. He studied physics and mathematics from 1914 to 1921 at the University of Göttingen. On receiving his doctorate, he became an assistant at Göttingen, but soon became an assistant to Peter Debye at Zürich. It was there that he and Debye developed their theory (the Debye–Hückel theory, in 1923) of electrolytic solutions, elucidating the behavior of strong electrolytes by considering interionic forces, in order to account for their electrical conductivity and their thermodynamic activity coefficients. After spending 1928 and 1929 in England and Denmark, working briefly with Niels Bohr, Hück ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Lennard-Jones
Sir John Edward Lennard-Jones (27 October 1894 – 1 November 1954) was a British mathematician and professor of theoretical physics at the University of Bristol, and then of theoretical science at the University of Cambridge. He was an important pioneer in the development of modern computational chemistry and theoretical chemistry. Early life and education Lennard-Jones was born on 27 October 1894 at Leigh, Lancashire, the eldest son of Mary Ellen and Hugh Jones, an insurance agent. He was educated at Leigh Grammar School, going on to study at the University of Manchester, graduating in 1915 with a first-class honours degree in mathematics. Career Lennard-Jones is well known among scientists for his work on molecular structure, valency and intermolecular forces. Much research of these topics over several decades grew from a paper he published in 1929. His theories of liquids and of surface catalysis also remain influential. He wrote few, albeit influential, papers. His ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John C
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
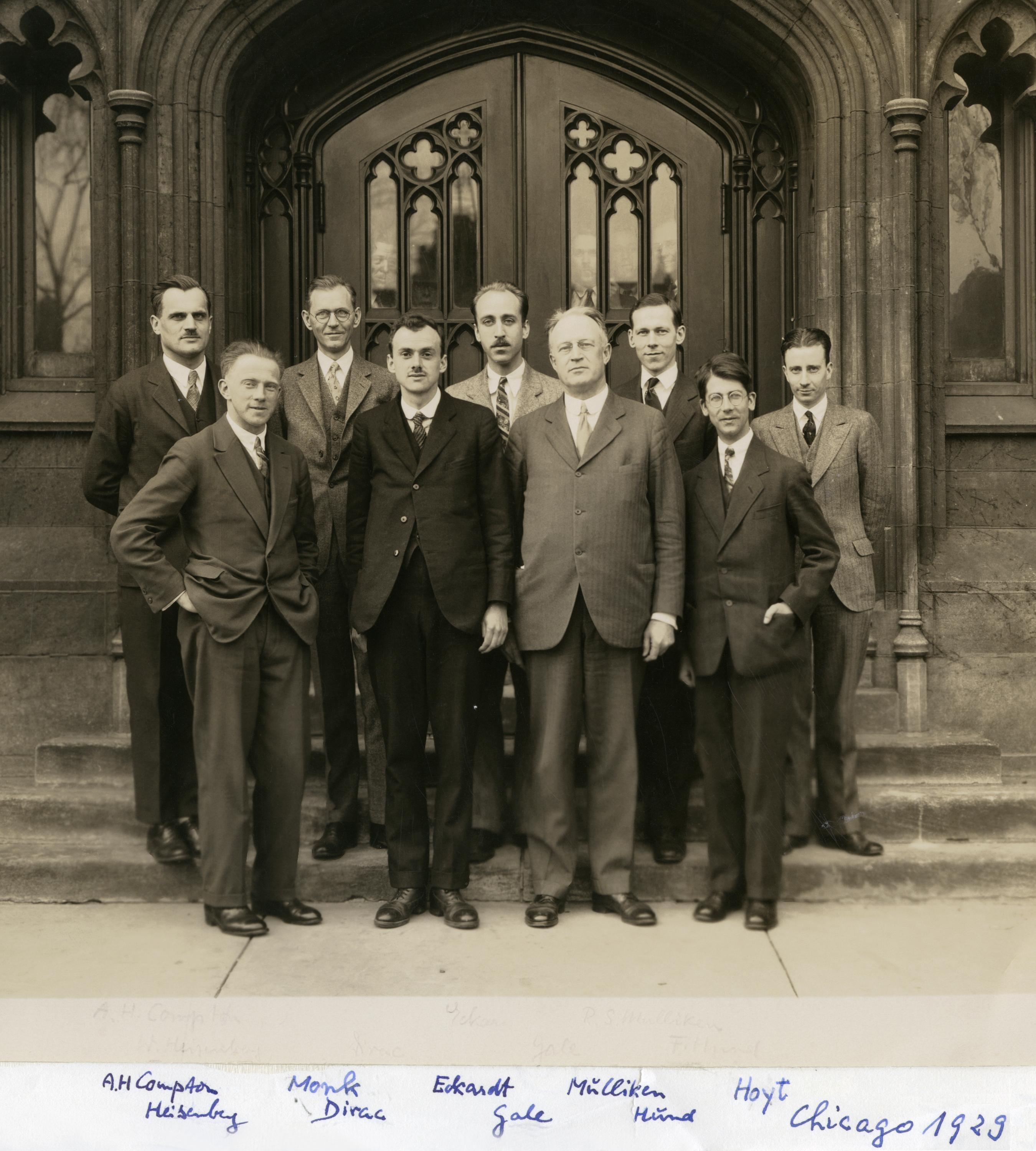
Robert Mulliken
Robert Sanderson Mulliken Note Longuet-Higgins' amusing title for reference B238 1965 on page 354 of this Biographical Memoir. The title should be "Selected papers of Robert S Mulliken." (June 7, 1896 – October 31, 1986) was an American physicist and chemist, primarily responsible for the early development of molecular orbital theory, i.e. the elaboration of the molecular orbital method of computing the structure of molecules. Mulliken received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1966 and the Priestley Medal in 1983. Early years Robert Mulliken was born in Newburyport, Massachusetts. His father, Samuel Parsons Mulliken, was a professor of organic chemistry at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. As a child, Robert Mulliken learned the name and botanical classification of plants and, in general, had an excellent, but selective, memory. For example, he learned German well enough to skip the course in scientific German in college, but could not remember the name of his high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Hund
Friedrich Hermann Hund (4 February 1896 – 31 March 1997) was a German physicist from Karlsruhe known for his work on atoms and molecules. Scientific career Hund worked at the Universities of Rostock, Leipzig, Jena, Frankfurt am Main, and Göttingen. Hund worked with such prestigious physicists as Schrödinger, Dirac, Heisenberg, Max Born, and Walter Bothe. At that time, he was Born's assistant, working with quantum interpretation of band spectra of diatomic molecules. After his studies of mathematics, physics, and geography in Marburg and Göttingen, he worked as a private lecturer for theoretical physics in Göttingen (1925), professor in Rostock (1927), Leipzig University (1929), Jena (1946), Frankfurt/Main (1951) and from 1957 again in Göttingen. Additionally, he stayed in Copenhagen (1926) with Niels Bohr and lectured on the atom at Harvard University (1928). He published more than 250 papers and essays in total. Hund made pivotal contributions to quantum theory - es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Combination Of Atomic Orbitals
A linear combination of atomic orbitals or LCAO is a quantum superposition of atomic orbitals and a technique for calculating molecular orbitals in quantum chemistry. In quantum mechanics, electron configurations of atoms are described as wavefunctions. In a mathematical sense, these wave functions are the basis set of functions, the basis functions, which describe the electrons of a given atom. In chemical reactions, orbital wavefunctions are modified, i.e. the electron cloud shape is changed, according to the type of atoms participating in the chemical bond. It was introduced in 1929 by Sir John Lennard-Jones with the description of bonding in the diatomic molecules of the first main row of the periodic table, but had been used earlier by Linus Pauling for H2+. Mathematical description An initial assumption is that the number of molecular orbitals is equal to the number of atomic orbitals included in the linear expansion. In a sense, ''n'' atomic orbitals combine to f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Symmetry
Molecular symmetry in chemistry describes the symmetry present in molecules and the classification of these molecules according to their symmetry. Molecular symmetry is a fundamental concept in chemistry, as it can be used to predict or explain many of a molecule's chemical properties, such as whether or not it has a dipole moment, as well as its allowed spectroscopic transitions. To do this it is necessary to use group theory. This involves classifying the states of the molecule using the irreducible representations from the character table of the symmetry group of the molecule. Symmetry is useful in the study of molecular orbitals, with applications to the Hückel method, to ligand field theory, and to the Woodward-Hoffmann rules. Many university level textbooks on physical chemistry, quantum chemistry, spectroscopy and inorganic chemistry discuss symmetry. Another framework on a larger scale is the use of crystal systems to describe crystallographic symmetry in bulk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |