|
Molecular Query Language
The Molecular Query Language (MQL) was designed to allow more complex, problem-specific search methods in chemoinformatics. In contrast to the widely used SMARTS queries, MQL provides for the specification of spatial and physicochemical properties of atoms and bonds. Additionally, it can easily be extended to handle non-atom-based graphs, also known as "reduced feature" graphs. The query language is based on an extended Backus–Naur form In computer science, extended Backus–Naur form (EBNF) is a family of metasyntax notations, any of which can be used to express a context-free grammar. EBNF is used to make a formal description of a formal language such as a computer programmi ... (EBNF) using JavaCC. Notes and references * E. Proschak, J. K. Wegner, A. Schüller, G. Schneider, U. Fechner, ''Molecular Query Language (MQL)-A Context-Free Grammar for Substructure Matching'', J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2007, ''47'', 295-301. See also * SMARTS * International Chemical Identi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemoinformatics
Cheminformatics (also known as chemoinformatics) refers to use of physical chemistry theory with computer and information science techniques—so called "''in silico''" techniques—in application to a range of descriptive and prescriptive problems in the field of chemistry, including in its applications to biology and related molecular fields. Such ''in silico'' techniques are used, for example, by pharmaceutical companies and in academic settings to aid and inform the process of drug discovery, for instance in the design of well-defined combinatorial libraries of synthetic compounds, or to assist in structure-based drug design. The methods can also be used in chemical and allied industries, and such fields as environmental science and pharmacology, where chemical processes are involved or studied. History Cheminformatics has been an active field in various guises since the 1970s and earlier, with activity in academic departments and commercial pharmaceutical research and de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Query Language
Query languages, data query languages or database query languages (DQL) are computer languages used to make queries in databases and information systems. A well known example is the Structured Query Language (SQL). Types Broadly, query languages can be classified according to whether they are database query languages or information retrieval query languages. The difference is that a database query language attempts to give factual answers to factual questions, while an information retrieval query language attempts to find documents containing information that is relevant to an area of inquiry. Other types of query languages include: * Full-text. The simplest query language is treating all terms as bag of words that are to be matched with the postings in the inverted index and where subsequently ranking models are applied to retrieve the most relevant documents. Only tokens are defined in the CFG. Web search engines often use this approach. * Boolean. A query language that also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
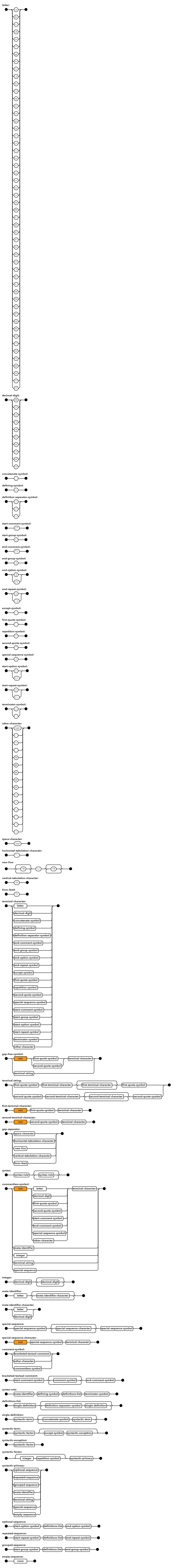
Extended Backus–Naur Form
In computer science, extended Backus–Naur form (EBNF) is a family of metasyntax notations, any of which can be used to express a context-free grammar. EBNF is used to make a formal description of a formal language such as a computer programming language. They are extensions of the basic Backus–Naur form (BNF) metasyntax notation. The earliest EBNF was developed by Niklaus Wirth, incorporating some of the concepts (with a different syntax and notation) from Wirth syntax notation. Today, many variants of EBNF are in use. The International Organization for Standardization adopted an EBNF Standard, ISO/IEC 14977, in 1996. According to Zaytsev, however, this standard "only ended up adding yet another three dialects to the chaos" and, after noting its lack of success, also notes that the ISO EBNF is not even used in all ISO standards. Wheeler argues against using the ISO standard when using an EBNF and recommends considering alternative EBNF notations such as the one from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JavaCC
JavaCC (Java Compiler Compiler) is an open-source parser generator and lexical analyzer generator written in the Java programming language. JavaCC is similar to yacc in that it generates a parser from a formal grammar written in EBNF notation. Unlike yacc, however, JavaCC generates top-down parsers. JavaCC can resolve choices based on the next ''k'' input tokens, and so can handle LL(''k'') grammars automatically; by use of "lookahead specifications", it can also resolve choices requiring unbounded look ahead. JavaCC also generates lexical analyzers in a fashion similar to lex. The tree builder that accompanies it, JJTree, constructs its trees from the bottom up. JavaCC is licensed under a BSD license. History In 1996, Sun Microsystems released a parser generator called ''Jack''. The developers responsible for ''Jack'' created their own company called Metamata and changed the ''Jack'' name to JavaCC. Metamata eventually became part of WebGain. After WebGain shut down its o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Chemical Identifier
The International Chemical Identifier (InChI or ) is a textual identifier for chemical substances, designed to provide a standard way to encode molecular information and to facilitate the search for such information in databases and on the web. Initially developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) from 2000 to 2005, the format and algorithms are non-proprietary. Since May 2009, it has been developed by the InChI Trust, a nonprofit charity from the United Kingdom which works to implement and promote the use of InChI. The identifiers describe chemical substances in terms of ''layers'' of information — the atoms and their bond connectivity, tautomeric information, isotope information, stereochemistry, and electronic charge information. Not all layers have to be provided; for instance, the tautomer layer can be omitted if that type of information is not relevant to the particular a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |