|
Models Of Communication
Models of communication are simplified representations of the process of communication. Most models try to describe both verbal and non-verbal communication and often understand it as an exchange of messages. Their function is to give a compact overview of the complex process of communication. This helps researchers formulate hypotheses, apply communication-related concepts to real-world cases, and test predictions. Despite their usefulness, many models are criticized based on the claim that they are too simple because they leave out essential aspects. The different components and their interactions are usually presented in the form of a diagram. Several basic components and interactions reappear in many of the models. They include the idea that a sender encodes information in the form of a message and sends it to a receiver through a channel. The receiver needs to decode the message to understand the initial idea and provides some form of feedback. In both cases, noise may int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Components Of Models Of Communication
Common may refer to: Places * Common, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Boston Common, a central public park in Boston, Massachusetts * Cambridge Common, common land area in Cambridge, Massachusetts * Clapham Common, originally common land, now a park in London, UK * Common Moss, a townland in County Tyrone, Northern Ireland * Lexington Battle Green, Lexington Common, a common land area in Lexington, Massachusetts * Salem Common Historic District (Salem, Massachusetts), Salem Common Historic District, a common land area in Salem, Massachusetts People * Common (rapper) (born 1972), American hip hop artist, actor, and poet * Andrew Ainslie Common (born 1841), English amateur astronomer * Andrew Common (born 1889), British shipping director * John Common, American songwriter, musician and singer * Thomas Common (born 1850), Scottish translator and literary critic Arts, entertainment, and media * Common (film), ''Common'' (film), a 2014 BBC One film, written by Jimmy M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC (though this excludes a number of Greek city-states free from Alexander's jurisdiction in the western Mediterranean, around the Black Sea, Cyprus, and Cyrenaica). In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Roughly three centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conceptual Framework
A conceptual framework is an analytical tool with several variations and contexts. It can be applied in different categories of work where an overall picture is needed. It is used to make conceptual distinctions and organize ideas. Strong conceptual frameworks capture something real and do this in a way that is easy to remember and apply. Isaiah Berlin used the metaphor of a "fox" and a "hedgehog" to make conceptual distinctions in how important philosophers and authors view the world. London: Weidenfeld & Nicolson; 1986 New York: Simon and Schuster, introduction by M. Walzer. Berlin describes hedgehogs as those who use a single idea or organizing principle to view the world (such as Dante Alighieri, Blaise Pascal, Fyodor Dostoyevsky, Plato, Henrik Ibsen and Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel). Foxes, on the other hand, incorporate a type of pluralism and view the world through multiple, sometimes conflicting, lenses (examples include Johann Wolfgang von Goethe, James Joyce, William S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communication Theory
Communication theory is a proposed description of communication phenomena, the relationships among them, a storyline describing these relationships, and an argument for these three elements. Communication theory provides a way of talking about and analyzing key events, processes, and commitments that together form communication. Theory can be seen as a way to map the world and make it navigable; communication theory gives us tools to answer empirical, conceptual, or practical communication questions. Communication is defined in both commonsense and specialized ways. Communication theory emphasizes its symbolic and social process aspects as seen from two perspectives—as exchange of information (the transmission perspective), and as work done to connect and thus enable that exchange (the ritual perspective). Sociolinguistic research in the 1950s and 1960s demonstrated that the level to which people change their formality of their language depending on the social context that the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Communication
Human communication, or anthroposemiotics, is a field of study dedicated to understanding how humans Communication, communicate. Humans ability to communicate with one another would not be possible without an understanding of what we are referencing or thinking about. Because humans are unable to fully understand one another's perspective, there needs to be a creation of commonality through a shared mindset or viewpoint. The field of communication is very diverse, as there are multiple layers of what communication is and how we use its different features as human beings. Humans have communicatory abilities other animals do not, for example, humans are able to communicate about time and place as though they are solid objects. Humans communicate to request help, to inform others, and to share attitudes for bonding. Communication is a joint activity largely dependent on the ability to maintain common attention. We share relevant background knowledge and joint experience in order to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Communication
Animal communication is the transfer of information from one or a group of animals (sender or senders) to one or more other animals (receiver or receivers) that affects the current or future behavior of the receivers. Information may be sent intentionally, as in a courtship display, or unintentionally, as in the transfer of scent from predator to prey. Information may be transferred to an "audience" of several receivers. Animal communication is a rapidly growing area of study in disciplines including animal behavior, sociology, neurology and animal cognition. Many aspects of animal behavior, such as symbolic name use, emotional expression, learning and sexual behavior, are being understood in new ways. When the information from the sender changes the behavior of a receiver, the information is referred to as a "signal". Signalling theory predicts that for a signal to be maintained in the population, both the sender and receiver should usually receive some benefit from the interact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olfactory
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste. In humans, it occurs when an odor binds to a receptor within the nasal cavity, transmitting a signal through the olfactory system. Glomeruli aggregate signals from these receptors and transmit them to the olfactory bulb, where the sensory input will start to interact with parts of the brain responsible for smell identification, memory, and emotion. There are many different causes for alteration, lack, or disturbance to a normal sense of smell, and can include damage to the nose or smell receptors, or central problems affecting the brain. Some causes include upper respiratory infections, traumatic brain injury, and neurodegenerative disease. History of study Early scientific study of the sense of smell includes the extensive doctoral dissertation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
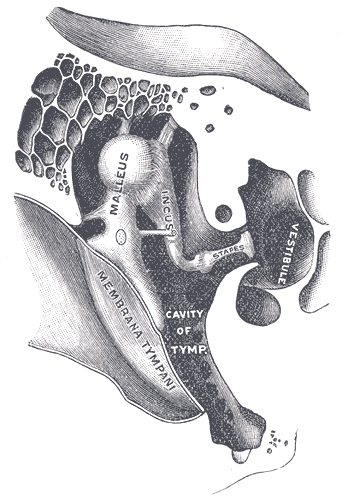
Hearing
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid. In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ... through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting Vibration, vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid, liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduction (physiology), transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual
The visual system comprises the sensory organ (the eye) and parts of the central nervous system (the retina containing photoreceptor cells, the optic nerve, the optic tract and the visual cortex) which gives organisms the sense of sight (the ability to detect and process visible light) as well as enabling the formation of several non-image photo response functions. It detects and interprets information from the optical spectrum perceptible to that species to "build a representation" of the surrounding environment. The visual system carries out a number of complex tasks, including the reception of light and the formation of monocular neural representations, colour vision, the neural mechanisms underlying stereopsis and assessment of distances to and between objects, the identification of a particular object of interest, motion perception, the analysis and integration of visual information, pattern recognition, accurate motor coordination under visual guidance, and more. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnlund's Model
Barnlund's model is an influential transactional model of communication. It was first published by Dean Barnlund in 1970. It is formulated as an attempt to overcome the limitations of earlier models of communication. In this regard, it rejects the idea that communication consists in the transmission of ideas from a sender to a receiver. Instead, it identifies communication with the production of meaning in response to internal and external cues. Barnlund holds that the world and its objects are meaningless in themselves: their meaning depends on people who create meaning and assign it to them. The aim of this process is to reduce uncertainty and arrive at a shared understanding. Meaning is in constant flux since the interpretation habits of people keep changing. Barnlund's model is based on a set of fundamental assumptions holding that communication is dynamic, continuous, circular, irreversible, complex, and unrepeatable. Cues are of central importance in Barnlund's model. A cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schramm's Model
Schramm's model of communication is an early and influential model of communication. It was first published by Wilbur Schramm in 1954 and includes important innovations over previous models, such as the inclusion of a feedback loop and the discussion of the role of fields of experience. For Schramm, communication is about sharing information or having a common attitude towards signs. His model is based on three fundamental components: a source, a destination, and a message. The process starts with an idea in the mind of the source. This idea is then encoded into a message using signs and sent to the destination. The destination needs to decode and interpret the signs in order to reconstruct the original idea. In response, they formulate their own message, encode it, and send it back as a form of feedback. Feedback is an important part of many forms of communication and can be used to mitigate processes that may undermine successful communication, such as external noise or errors in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlo's Model
The Source-Message-Channel-Receiver model is a linear transmission model of communication. It is also referred to as SMCR model, Sender-Message-Channel-Receiver model, and Berlo's model. It was first published by David Berlo in his 1960 book ''The Process of Communication''. It contains a detailed discussion of the four main components of communication (source, message, channel, and receiver) in the form of an analysis of the different features of each component and how these features affect the efficiency of communication. Berlo understands communication in a wide sense that includes verbal and non-verbal communication. Source and receiver are usually distinct individuals but can also be groups and, in some cases, the same entity acts both as source and receiver. Berlo sees all these forms of communication as attempts by the source to influence the behavior of the receiver. The source tries to achieve this by formulating a communicative intention and encoding it in the form of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
_great-egret-8243-web_(324180866).jpg)